Deoxyguanosine kinase
Deoxyribonucleoside kinases such as deoxyguanoside kinase (dGK) phosphorylate deoxyribonucleosides. The human form is highly specific for purine substrates. Deoxynucleoside kinases are key targets in chemotherapy of cancer as they are recquired to activate nucleoside analogues by phosphorylation. dGK is involved in the regulation of dGTP and dATP pools, and may have a role in apoptosis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q16854
 (2.7.1.76, 2.7.1.113)
(2.7.1.76, 2.7.1.113)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
2ocp
- Crystal Structure of Human Deoxyguanosine Kinase
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.300
 (see all for 2ocp)
(see all for 2ocp)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.1.113)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Activation of the 5'-OH of the deoxyribose by deprotonation with Glu 70 allows a nucleophilic attack of the gamma-phosphate of the phosphate donor. Arg 142 as well as the magnesium cation stabilise the trigonal bypyrimidal transition state formed in the reaction. The magnesium ion will coordinate to the ATP phosphate groups however exact Mg2+ ligand positions have not been identified across deoxynucleoside kinases.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2ocp) | ||
| Glu70 | Glu70(34)A | Acts as a general base, deprotonating the 5'OH group of the nucleoside. | activator, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg142 | Arg142(106)A | Positions Glu 70 by forming hydrogen bonds and also stabilises the negative charges from the transition state in the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Eriksson S et al. (2002), Cell Mol Life Sci, 59, 1327-1346. Structure and function of cellular deoxyribonucleoside kinases. DOI:10.1007/s00018-002-8511-x. PMID:12363036.
- Egeblad-Welin L et al. (2007), FEBS J, 274, 1542-1551. Functional studies of active-site mutants from Drosophila melanogaster deoxyribonucleoside kinase. Investigations of the putative catalytic glutamate-arginine pair and of residues responsible for substrate specificity. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05701.x. PMID:17302737.
- Sandrini MP et al. (2005), Trends Biochem Sci, 30, 225-228. Deoxyribonucleoside kinases: two enzyme families catalyze the same reaction. DOI:10.1016/j.tibs.2005.03.003. PMID:15896737.
- Wang L et al. (2003), FEBS Lett, 554, 319-322. Mitochondrial deoxyguanosine kinase mutations and mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(03)01181-5. PMID:14623087.

Step 1. Glu70 acts as an initiating base to increase nucleophilicity of the 5' OH on the substrate. The 5' OH then attacks the gamma phosphate on ATP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg142(106)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu70(34)A | activator |
| Arg142(106)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu70(34)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg142(106)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu70(34)A | proton donor |
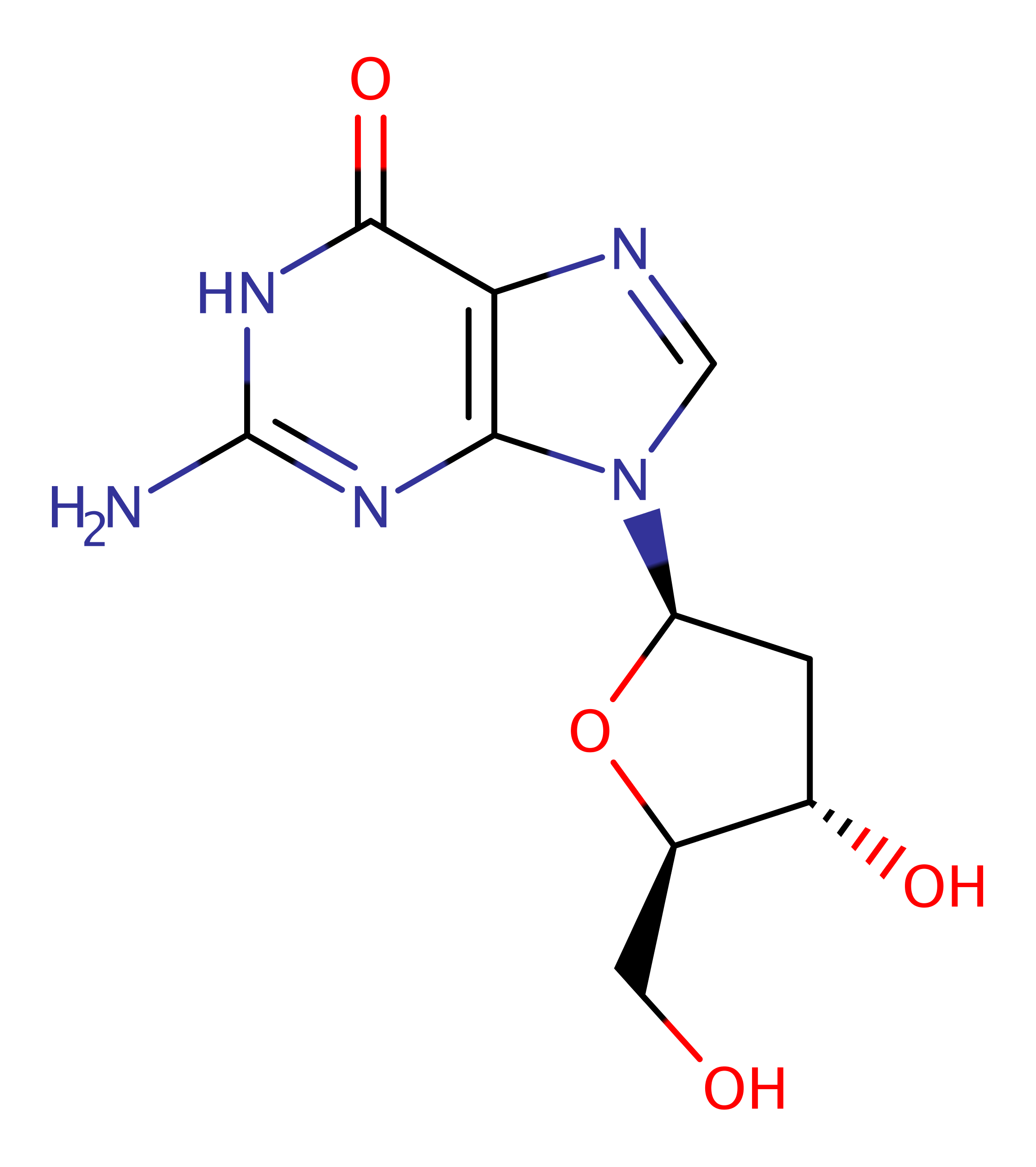




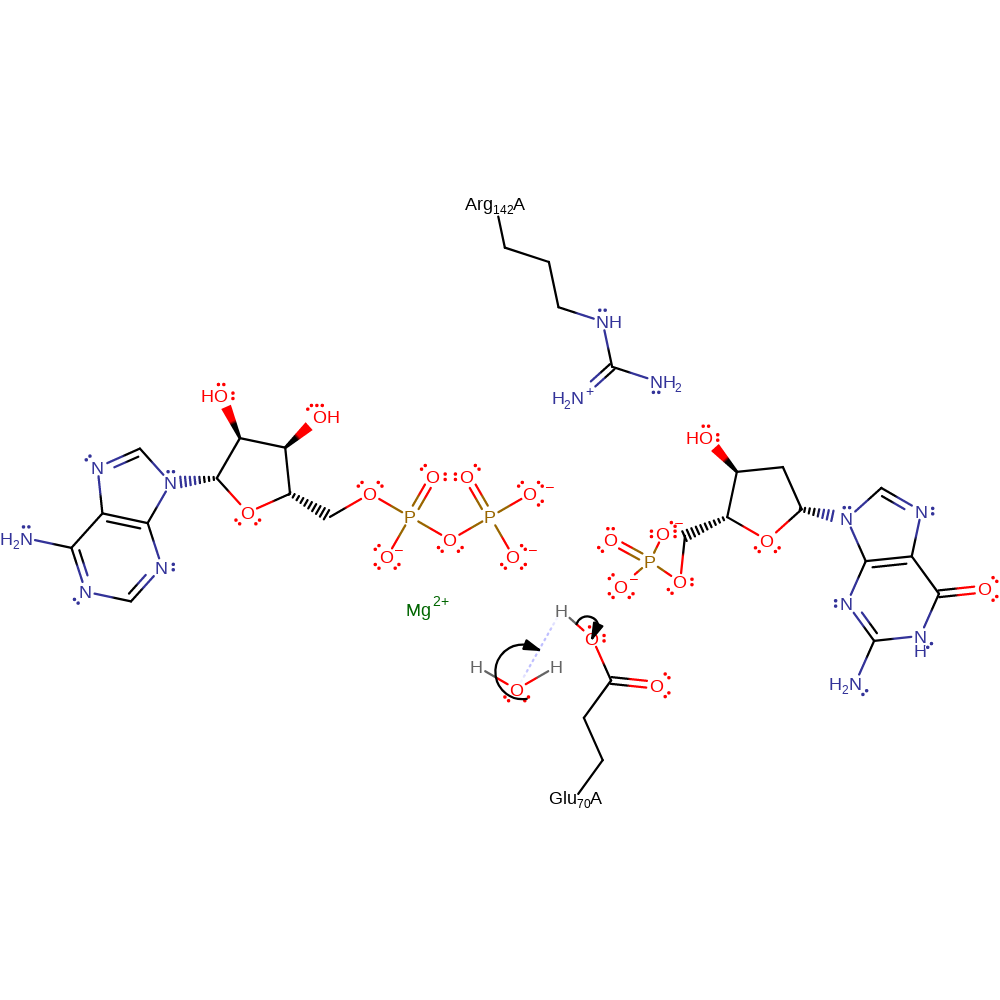
 Download:
Download: