DNA topoisomerase (type III)
Topoisomerases catalyse the winding and unwinding of super-coiled DNA, a process vital during DNA replication, transcription and repair. Type I topoisomerases reversibly cut one strand of the DNA helix, and can only relax supercoils. Analysis of sequence and mutagenesis data indicates that the type Ia topoisomerases (those found in prokaryotes, and the example given here) may be related to the major family of type II topoisomerases (found in all life apart from some archaea). Type II topoisomerases cut both strands and can either relax or tighten super-coils, but require ATP hydrolysis for catalytic turnover. All topoisomerases recorded form an intermediate with a tyr-DNA covalent bond during catalysis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P14294
 (5.6.2.1)
(5.6.2.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1d6m
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF E. COLI DNA TOPOISOMERASE III
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.290.10
 3.40.50.140
3.40.50.140  (see all for 1d6m)
(see all for 1d6m)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.6.2.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The Tyr328 acts as a nucleophile towards the phosphorous of the DNA molecule, forming a pentavalent transition state before eliminating the 5' DNA with concomitant deprotonation of Glu7. The DNA uncoils before Glu7 can deprotonate the 5'-OH, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the phosphorous atom. This again proceeds through a pentavalent transition state before eliminating Tyr328 and restoring the enzyme active site. The reaction requires Mg(II), which is bound by acidic glutamine residues. The metal's importance is shown by the detrimental effect to binding and activity brought about by mutation at these sites, however the role of the Mg as either structurally or catalytically essential is still uncertain.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1d6m) | ||
| Glu7 | Glu7A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr328 | Tyr328A | Acts as the catalytic nucleophile. | hydrogen bond acceptor, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Arg330, Lys8 | Arg330A, Lys8A | Stabilises the reactive intermediates and are essential for bringing the two halves back together again. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp103 | Asp103A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp105, Asp103 | Asp105A, Asp103A | Forms part of the magnesium 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Changela A et al. (2001), Nature, 411, 1077-1081. Crystal structure of a complex of a type IA DNA topoisomerase with a single-stranded DNA molecule. DOI:10.1038/35082615. PMID:11429611.
- Zhang Z et al. (2011), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 108, 6939-6944. Crystal structure of a covalent intermediate in DNA cleavage and rejoining by Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1100300108. PMID:21482796.
- Narula G et al. (2011), J Biol Chem, 286, 18673-18680. The Strictly Conserved Arg-321 Residue in the Active Site of Escherichia coli Topoisomerase I Plays a Critical Role in DNA Rejoining. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m111.229450. PMID:21478161.
- Bugreev DV et al. (2009), Biochemistry (Mosc), 74, 1467-1481. Structure and mechanism of action of type IA DNA topoisomerases. DOI:10.1134/s0006297909130045. PMID:20210704.
- Xiong B et al. (2008), Proteins, 71, 1984-1994. The type IA topoisomerase catalytic cycle: A normal mode analysis and molecular dynamics simulation. DOI:10.1002/prot.21876. PMID:18186484.
- Champoux JJ (2002), Trends Pharmacol Sci, 23, 199-201. A first view of the structure of a type IA topoisomerase with bound DNA. DOI:10.1016/s0165-6147(02)01997-1. PMID:12007989.
- Chen SJ et al. (1998), J Biol Chem, 273, 6050-6056. Identification of Active Site Residues in Escherichia coli DNA Topoisomerase I. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.11.6050. PMID:9497321.
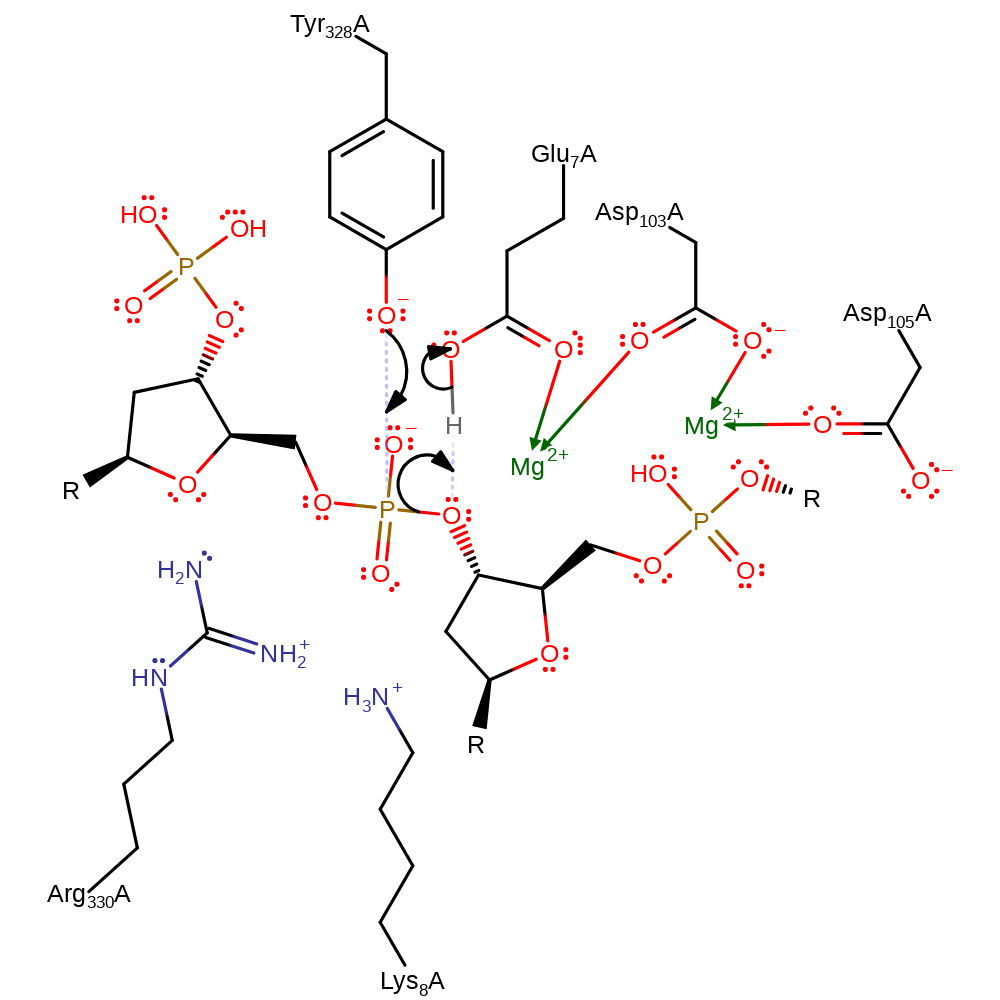
Step 1. Tyr328 acts as a nucleophile, attacking the phosphorous of the DNA molecule, which proceeds through a pentavalent transition state, before eliminating the 5' DNA, with concomitant deprotonation of Glu7.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys8A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu7A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr328A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg330A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu7A | metal ligand |
| Asp103A | metal ligand |
| Asp105A | metal ligand |
| Glu7A | proton donor |
| Tyr328A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
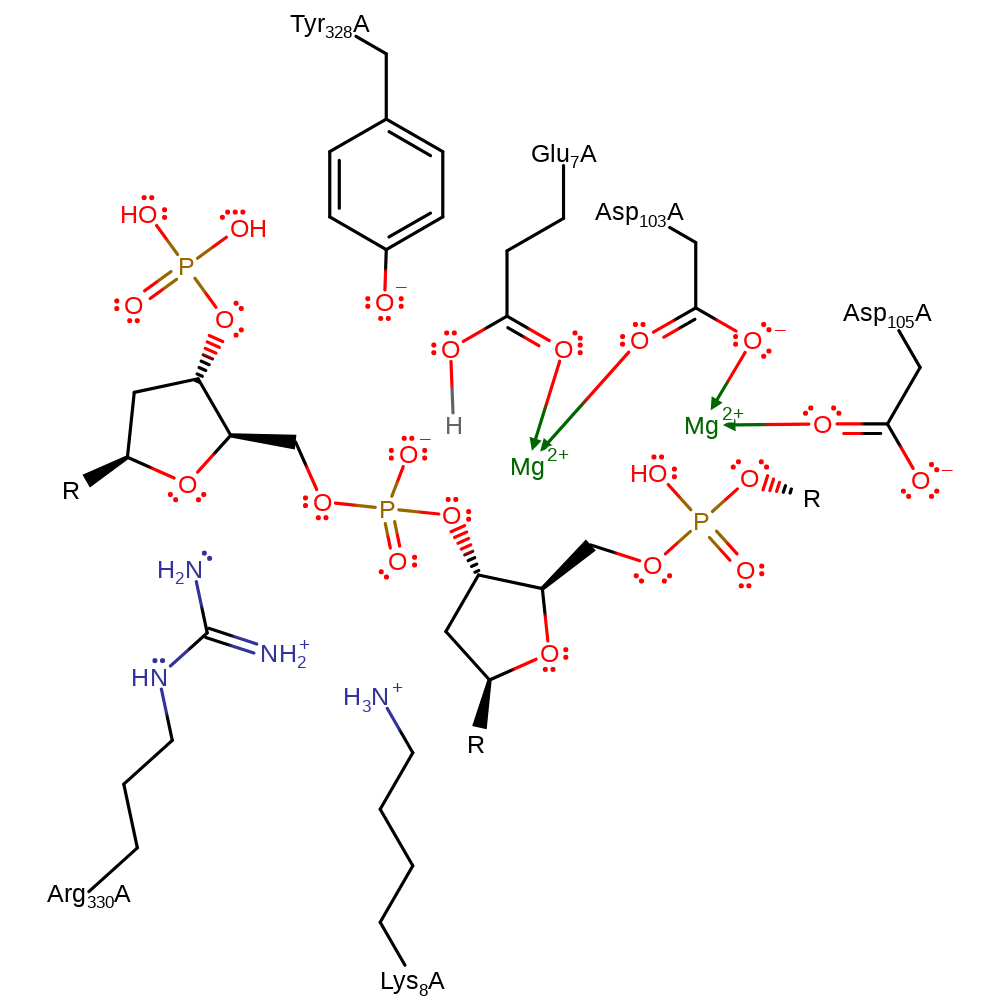
Step 2. The DNA uncoils before Glu7 deprotonates the 5'-OH, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the phosphorous atom, which proceeds through a pentavalent transition state, before eliminating Tyr328.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr328A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys8A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu7A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg330A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu7A | metal ligand |
| Asp103A | metal ligand |
| Asp105A | metal ligand |
| Glu7A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr328A | nucleofuge |

 Download:
Download: