Phosphoribosylaminoimidazolecarboxamide formyltransferase
The enzyme AITC is bifunctional being involved in the production of IMP, the final product of the de novo purine synthesis pathway.. The catalytic centre described here catalyses the first step in AIRC activity, the formylation of AICAR to form 5-formyl AICAR which can then be cyclised by the second catalytic centre. The enzyme shows a high degree of sequence conservation among organisms from E.coli to man, but does not show homology to other formyl transferases, suggesting that the bifunctionality has evolved from one gene rather than two.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P31939
 (2.1.2.3, 3.5.4.10)
(2.1.2.3, 3.5.4.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1p4r
- Crystal Structure of Human ATIC in complex with folate-based inhibitor BW1540U88UD
(2.55 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.140.20
 (see all for 1p4r)
(see all for 1p4r)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.2.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The cofactor which supplies the formyl group is N10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate (10-f-THF). During the reaction nucleophilic attack by the amino group of AICAR, facilitated by deprotonation by His 267, forms a tetrahedral intermediate, stabilised by Lys 266 and Asn 431. This collapses following protonation of the cofactor by Lys 266 to release the product. His 267 is activated towards its role as a general base by Asn 431 and His 593.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1p4r) | ||
| Lys266 | Lys266A | Stabilises transition state by forming electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged oxygen of the tetrahedral intermediate, then protonates the THF cofactor to allow it to act as a leaving group for the reaction so that the tetrahedral intermediate collapses. | proton acceptor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| His267 | His267A | Deprotonates AICAR to allow its amino group to attack THF as a nucleophile, forming the tetrahedral intermediate that collapses to the product. | proton relay, proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| His592 | His592B | Acts as a primer by modifying the pKa of His 267 so that it can act as a general acid base during the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| Asn431 | Asn431B | Stabilises tetrahedral intermediate through hydrogen bonding, and also acts to modify the pKa of His 267 to allow it to function as a general acid base. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton relay, proton transfer, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formed, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms)References
- Shim JH et al. (2001), J Am Chem Soc, 123, 4687-4696. Evaluation of the Catalytic Mechanism of AICAR Transformylase by pH-Dependent Kinetics, Mutagenesis, and Quantum Chemical Calculations. DOI:10.1021/ja010014k. PMID:11457277.
- Cheong CG et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 18034-18045. Crystal Structures of Human Bifunctional Enzyme Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide Ribonucleotide Transformylase/IMP Cyclohydrolase in Complex with Potent Sulfonyl-containing Antifolates. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m313691200. PMID:14966129.
- Wolan DW et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 15505-15513. Structural Insights into the Avian AICAR Transformylase Mechanism†. DOI:10.1021/bi020505x. PMID:12501179.
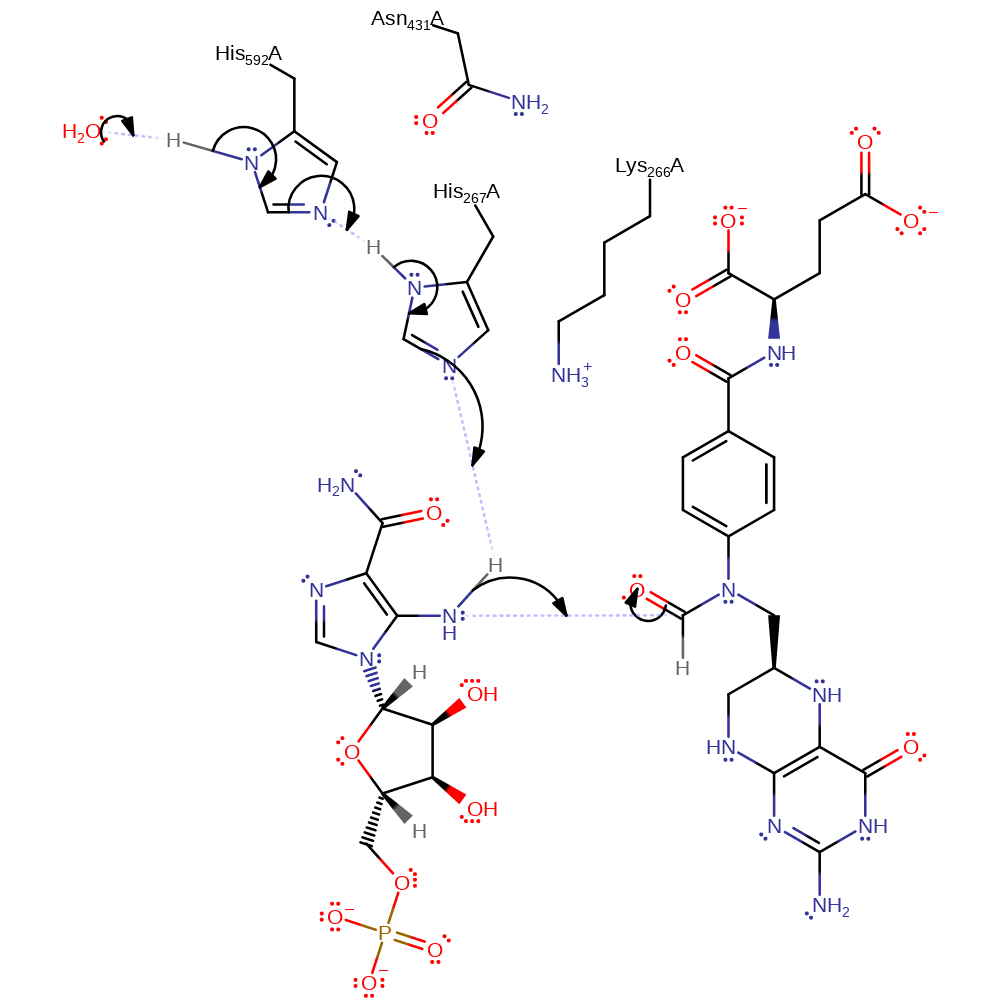
Step 1. Solvent deprotoantes His592 which triggers the subsequent deprotonation of His267 and the substrate amine group. The amine then attacks the aldehyde group of 10-f-THF.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn431B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys266A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His592B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His267A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His592B | modifies pKa |
| Asn431B | modifies pKa |
| His267A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| His592B | proton donor, proton acceptor, proton relay |
| His267A | proton relay |
Chemical Components
proton relay, proton transfer, overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses to form the product and the cofactor is protonated by Lys266. The native state of the enzyme is regenerated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His267A | proton relay |
| His592B | proton relay |
| Asn431B | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| His267A | proton donor |
| Lys266A | proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| His592B | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His267A | proton acceptor |
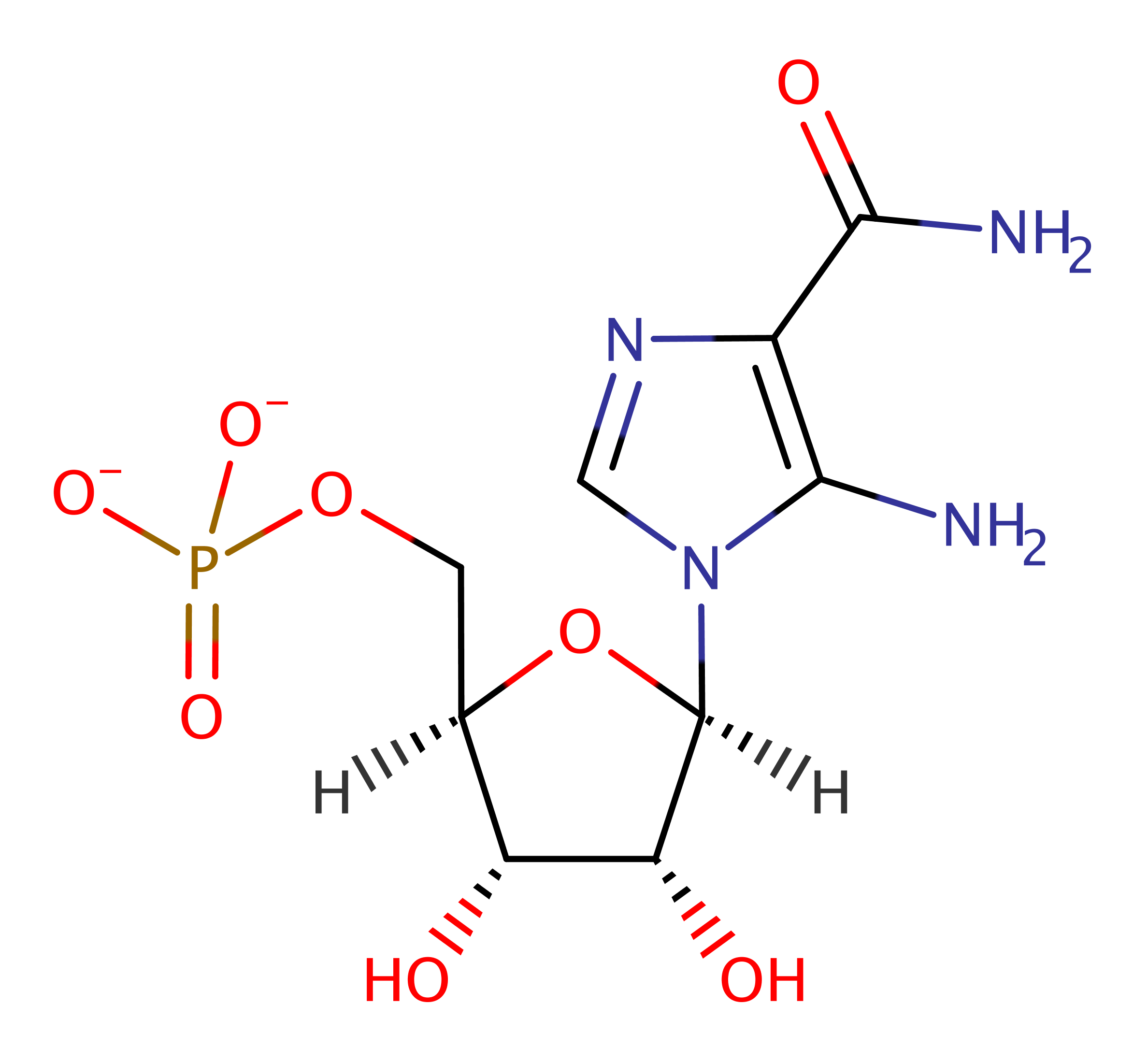



 Download:
Download: