HslU---HslV peptidase
HslVU is an ATP-dependent prokaryotic proteasome. It is a homolog of the eukaryotic 26S proteasome. It is responsible for the degradation of a majority of proteins in the cell, including regulatory protein factors and abnormally folded proteins. HslVU has two protein components, HslV and HslU. HslV is a protease. By itself, HslV has a low catalytic activity. Its activity is enhanced greatly by the interaction with HslU to form HslVU complex. HslU consists of ATPase and chaperone activities. It belongs to the Hsp100/Clp family of molecular chaperones, which is a member of the extended AAA(ATPase associated with a variety of cellular activities) family. It was found that the degradation of polypeptides by HslVU has an ATP requirement. For at least one substrate, SulA protein, ATP hydrolysis is required for degradation. Though ATP hydrolysis does not seem to be mandatory.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P0A7B8
 (3.4.25.2)
(3.4.25.2)
P0A6H5
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ht1
- Nucleotide-Dependent Conformational Changes in a Protease-Associated ATPase HslU
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.20.10
 (see all for 1ht1)
(see all for 1ht1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.25.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
HslV is an N-terminal nucleophilic (Ntn) hydrolase. N-terminal threonine residue(Thr1) hydroxyl group is deprotonated by its own -NH2 group as it attacks the substrate carbonyl to form a tetrahedral intermediate, which is stabilised by an oxyanion hole formed by the backbone NH group of Gly 45. Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate with protonation of the departing amine group by the terminal -NH3+ group generates an acyl enzyme intermediate; this is then attacked by a water molecule that is deprotonated by the terminal -NH2 group of Thr 1 acting again as a general base. The nearby Lys 33 (in its protonated form) hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl group oxygen atom of Thr 1 and provide a positive charge to promote deprotonation of this group in the first step of the reaction. Conserved Ser124 appears to hydrogen bond with the Thr1 N and maybe necessary to control the protonation of Thr1 N. In addition, the binding and hydrolysis of ATP by HsIU is essential for activation of protease activity in HsIV.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ht1) | ||
| Thr2, Thr2 (N-term) | Thr1A(E), Thr1A(E) (N-term) | Its hydroxyl group, upon deprotonation by its -NH2, acts as a nucleophile to attack the substrate carbonyl to form a tetrahedral intermediate. Its NH3+ group then protonates the departing amine group to generate the acyl enzyme intermediate; this is then attacked by a water molecule that is deprotonated by the terminal -NH2 group of Thr 1. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gly46 (main-N) | Gly45A(E) (main-N) | Its backbone amide forms an oxyanion hole to stabilise the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys34 | Lys33A(E) | It forms a hydrogen bond with the hydroxyl group oxygen atom of Thr 1 and provides a positive charge to promote deprotonation of this group in the first step of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser125 | Ser124A(E) | It hydrogen bonds with the Thr 1 N and controls the protonation of Thr 1 N. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Bochtler M et al. (1997), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 94, 6070-6074. Crystal structure of heat shock locus V (HslV) from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1073/pnas.94.12.6070. PMID:9177170.
- Marques AJ et al. (2009), Chem Rev, 109, 1509-1536. Catalytic mechanism and assembly of the proteasome. DOI:10.1021/cr8004857. PMID:19265443.
- Yoo SJ et al. (1997), FEBS Lett, 412, 57-60. Mutagenesis of two N-terminal Thr and five Ser residues in HslV, the proteolytic component of the ATP-dependent HslVU protease. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00742-4. PMID:9257689.
- Rohrwild M et al. (1996), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 93, 5808-5813. HslV-HslU: A novel ATP-dependent protease complex in Escherichia coli related to the eukaryotic proteasome. DOI:10.1073/pnas.93.12.5808. PMID:8650174.

Step 1. N-terminal Thr 1 is deprotonated by its own -NH2 group via a water molecule. This activates Thr 1 to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the carbonyl.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly45A(E) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys33A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser124A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr1A(E) | proton donor, nucleophile |
| Thr1A(E) (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The N-terminal product then deprotonates the N-terminus of Thr 1.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys33A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly45A(E) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser124A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr1A(E) (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 3. The N-terminus of Thr 1 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the ester bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys33A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly45A(E) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser124A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr1A(E) (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates another elimination which results in the release of Thr 1 which now accepts a proton from its N-terminus which returns the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys33A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly45A(E) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser124A(E) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr1A(E) | proton acceptor |
| Thr1A(E) (N-term) | proton donor |
| Thr1A(E) | nucleofuge |






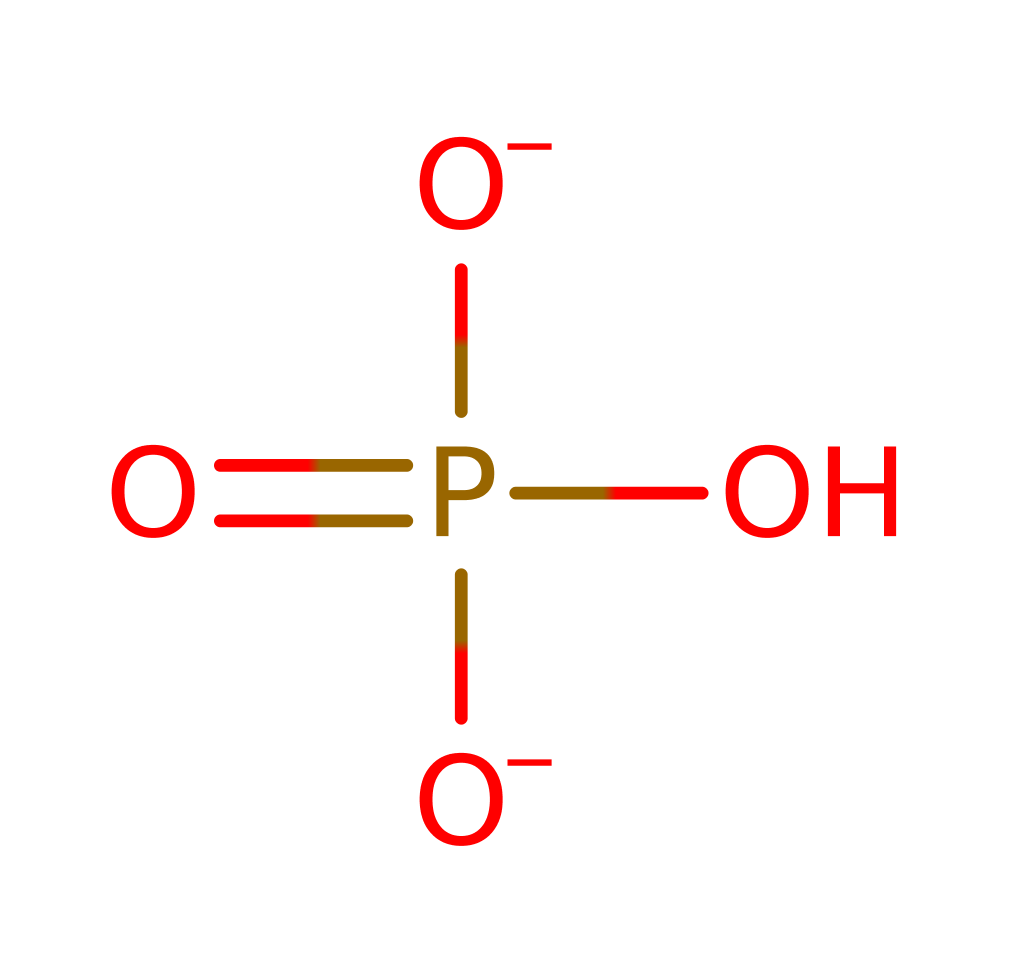
 Download:
Download: