Peptide chain release factor N5-glutamine methyltransferase
Post translational methylation of release factors on the glutamine residue of a conserved GGQ motif is required for efficient termination of protein synthesis. This methylation is performed by an N5-glutamine methyltransferase called HemK. Release factor 1 and 2 contain a conserved GGQ motif that is thought to play a role in activating or positioning the water molecule involved in hydrolysis at the peptidyl transferase active site.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9WYV8
 (2.1.1.297)
(2.1.1.297)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1vq1
- Crystal structure of N5-glutamine methyltransferase, HemK(EC 2.1.1.-) (TM0488) from Thermotoga maritima at 2.80 A resolution
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.150
 (see all for 1vq1)
(see all for 1vq1)
- Cofactors
- S-adenosyl-l-methionine (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.1.297)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
HemK catalyzes the methyl-transfer reaction by converting S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and N5-glutamine (NGLN) into corresponding S-adensoyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) and methyl-glutamine (MGLN), which is the key step for the enzymatic reaction. Asn197 and Pro198 play a pivotal role in stabilising the transition state and regulating the positioning of reactive groups. The N5 lone pair of glutamine is held in position by Asn197 and Pro198. The SAM methyl group on the S atom is positioned linearly with respect to the N lone pair. The reaction proceeds with inversion of symmetry surrounding the methyl group in a typical SN2-type reaction. The N centre is stabilised by Asn197 and Pro198. Possibly the carbocation is stabilised by Ala218 through the transition state. This yields a charged sp3-hybridized nitrogen center on the product MGLN and SAH. The neutral product is formed by loss of a proton to the solvent during or after MGLN leaves the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1vq1) | ||
| Phe100 | Phe100(112)A | May function to destabilize the charged S of SAM. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn197 | Asn197(209)A | Hydrogen bonds to N5 to position it correctly with respect to SAM. This bonding also stabilises the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pro198 (main-C) | Pro198(210)A (main-C) | Hydrogen bonds to N5 to position it correctly with respect to SAM. This bonding also stabilises the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, cofactor used, overall reactant used, proton transfer, overall product formedReferences
- Schubert HL et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 5592-5599. Structures along the Catalytic Pathway of PrmC/HemK, anN5-Glutamine AdoMet-Dependent Methyltransferase†. DOI:10.1021/bi034026p. PMID:12741815.
- Wu R et al. (2008), J Comput Chem, 29, 350-357. QM/MM study of catalytic methyl transfer by theN5-glutamine SAM-dependent methyltransferase and its inhibition by the nitrogen analogue of coenzyme. DOI:10.1002/jcc.20793. PMID:17591721.
- Yang Z et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 340, 695-706. Structural Characterization and Comparative Phylogenetic Analysis of Escherichia coli HemK, a Protein (N5)-glutamine Methyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.019. PMID:15223314.

Step 1. In an SN2 reaction the N5 of glutamine attacks the methyl group of SAM.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe100(112)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pro198(210)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn197(209)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, cofactor used, overall reactant used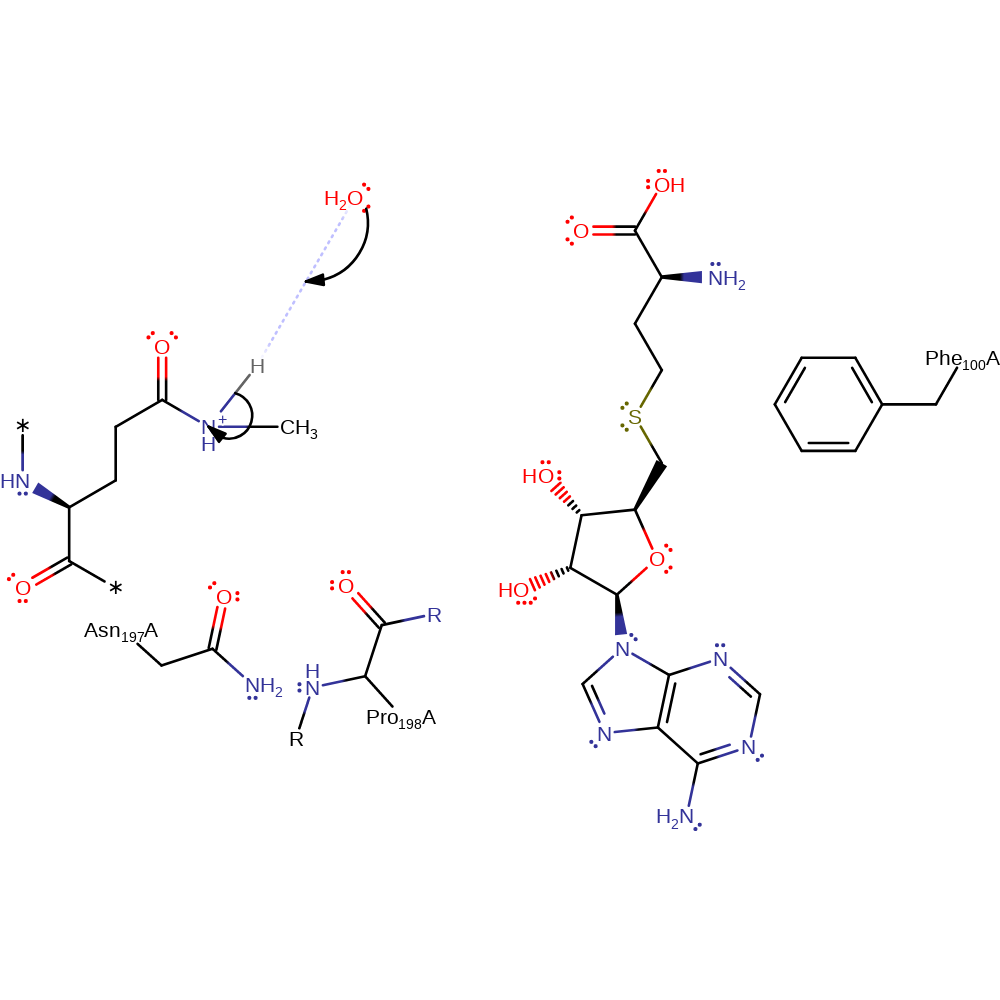
Step 2. The charged nitrogen on the product loses a proton to solvent to form neutral MGLN.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe100(112)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn197(209)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pro198(210)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |





 Download:
Download: