Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase
The alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (KGDC), also known as the oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (OGDC), is composed of multiple copies of three enzymes: oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (E1o), dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2o), and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3o). The E2o component of the KGDC is a modular protein that is composed of one lipoyl domain at the N-terminus, followed by an E1o- and/or E3o-binding domain, and then by a carboxyl terminal catalytic domain. Although the catalytic domain forms trimers, the enzyme forms the octahedral inner core of the multienzyme complex, an aggregation of 24 subunits arranged with 432 point group symmetry. The substrate (dihydrolipoamide) is covalently bound to a specific lysine residue in the lipoyl domain. The enzyme catalyses the transfer of a succinyl group from the S-succinyldihydrolipoyl moiety to coenzyme A.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0AFG6
 (2.3.1.61)
(2.3.1.61)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1c4t
- CATALYTIC DOMAIN FROM TRIMERIC DIHYDROLIPOAMIDE SUCCINYLTRANSFERASE
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.559.10
 (see all for 1c4t)
(see all for 1c4t)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.61)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The first step is the deprotonation of the thiol group of coenzyme A by the active site residue His375. The activated thiolate attacks the carbonyl carbon of the succinylated dihydrolipoyl moiety to form a tetrahedral intermediate, which is stabilised by Thr323'. The collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate results in the succinylation of coenzyme A, and the protonation of the dihydrolipoyl moiety.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1c4t) | ||
| Thr324 | Thr323(152)C | Thr323 stabilises the tetrahedral intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| His376 | His375(204)A | His375 deprotonates the thiol group of coenzyme A to form the nucleophile thiolate. | activator, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Knapp JE et al. (2000), Protein Sci, 9, 37-48. Expression, purification, and structural analysis of the trimeric form of the catalytic domain of the Escherichia coli dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase. DOI:10.1110/ps.9.1.37. PMID:10739245.
- Perham RN (2000), Annu Rev Biochem, 69, 961-1004. Swinging Arms and Swinging Domains in Multifunctional Enzymes: Catalytic Machines for Multistep Reactions. DOI:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.961. PMID:10966480.
- Knapp JE et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 280, 655-668. Crystal structure of the truncated cubic core component of the Escherichia coli 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.1924. PMID:9677295.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr323(152)C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His375(204)A | activator |
| Thr323(152)C | polar interaction |
| His375(204)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 2. Activated thiolate performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon on the succinyl dihydrolipoyl moiety to form a tetrahedral intermediate stabilised by Thr323.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr323(152)C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr323(152)C | polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 3. Tetrahedral intermediate collapse which sees the succinyl group transferred to CoA.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr323(152)C | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His375(204)A | proton donor |

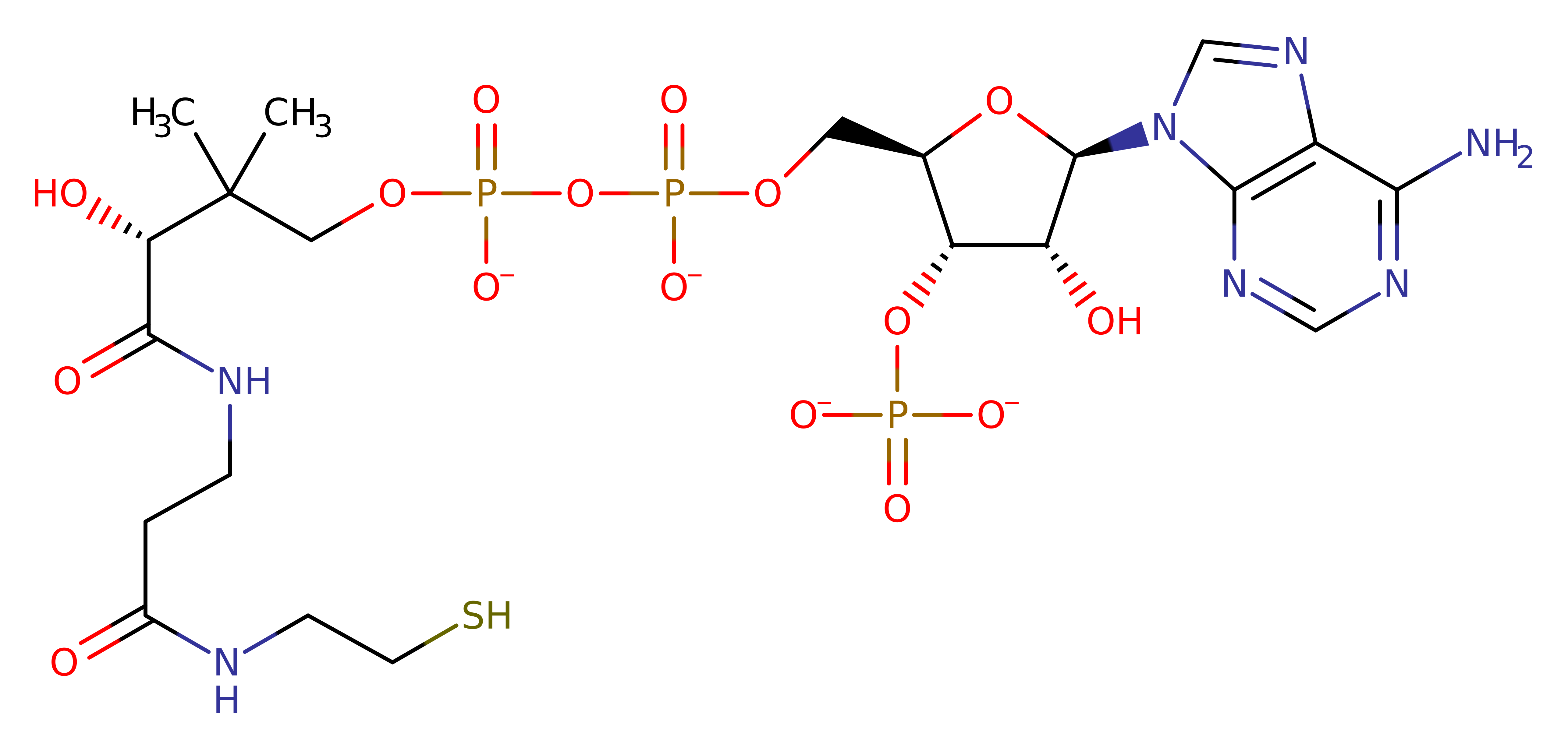



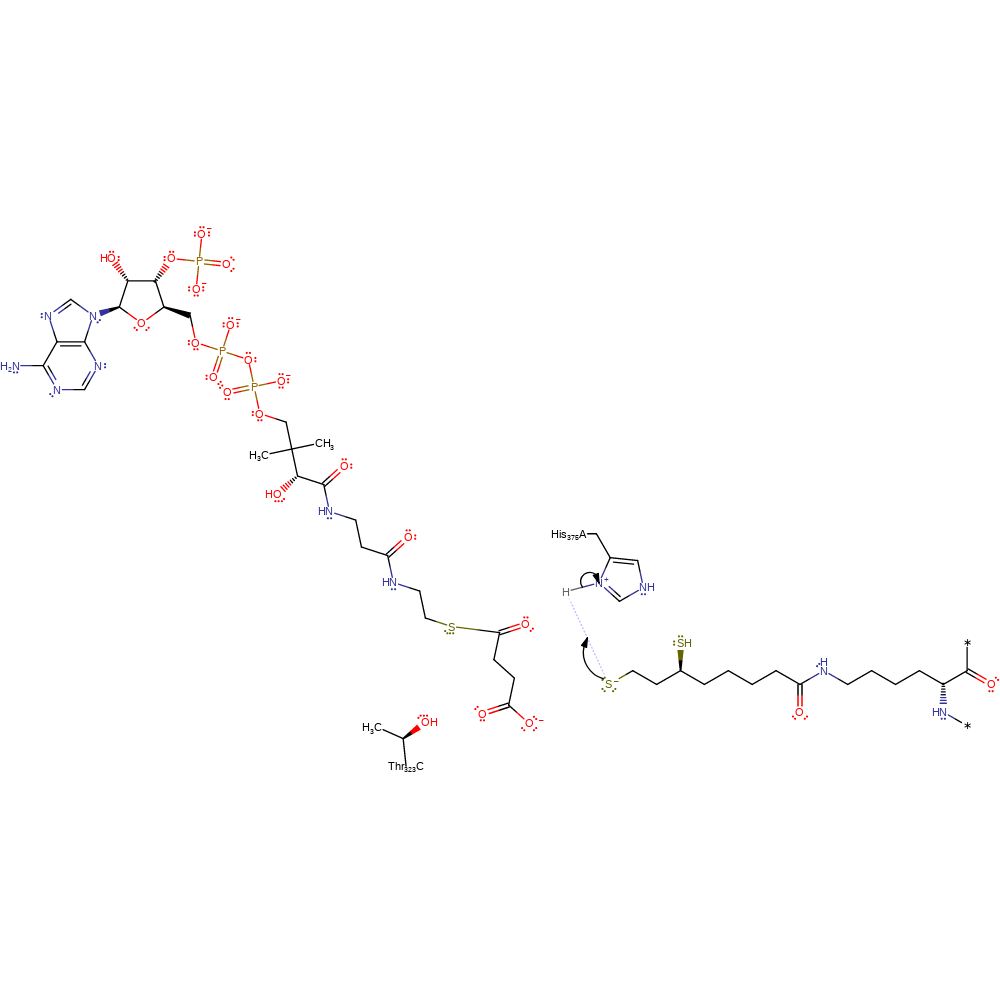
 Download:
Download: