Protein-methionine-S-oxide reductase (MsrB)
The oxidation of methionine residues to methionine sulfoxide is implicated in ageing processes; the reduction of methionine sulfoxide protein residues is similarly implicated in antioxidant repair activity, but also the virulence of pathogenic organisms, such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae which secretes pilB. The modular pilB contains three domains; one is a methionine sulfoxide reductase (MsrA) which reduces S-methionine sulfoxide (S-chiral at sulphur), and another an MsrB (this entry) which reduces R-methionine sulfoxide. The two domains have no sequence homology but use the same mechanism - an example of the fusion of two convergently evolved enzymes.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P14930
 (1.8.4.11, 1.8.4.12)
(1.8.4.11, 1.8.4.12)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1l1d
- Crystal structure of the C-terminal methionine sulfoxide reductase domain (MsrB) of N. gonorrhoeae pilB
(1.85 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.170.150.20
 (see all for 1l1d)
(see all for 1l1d)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.8.4.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
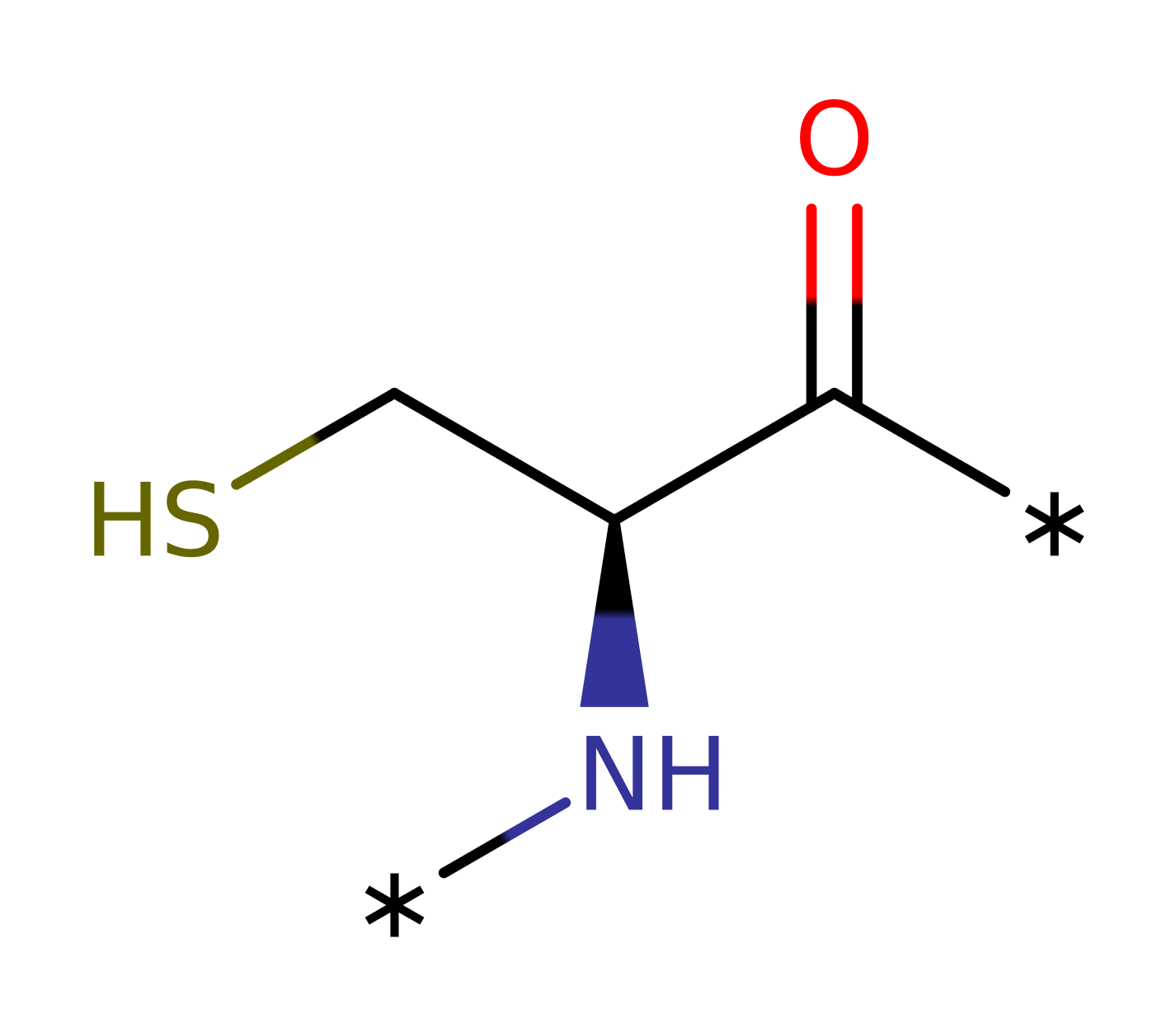
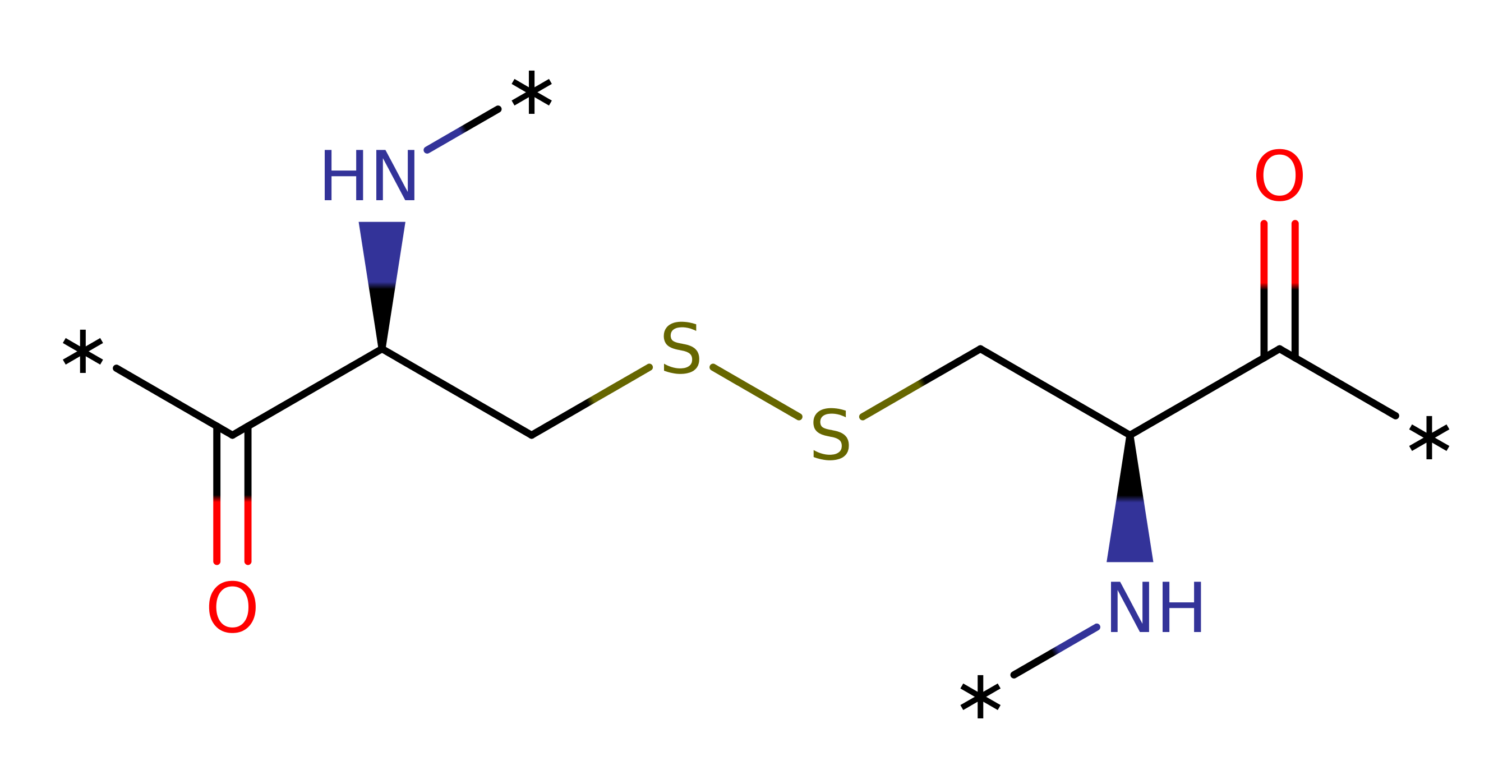
Cys 495 exists as a thiolate due to the conserved interactions with Arg 493 and Asp 484. Attack of Cys 495 on the sulphur of methionine sulfoxide leads to a 1,3-sigmatropic rearrangement involving the sulphur of Cys 495, and the S=O atoms of the substrate. The trigonal bipyramid transition state (one equatorial position occupied by the substrate sulphur lone pair) is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to His 480 and a fixed water molecule. The transition state collapses to yield methionine and a sulfenic acid intermediate, with Cys 495 hydroxylated as Cys 495-SOH . Cys 440 is also a thiolate and forms a disulfide bond with Cys 495, releasing the hydroxyl group as water. The disulfide bond is reduced by thioredoxin to regenerate the free thiolates.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l1d) | ||
| Cys440 | Cys440(70)B | Cys 440 attacks the sulfenic acid intermediate of Cys 495, forming a disulfide bond and displacing the hydroxyl as water. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor |
| His480 | His480(110)B | His 480 is the oxyanion hole, stabilising the trigonal bipyramid transition state via hydrogen bonding to the negative charge on the substrate oxygen. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp484 | Asp484(114)B | Asp 484 hydrogen bonds to Arg 493, making Arg 493 a better stabiliser of the thiolate charge. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493 | Arg493(123)B | Arg 493 hydrogen bonds to the Cys 495 thiolate, stabilising the negative charge (i.e. lowers the pKa of the neutral form). | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys495 | Cys495(125)B | The Cys 495 thiolate attacks the sulphur of the methionine sulfoxide residue, leading to a 1,3-sigmatropic rearrangement with the sulfoxide group. The oxygen of the sulfoxide is therefore transferred to Cys 495 to give a sulfenic acid intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, electrofuge, electrophile |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, sigmatropic rearrangement, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavageReferences
- Olry A et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 11616-11622. Kinetic Characterization of the Catalytic Mechanism of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase B fromNeisseria meningitidis†. DOI:10.1021/bi049306z. PMID:15350148.
- Olry A et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 12016-12022. Characterization of the Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase Activities of PILB, a Probable Virulence Factor fromNeisseria meningitidis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m112350200. PMID:11812798.
- Lowther WT et al. (2002), Nat Struct Biol, 9, 348-352. The mirrored methionine sulfoxide reductases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilB. DOI:10.1038/nsb783. PMID:11938352.

Step 1. Catalysis begins with nucleophilic attack of Cys495 on the sulfoxide group of the reactant. The developing oxyanion abstracts a proton from His480.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His480(110)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493(123)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys495(125)B | covalently attached |
| Asp484(114)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys495(125)B | nucleophile |
| His480(110)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 2. There is a 1,3 sigmatropic rearrangement leading to the formation of a sulfenic acid intermediate and the release of the methionine product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys495(125)B | covalently attached |
| His480(110)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp484(114)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493(123)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys495(125)B | electrophile, electrofuge |
Chemical Components
sigmatropic rearrangement, overall product formed
Step 3. Cys495 is subject to nucleophilic attack by Cys440, releasing the hydroxyl group which accepts a proton from a donor to form water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His480(110)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp484(114)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493(123)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys495(125)B | electrofuge, electrophile |
| Cys440(70)B | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution
Step 4. In a series of inferred steps the newly formed disulfide bond between Cys440 and Cys495 is reduced by thioredoxin. This begins with nucleophilic attack on the disulfide bond by a thioredoxin thiol.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys495(125)B | electrophile |
| Cys440(70)B | nucleofuge |
| Cys495(125)B | electrofuge |
| Cys440(70)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 5. The second thioredoxin residue initiates nucleophilic attack on the thioredoxin Cys495 disulfide bond, eliminating Cys495 and forming a new disulfide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys495(125)B | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution
Step 6. In an inferred step His480 is reprotonated to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His480(110)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transferIntroduction
In a computational study a mechanism involving a sulfonium ion intermediate was proposed. The reaction begins with nucleophilic attack of Cys495 on the sulfoxide of the substrate, within concomitant proton transfer from His480. Next, protonation of the sulfurane oxygen by His477 occurs. Finally there is direct nucleophilic attack of Cys440 on the Cys495-substrate bond, releasing water and methionine. The Cys440-Cys495 disulfide bond is reduced by thioredoxin to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l1d) | ||
| His477 | His477(107)B | His477 is the most likely proton source for protonation of the oxygen in the sulfurane intermediate. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys440 | Cys440(70)B | Cys 440 attacks the sulfonium ion intermediate of Cys 495, forming a disulfide bond and displacing the hydroxyl as water. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor |
| His480 | His480(110)B | His 480 protonates and forming oxyanion on the sulfurane intermediate after nucleophilic attack of the substrate by Cys 495. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp484 | Asp484(114)B | Asp 484 hydrogen bonds to Arg 493, making Arg 493 a better stabiliser of the thiolate charge. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493 | Arg493(123)B | Arg 493 hydrogen bonds to the Cys 495 thiolate, stabilising the negative charge (i.e. lowers the pKa of the neutral form). | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys495 | Cys495(125)B | The Cys495 thiolate attacks the sulphur of the methionine sulfoxide residue, forming an enzyme-substrate complex. The disulfide bond is cleaved after nucleophilic attack from Cys440. | electrophile, electrofuge, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Robinet JJ et al. (2011), J Phys Chem B, 115, 9202-9212. A sulfonium cation intermediate in the mechanism of methionine sulfoxide reductase B: a DFT study. DOI:10.1021/jp111681e. PMID:21721538.
- Olry A et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 11616-11622. Kinetic Characterization of the Catalytic Mechanism of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase B fromNeisseria meningitidis†. DOI:10.1021/bi049306z. PMID:15350148.
- Olry A et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 12016-12022. Characterization of the Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase Activities of PILB, a Probable Virulence Factor fromNeisseria meningitidis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m112350200. PMID:11812798.

Step 1. Cys495 initiates nucleophilic attack on the sulfoxide sulfur of the reactant. The developing oxyanion is protonated by His480.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp484(114)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493(123)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His480(110)B | proton donor |
| Cys495(125)B | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer
Step 2. The sulfurane intermediate is protonated to form a sulfonium ion intermediate. The proton source is most likely to be His477.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His480(110)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp484(114)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg493(123)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His477(107)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 3. There is direct nucleophilic attack of Cys440 on Cys495, forming methionine and releasing water in the process.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys440(70)B | nucleophile |
| Cys495(125)B | electrofuge, electrophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 4. In a series of inferred steps the newly formed disulfide bond between Cys440 and Cys495 is reduced by thioredoxin. This begins with nucleophilic attack on the disulfide bond by a thioredoxin thiol.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys495(125)B | electrofuge |
| Cys440(70)B | proton acceptor |
| Cys495(125)B | electrophile |
| Cys440(70)B | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 5. The second thioredoxin residue initiates nucleophilic attack on the thioredoxin Cys495 disulfide bond, eliminating Cys495 and forming a new disulfide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys495(125)B | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated
Step 6. In an inferred step His480 and His477 are both reprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His480(110)B | proton acceptor |
| His477(107)B | proton acceptor |



 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: