Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase
The HisF subunit of Thermotoga maritima imidazole glycerol phosphate (ImGP) synthase catalyses the reaction of N'-((5'-phosphoribulosyl)formimino)-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-ribonucleotide (PRFAR) with ammonia to form an imine, loss of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribotide (AICAR), and the subsequent cyclisation to form ImGP. This reaction is the second half of the fifth step in histidine biosynthesis. ImGP and AICAR are used in histidine and purine biosynthesis respectively. Ammonia is delivered to the active site directly from an associated subunit, HisH, which hydrolyses glutamine to glutamate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9X0C6
 (4.3.2.10)
(4.3.2.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2a0n
- Crystal structure of Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase subunit hisF (EC 4.1.3.-) (tm1036) from Thermotoga maritima at 1.64 A resolution
(1.64 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 2a0n)
(see all for 2a0n)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.3.-)

Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
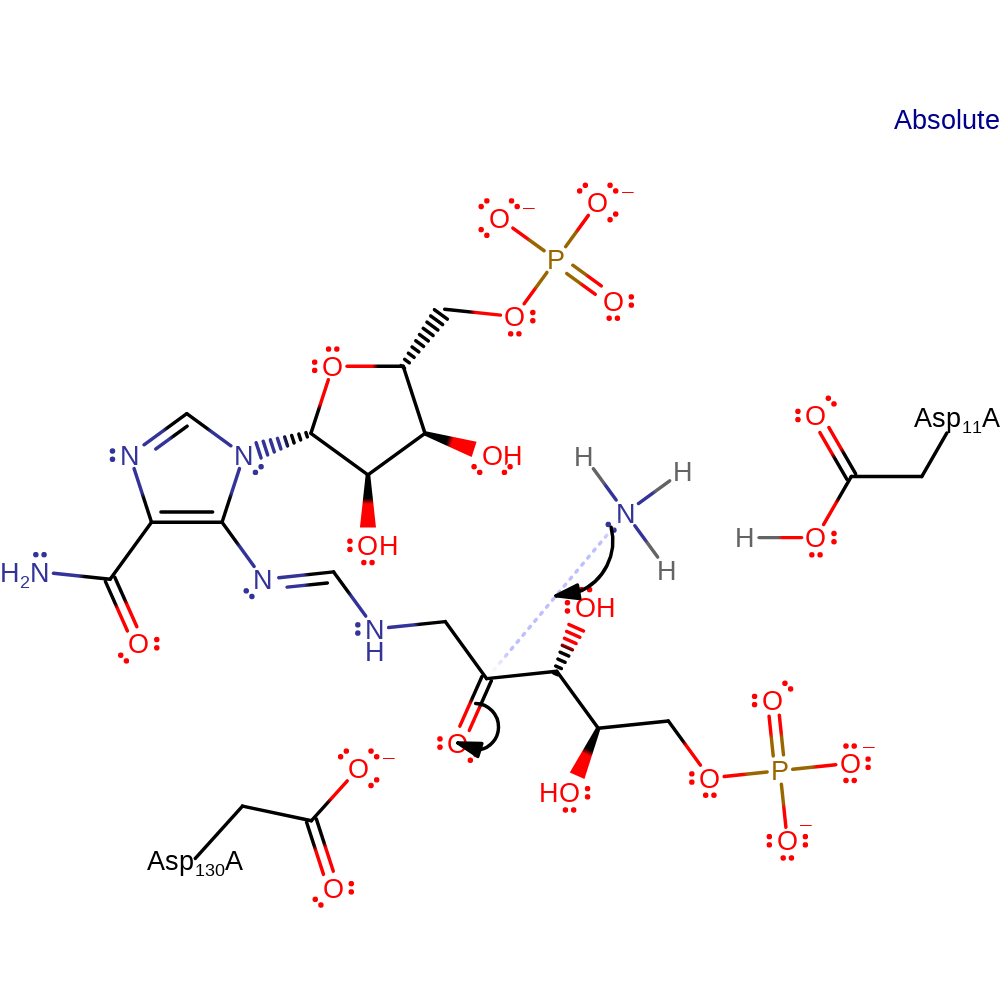
The reaction of PRFAR and ammonia moves through a series of imine intermediates. A nucleophilic ammonia molecule attacks the carbonyl group next to the phosphoglycerol, with subsequent imine formation. Water then hydrolyses the imine group linking the ribosephosphate and phosphoglycerol moieties, separating the substrate into a formamide and AICAR. These steps may be catalysed solely by enzyme binding, or be catalysed by the Asp 11 and Asp 130 residues necessary for the cyclisation steps. Asp 130 deprotonates -CH2- as the imine group intramolecularly attacks the electrophilic formamide group through the imine's nitrogen, with a protonated Asp 11 supplying the proton for the carbonyl oxygen atom. The resulting intermediate is cyclic with adjacent -C(OH)- and -NH- groups. Asp 11 can deprotonate -NH- leading to C=N imine bond formation, with the OH leaving as water with the proton from Asp 130.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2a0n) | ||
| Asp11 | Asp11(23)A | Asp 11 deprotonates the -CH2- group of the formamide intermediate. This occurs simultaneously with nucleophilic attack of the imine on the formamide. Asp 11 is now protonated and can act as a general acid to the hydroxy group, giving water as a leaving group. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp130 | Asp130(142)A | Asp 130 is protonated and can act as a general acid to the formamide's carbonyl group to give the hydroxyl of the next intermediate. Asp 130 can then deprotonate the -NH- group to form the imine bond of the imidazole product. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intramolecular elimination, dehydration, schiff base formed, overall product formed, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, cyclisation, bimolecular eliminationReferences
- Beismann-Driemeyer S et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 20387-20396. Imidazole Glycerol Phosphate Synthase fromThermotoga maritima. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m102012200. PMID:11264293.
- Chaudhuri BN et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 7003-7012. Toward understanding the mechanism of the complex cyclization reaction catalyzed by imidazole glycerolphosphate synthase: crystal structures of a ternary complex and the free enzyme. DOI:10.1021/bi034320h. PMID:12795595.
Step 1. Ammonia performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of PRFAR.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, dehydration, schiff base formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
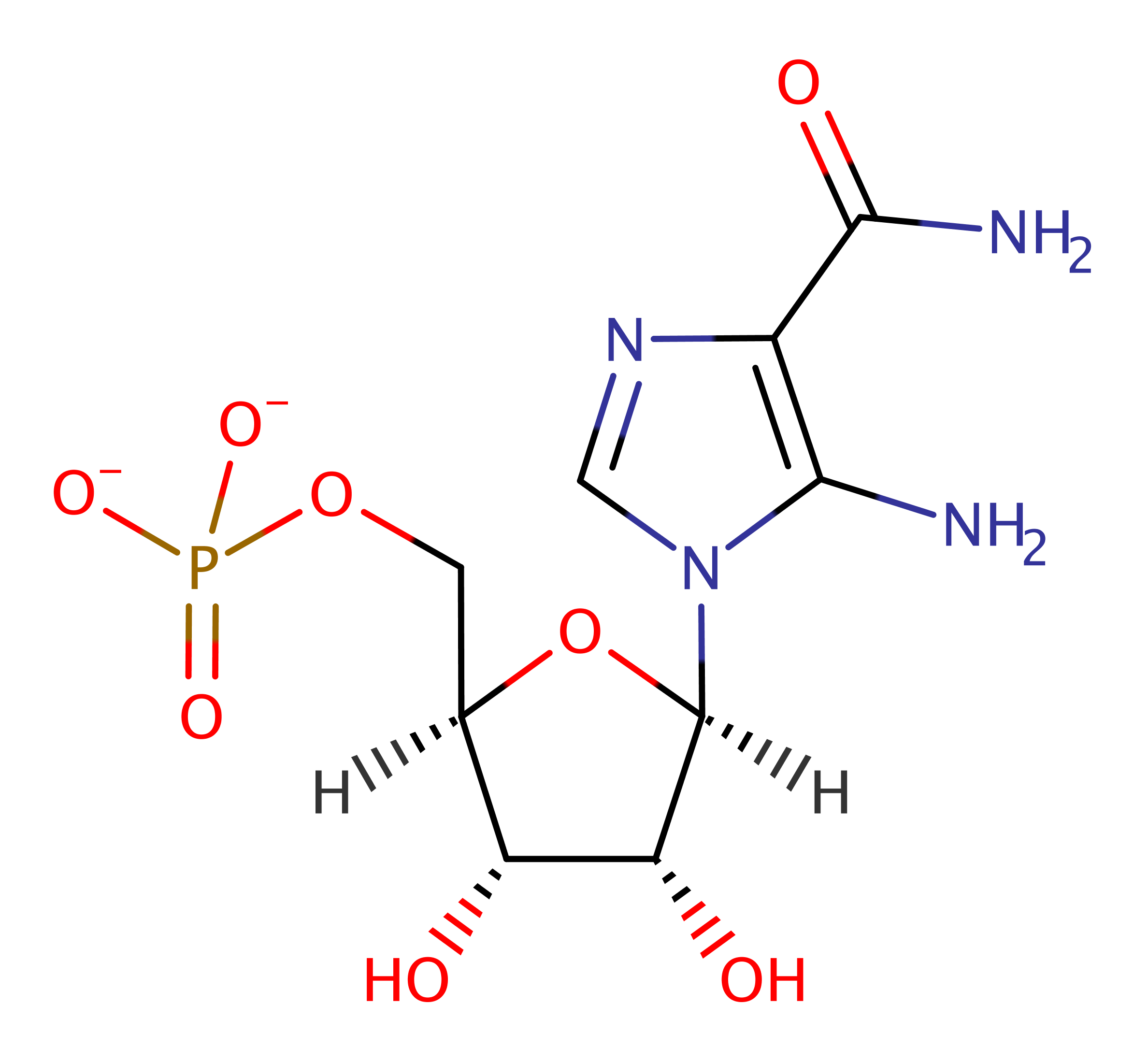
Step 4. The ribosephosphate moietie is then cleaved from the carbon and the product AICAR is released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, overall product formed
Step 5. Asp 130 deprotonates -CH2- as the imine group intramolecularly attacks the electrophilic formamide group through the imine's nitrogen, with a protonated Asp 11 supplying the proton for the carbonyl oxygen atom. This forms a cyclic intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp130(142)A | proton acceptor |
| Asp11(23)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, cyclisation
Step 6. Water is eliminated from the cyclic intermediate and the product is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp11(23)A | proton acceptor |
| Asp130(142)A | proton donor |






 Download:
Download: