Protein kinase C
Atypical protein kinase C iota (aPKC iota) from Homo sapiens catalyses the phosphorylation of a protein by hydrolysing ATP to ADP. aPKC iota can phosphorylate a number of different proteins, including interleukin receptor-associated kinase. aPKCs play critical roles in signalling pathways that control cell growth, differentiation and survival. Therefore they constitute targets for the development of novel therapeutics against cancer, for aPKC iota, specifically colon cancer and chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P41743
 (2.7.11.13)
(2.7.11.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1zrz
- Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of Atypical Protein Kinase C-iota
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.510.10
 (see all for 1zrz)
(see all for 1zrz)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.11.13)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
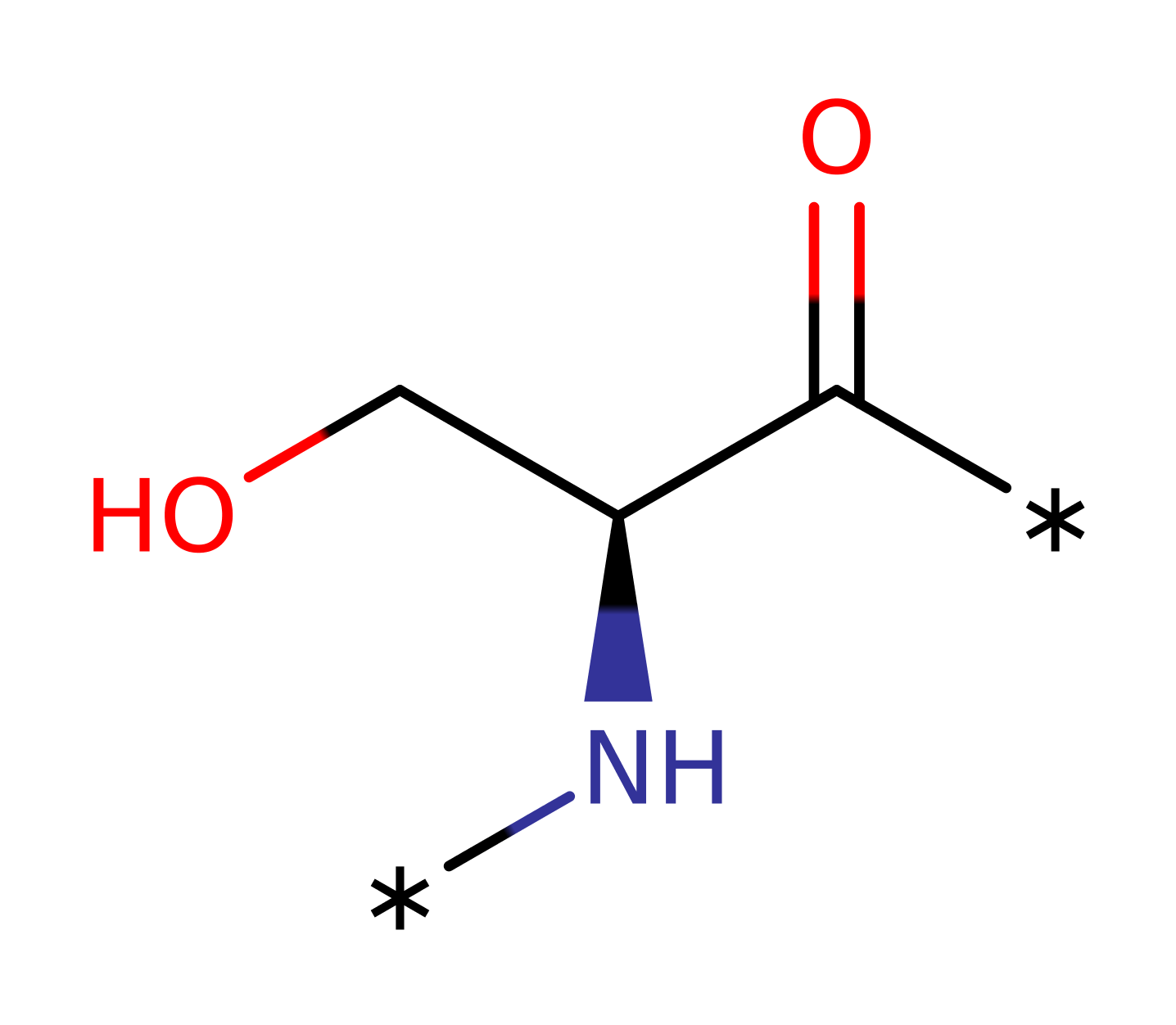
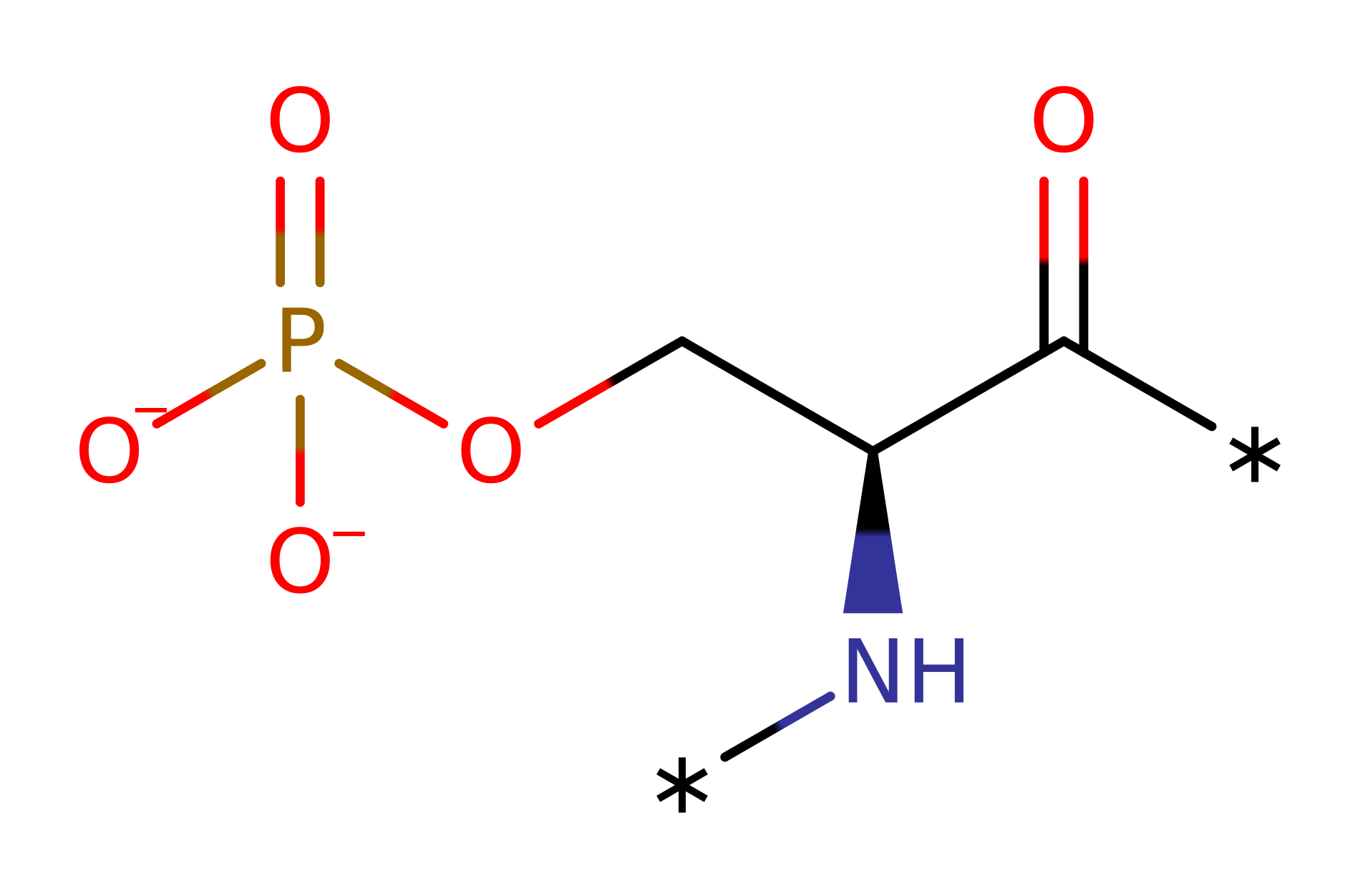
Asp 369 acts as a base by abstracting a proton from the phosphoacceptor, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the gamma phosphorus atom of ATP. Asp 369 is stabilised by a hydrogen bond to its main chain carbonyl from Asn 374. The reaction goes through a pentavalent transition state which is stabilised by Lys 371. The proton picked up by Asp 369 is then probably donated to the leaving group ADP.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1zrz) | ||
| Asp378 | Asp369(146)A | Acts as a general base, deprotonating the phosphoacceptor, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the gamma phosphate of ATP. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Lys380 | Lys371(148)A | Stabilises the transition state by hydrogen bonding to the gamma phosphate group of ATP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn383 | Asn374(151)A | Stabilises Asp 369 by hydrogen bonding to its main chain carboxylate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Messerschmidt A et al. (2005), J Mol Biol, 352, 918-931. Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of Human Atypical Protein Kinase C-iota Reveals Interaction Mode of Phosphorylation Site in Turn Motif. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.060. PMID:16125198.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn374(151)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp369(146)A | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Lys371(148)A | electrostatic stabiliser |