Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase
The control of sporulation in some bacteria is controlled by sigma factors, one of which is sigma-F which triggers the cascade of gene expression in the forespore compartment of the sporulating cell. Control of sigma-F is by the SpoII proteins: SpoIIAB, which binds to sigma-F and thereby inactivates it; SpoIIAA, a non-enzymatic protein which is phosphorylated by SpoIIAB, thus inducing release of sigma-F; and SpoIIE, a phosphatase which returns SpoII-P to the dephosphorylated state. SpoIIAB has the same ATP-binding domain as other members of the GHKL superfamily. It phosphorylates the Ser 58 residue of SpoIIAA, using up ATP.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
O32727
 (2.7.11.1)
(2.7.11.1)
O32728
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1l0o
- Crystal Structure of the Bacillus stearothermophilus Anti-Sigma Factor SpoIIAB with the Sporulation Sigma Factor SigmaF
(2.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.565.10
 (see all for 1l0o)
(see all for 1l0o)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.11.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The basic mechanism is the inline displacement of ADP, by nucleophilic attack of the SpoIIAA Ser 58 on the gamma-phosphate of ATP. Various residues and an Mg cofactor aid the reaction: Mg2+, bound by Asn 50 coordinates all three phosphate groups of ATP. This stabilises the transition state by reducing charge build-up. Arg 105 is in the correct position to stabilise the transition state by hydrogen bonding to two oxygens of the gamma-phosphate group. Glu 46 is the catalytic base.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l0o) | ||
| Asn50 | Asn50A | Chelates to the magnesium ion cofactor. | metal ligand |
| Glu46 | Glu46A | Glu 46 hydrogen bonds to the SpoIIAA Ser 58 hydroxyl, and probably acts as the catalytic base. | proton acceptor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg105 | Arg105A | Arg 105 stabilises the transition state by hydrogen bonding to two oxygens of the gamma-phosphate group. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step, proton transferReferences
- Campbell EA et al. (2002), Cell, 108, 795-807. Crystal structure of the Bacillus stearothermophilus anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB with the sporulation sigma factor sigmaF. DOI:10.2210/pdb1l0o/pdb. PMID:11955433.
- Masuda S et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 340, 941-956. Crystal Structures of the ADP and ATP Bound Forms of the Bacillus Anti-σ Factor SpoIIAB in Complex with the Anti-anti-σ SpoIIAA. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.040. PMID:15236958.

Step 1. Glu46 activates the Ser substrate by accepting a proton from it. Serine then attacks the gamma phosphate group from ATP, which gets displaced.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu46A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg105A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu46A | activator |
| Asn50A | metal ligand |
| Arg105A | polar interaction |
| Glu46A | proton acceptor |
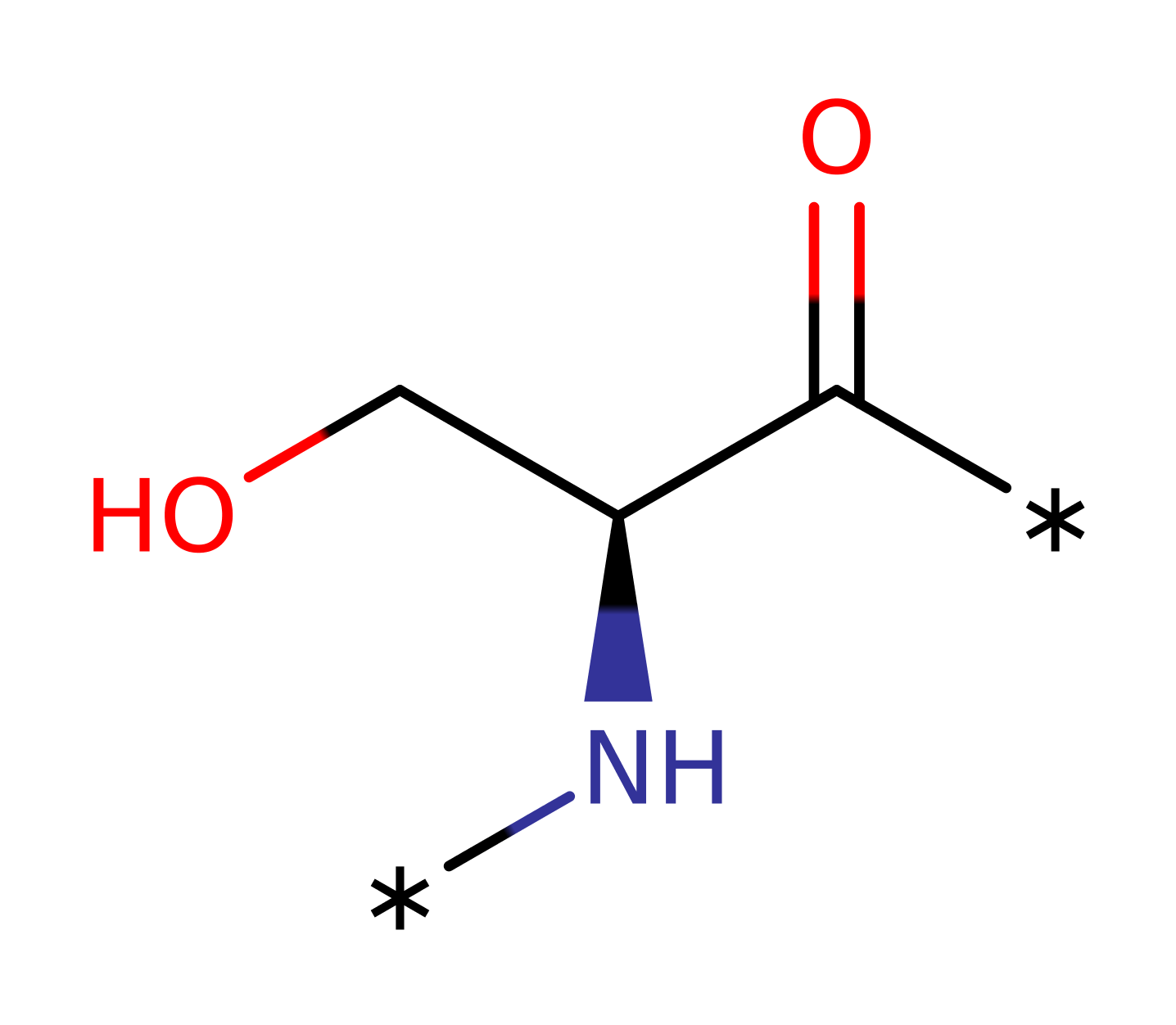



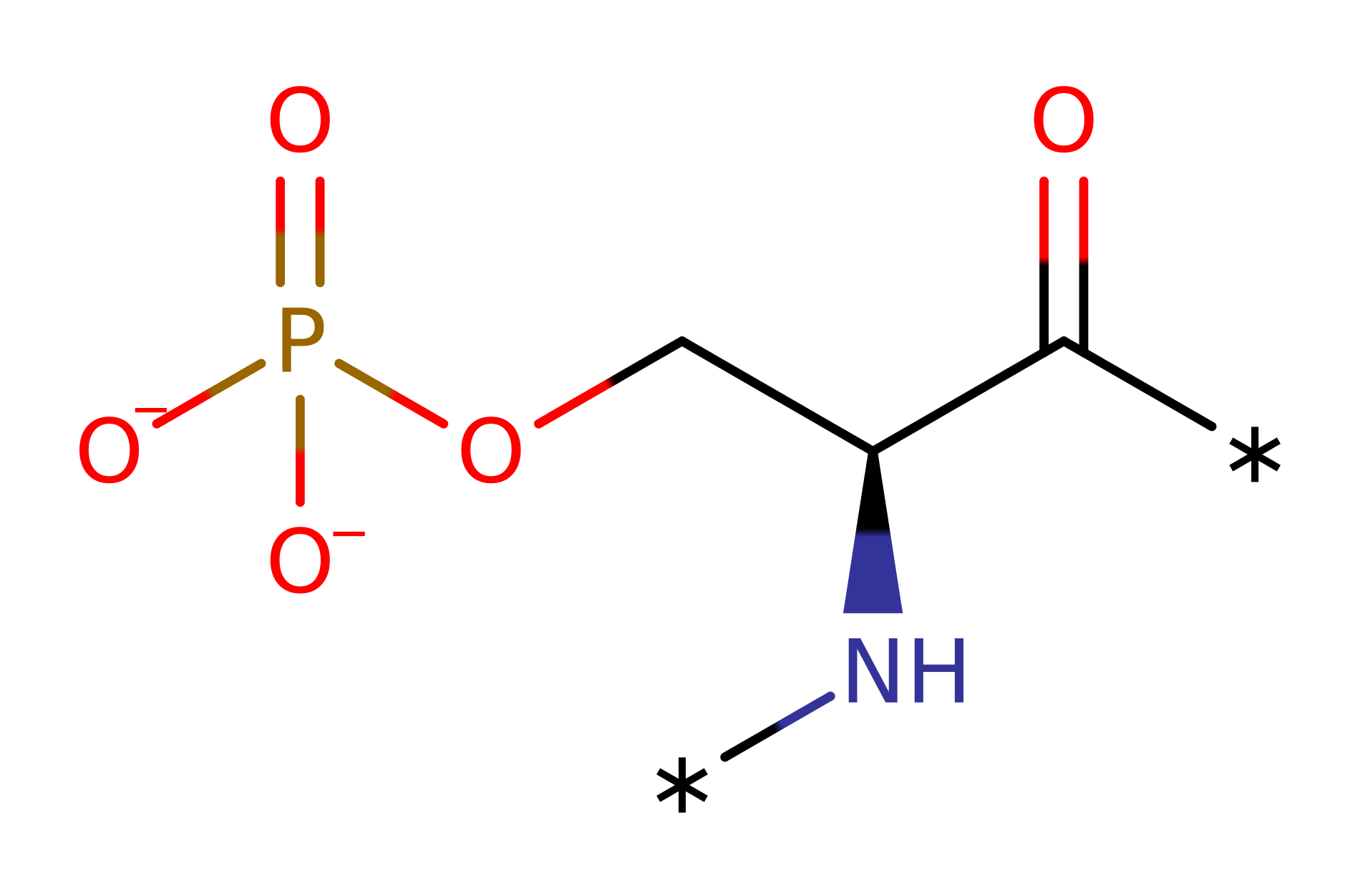
 Download:
Download: