Glycine C-acetyltransferase
Threonine is degraded into glycine and the acetyl group in a pathway common to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The pathway is two steps long; the first step is the oxidation of the hydroxy group of threonine to create 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate by L-threonine dehydrogenase. The second step is catalysed by 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate CoA ligase (KBL); this is a PLP-dependent acetyltransferase, transferring the newly formed acetyl group of the substrate to Coenzyme A to give glycine and acetyl-CoA. The two enzymes needed for the pathway form a complex; this is because the aminoketobutyrate intermediate (substrate for KBL) spontaneously decarboxylates in aqueous solution.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0AB77
 (2.3.1.29)
(2.3.1.29)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1fc4
- 2-AMINO-3-KETOBUTYRATE COA LIGASE
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.640.10
 (see all for 1fc4)
(see all for 1fc4)
- Cofactors
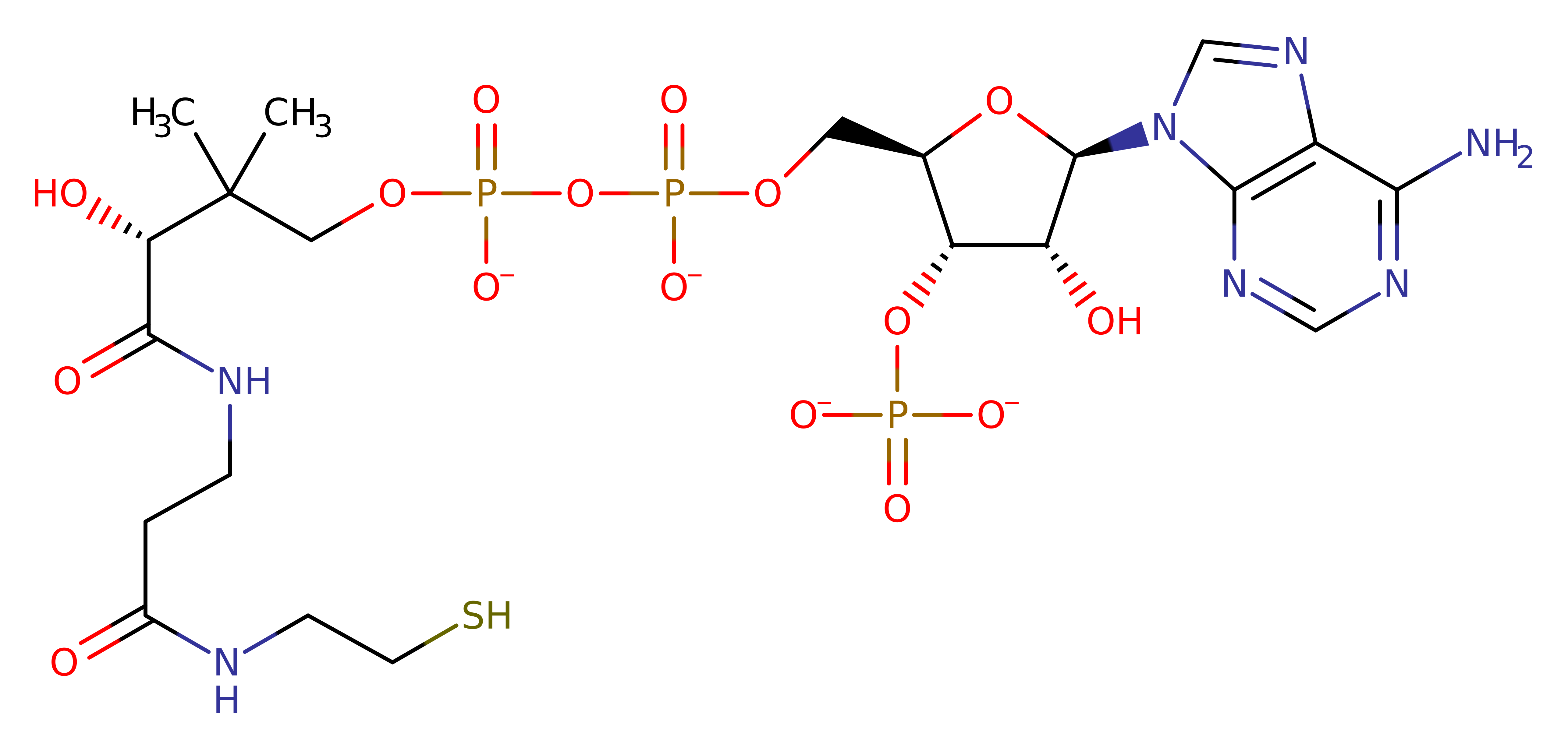
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.29)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
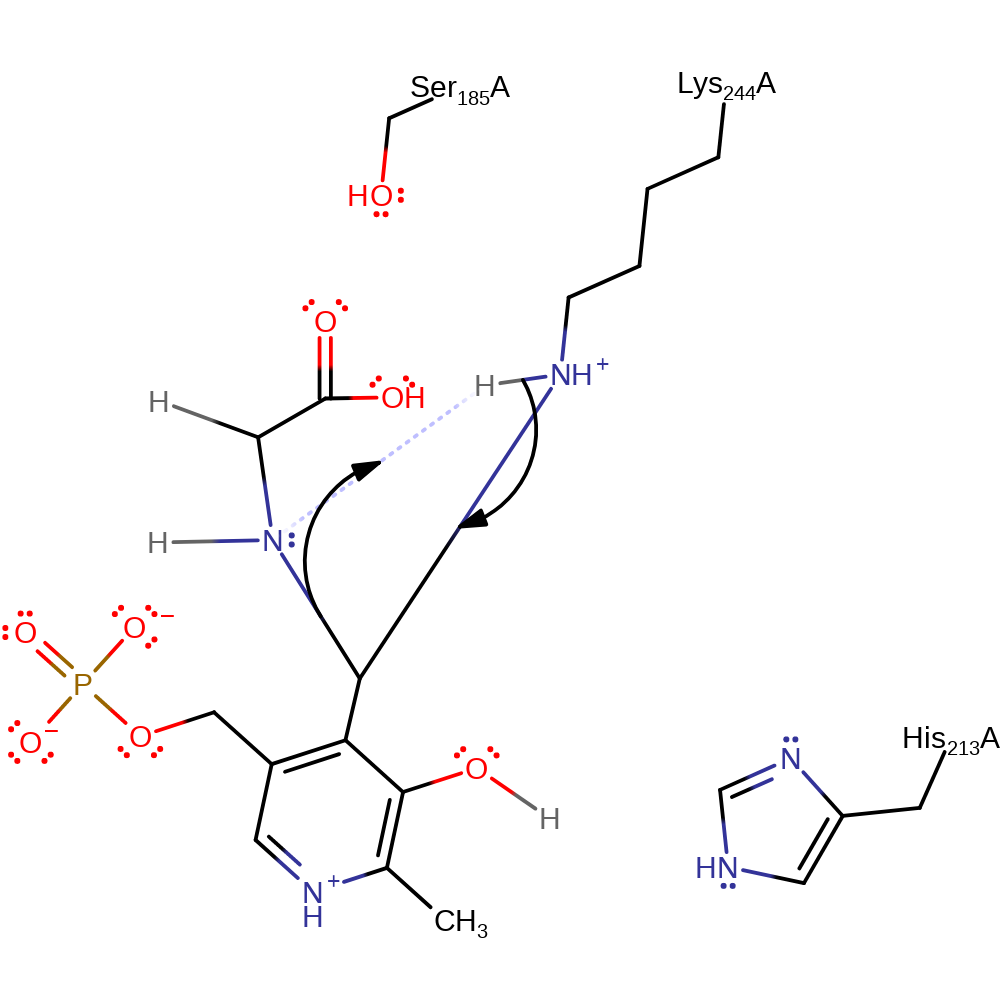
Lys 244 has a Schiff base linkage with the PLP cofactor. It is displaced by the amino acid substrate, in the usual fashion to give an external aldimine (PLP and threonine with a Schiff base linkage). In these steps His 213 acts as a general acid to the phenolic oxygen of PLP (with the phenolic proton being transferred to Lys 244), and a general base to the amino group of the joining threonine. The thiol of CoA is nucleophilic and attacks the carbon of the carbonyl group of the aldimine. This gives a tetrahedral intermediate where the oxyanion is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to Ser 185. Lys 244 deprotonates the sulphur atom. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses to release acetyl-CoA. The glycine moiety and PLP are held in a quinoid intermediate. Lys 244 protonates the nitrogen of the glycine moiety, regenerating the substrate-PLP Schiff base link. Lys 244 displaces the group bound to PLP in the usual fashion (His 213 again acting as a general acid/base) to release glycine and regenerate the original active PLP-enzyme adduct.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fc4) | ||
| Ser185 | Ser185(188)A | Forms a weak hydrogen bond with O3 of the oxyanion tetrahedral intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His213 | His213(216)A | His 213 acts as a general acid and base during the steps where the PLP Schiff base linkage is transferred from Lys 244 to the amino acid, and vice versa. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys244 | Lys244(247)A | Lys 244 is Schiff base-linked to the PLP cofactor in the resting state, and displaces the glycine product in the last step of the reaction. Lys 244 deprotonates the thiol after the formation of the tetrahedral intermediate. The proton is transferred to the nitrogen atom of the glycine moiety of the quinoid intermediate to regenerate the imine linkage. |
covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton donor, proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, heterolysis, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, schiff base formed, proton relay, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Schmidt A et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 5151-5160. Three-Dimensional Structure of 2-Amino-3-ketobutyrate CoA Ligase fromEscherichia coliComplexed with a PLP−Substrate Intermediate: Inferred Reaction Mechanism. DOI:10.1021/bi002204y. PMID:11318637.
- Mann S et al. (2011), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1814, 1459-1466. Pyridoxal-5′-phosphate-dependent enzymes involved in biotin biosynthesis: Structure, reaction mechanism and inhibition. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.12.004. PMID:21182990.

Step 1. His213 acts as an acid catalyst for the transaldimation reaction. The amine of the substrate L-2-amino-3-oxobutanoic acid attacks the PLP cofactor in a nucleophilic addition and the bound Lys244 deprotonates the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| His213(216)A | proton donor |
| Lys244(247)A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. His213 accepts a proton from the secondary amine that results from the initial attack which also initiates an elimination of the covalently bound lysine, resulting in free PLP and lysine in a neutral state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | nucleofuge |
| His213(216)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse
Step 3. CoA thiol group attacks PLP-substrate to form a tetrahedral intermediate in which Lys244 removes the excess proton. Ser185 stabilises oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser185(188)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys244(247)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate collapse
Step 4. Unimolecular elimination to form acetyl-CoA , which is released and also a quinoid intermediate, PLP acts an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser185(188)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, heterolysis, overall product formed
Step 5. Lys244 protonates the quinoid intermediate, PLP feeds an electron pair back to form the glycine external aldimine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
intermediate collapse, proton transfer
Step 6. In the reverse reaction, this is the first step of the His213 catalysed Lys244 displacing the product glycine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | covalently attached |
| His213(216)A | proton donor |
| Lys244(247)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapseCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | covalently attached, electron pair donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, schiff base formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, covalently attached |
| His213(216)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys244(247)A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: