Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (GnT I) is an inverting glycosyl transferase from Oryctolagus cuniculus catalyses the attachment of N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc) onto an oligomannose core, from UPD-N-acetyl glucosamine. It plays a critical role in mammalian development, involved in the transformation of oligomannose attached structures to complex N-glycans.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P27115
 (2.4.1.101)
(2.4.1.101)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)

- PDB
-
1foa
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINYLTRANSFERASE I
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.550.10
 (see all for 1foa)
(see all for 1foa)
- Cofactors
- Manganese(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.1.101)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This reaction occurs in an SN2 concerted mechanism, whereby induced fit interactions help destabilise the ground state promoting catalysis. Asp 291 acts as a general base to deprotonate a hydroxyl group of the oligomannose core sugar. The deprotonated oxygen atom then acts as a nucleophile and attacks C1 of UPD-N-acetyl glucosamine. The transition state is oxocarbenium ion-like. The C1 - UPD bond is broken, leaving the N-acetyl glucosamine bonded to the oligomannose core. Mn2+ stabilises the build up of negative charge on the beta-phosphate of the UPD. It is thought that Asp 291 then acts as an acid to protonate the UPD leaving group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1foa) | ||
| Asp213 | Asp213(114)A | Coordinates to Mn2+ ion, which is involved in stabilising the transition state. | metal ligand |
| Asp291 | Asp291(192)A | Asp 291 acts as a general base by accepting a proton from a hydroxyl group on the oligamannose core. It must then donate that proton back to the leaving group UDP phosphate ion. | activator, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Tvaroska I et al. (2003), Glycobiology, 13, 559-566. Catalytic mechanism of the inverting N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I: DFT quantum mechanical model of the reaction pathway and determination of the transition state structure. DOI:10.1093/glycob/cwg067. PMID:12672701.
- Tvaroška I (2015), Carbohydr Res, 403, 38-47. Atomistic insight into the catalytic mechanism of glycosyltransferases by combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods. DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2014.06.017. PMID:25060837.
- Unligil UM et al. (2000), EMBO J, 19, 5269-5280. X-ray crystal structure of rabbit N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I: catalytic mechanism and a new protein superfamily. DOI:10.1093/emboj/19.20.5269. PMID:11032794.

Step 1. Asp291 deprotonates the C2- OH on the mannose sugar, activating it for nucleophilic attack on C1 of UDP-GlcNAc.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp213(114)A | metal ligand |
| Asp291(192)A | activator |
| Asp291(192)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp213(114)A | metal ligand |
| Asp291(192)A | proton donor |


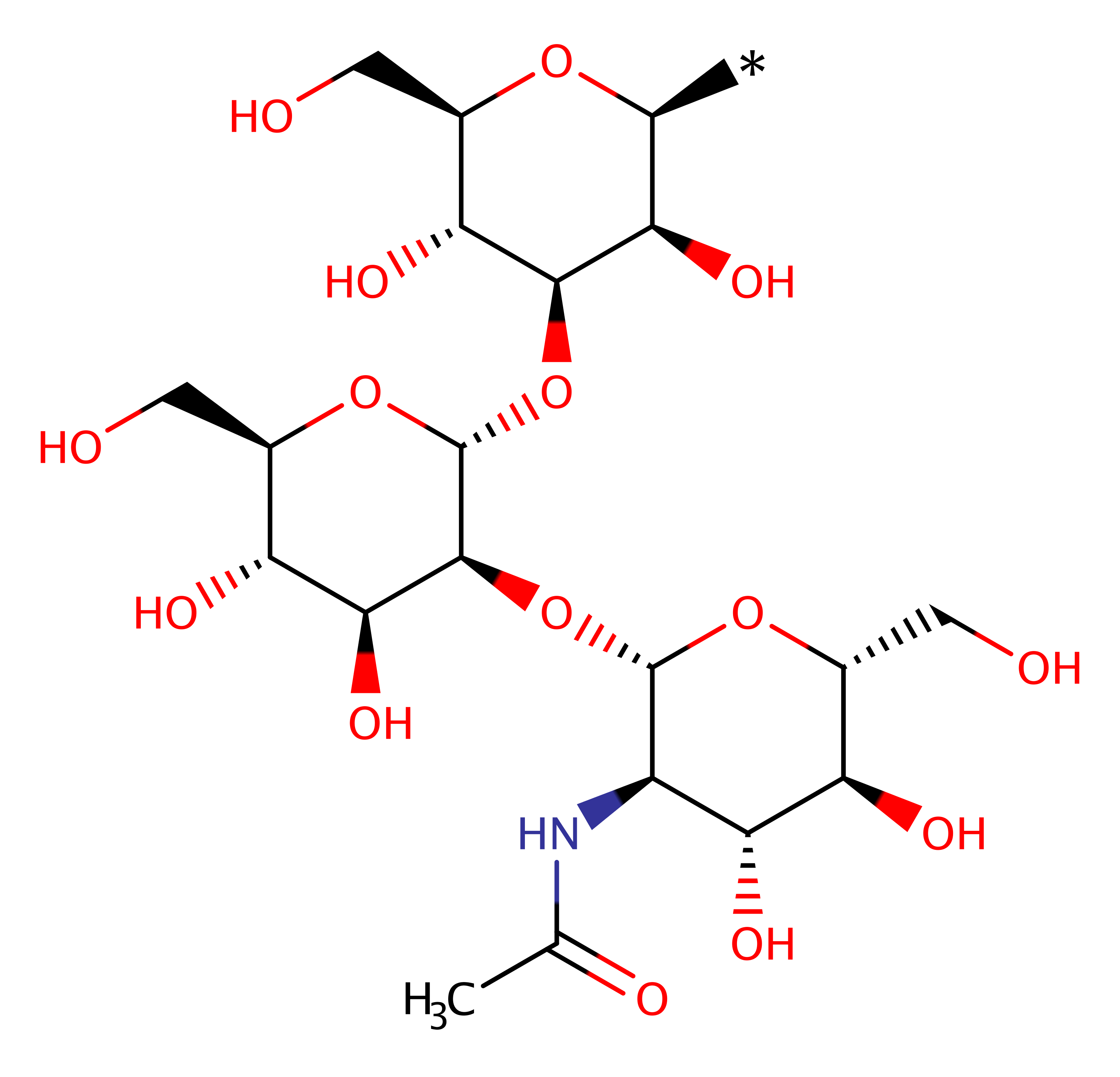



 Download:
Download: