Protein disulfide oxidoreductase
Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis requires the reduction of the the C2' atom of ribonucleotides. Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) catalyses this reaction via the formation of a disulfide bond in RNR itself. To regenerate active RNR, this disulfide must be reduced; glutaredoxin (Grx) is one of the enzymes which does this.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P68688

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1qfn
- GLUTAREDOXIN-1-RIBONUCLEOTIDE REDUCTASE B1 MIXED DISULFIDE BOND
(solution nmr
Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.30.10
 (see all for 1qfn)
(see all for 1qfn)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
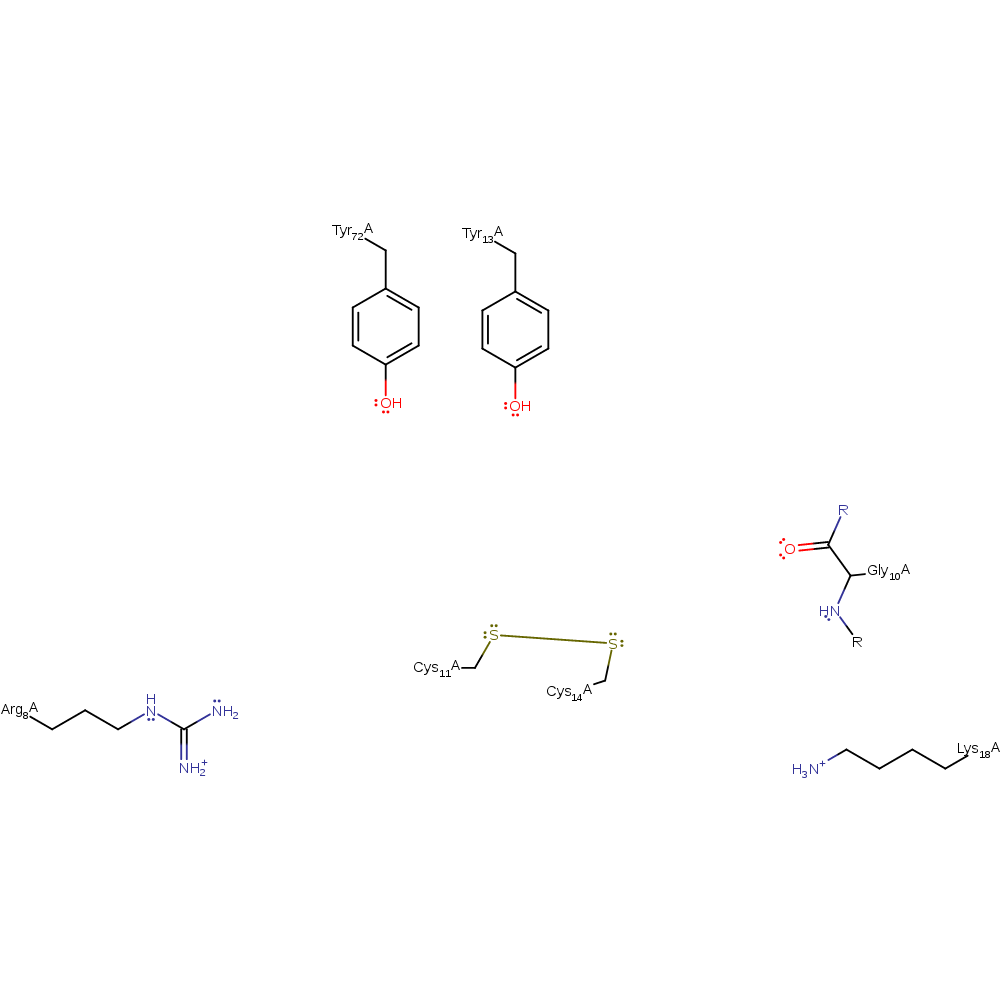
Oxidoreduction is via the formation and breaking of disulfide bonds between cysteine side groups: Oxidised RNR has a disulfide bond between Cys 143 and Cys 148. Cys 11 of Grx is nucleophilic and attacks Cys 148 in an SN2 fashion to break the Cys 143-Cys 148 bond. Cys 14 is in a low pKa environment and is nucleophilic; it attacks Cys 11 in an SN2 fashion to break the Cys 148-Cys 11 bond. Thus, the disulfide bond of RNR is transferred to Grx.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qfn) | ||
| Arg8 | Arg8A | Arg8 decreases the pKa of Cys11, making it more nucleophilic. It also increases the negative electrostatic potential surrounding Cys14, making it more nucleophilic. | modifies pKa, enhance reactivity |
| Tyr13 | Tyr13A | Tyr13 stabilises the transition state for the formation of the Cys754 thiol and helps to prevent the reaction from reversing. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys18 | Lys18A | Lys18 increases the negative electrostatic potential surrounding Cys14, making it more nucleophilic. | enhance reactivity |
| Tyr72 | Tyr72A | Tyr72 stabilises the transition state for the formation of the Cys754 thiol and helps to prevent the reaction from reversing. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys11, Cys14 | Cys11A, Ser14A | Act as catalytic nucleophiles. | electrofuge, electrophile, nucleophile |
| Gly10 (main-N) | Gly10A (main-N) | Gly10 is thought to be involved in proton transfer from Cys14 to the solvent. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Berardi MJ et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 292, 151-161. Binding specificity and mechanistic insight into glutaredoxin-catalyzed protein disulfide reduction. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3067. PMID:10493864.
- Foloppe N et al. (2004), Structure, 12, 289-300. The Glutaredoxin -C-P-Y-C- Motif: Influence of Peripheral Residues. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.01.009. PMID:14962389.
- Albright TD (1999), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 96, 7611-7613. More than one way to see it move? DOI:10.1073/pnas.96.14.7611. PMID:10393864.

Step 1. In a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction Cys11 attacks the S-S bond of RNR and displaces Cys143.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr13A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg8A | enhance reactivity, modifies pKa |
| Gly10A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys18A | enhance reactivity |
| Tyr72A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys11A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation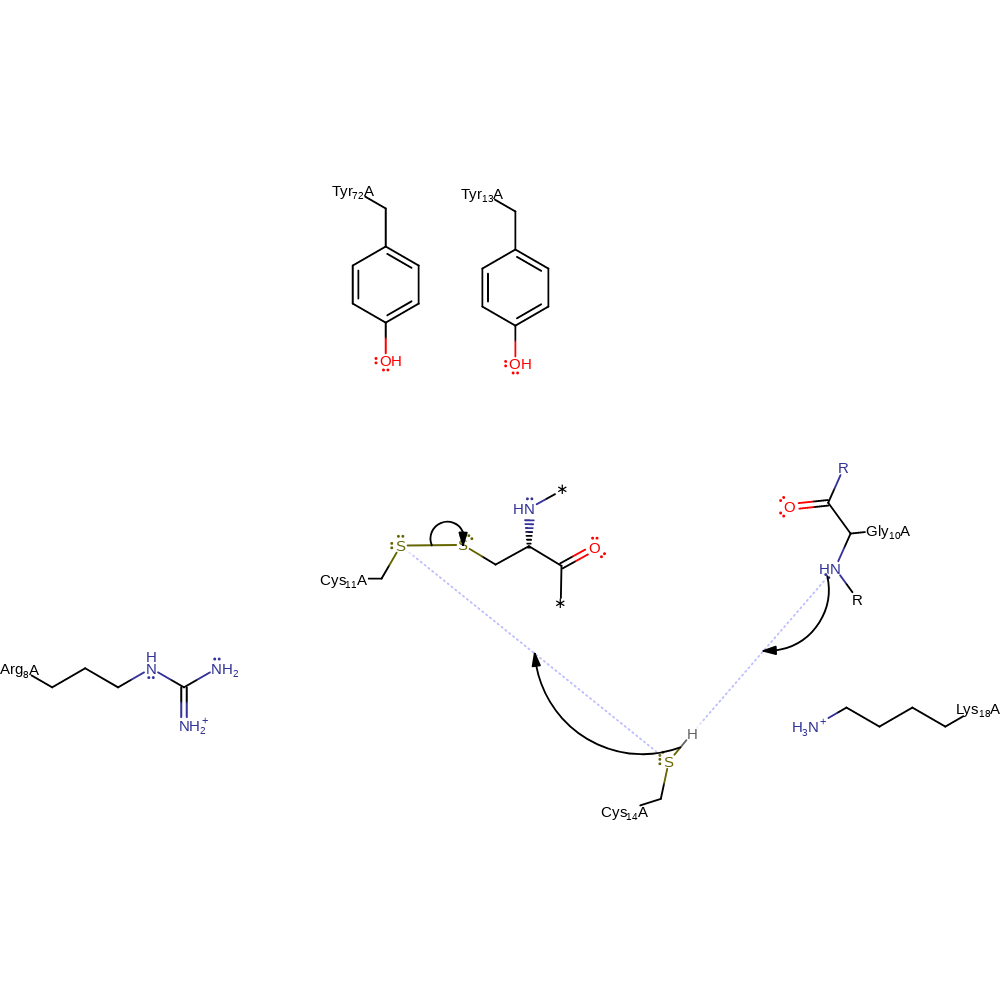
Step 2. Gly14 attacks Cys11 in an SN2 fashion to break the Cys148-Cys11 bond. Gly10 may be involved in deprotonating the Cys14 residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr13A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr72A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys18A | enhance reactivity |
| Arg8A | enhance reactivity |
| Ser14A | nucleophile |
| Gly10A (main-N) | proton acceptor |
| Ser14A | proton donor |
| Cys11A | electrophile, electrofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed
Step 3. In an inferred reaction step Gly10 is deprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly10A (main-N) | proton donor |
 Download:
Download: