Endo-alpha-sialidase
E. coli K1, a major cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis, surrounds itself in a capsule of poly alpha2,8-sialic acid (polySia), a sugar polymer that also acts as an important modulator of neuronal plasticity in the adult human host; hence, the mammalian immune system does not attack the bacterium. The bacteriophage K1F can hydrolyse this bacterial capsule using an endosialidase, which is a mushroom-shaped homotrimer. This enzyme may find use in the diagnosis or therapy of polySia-bearing tumours, and in the treatment of meningitis caused by polySia-encapsulated bacteria.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q04830
 (3.2.1.129)
(3.2.1.129)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterobacteria phage K1F (Virus)

- PDB
-
1v0e
- Endosialidase of Bacteriophage K1F
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.120.10.10
 (see all for 1v0e)
(see all for 1v0e)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.2.1.129)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
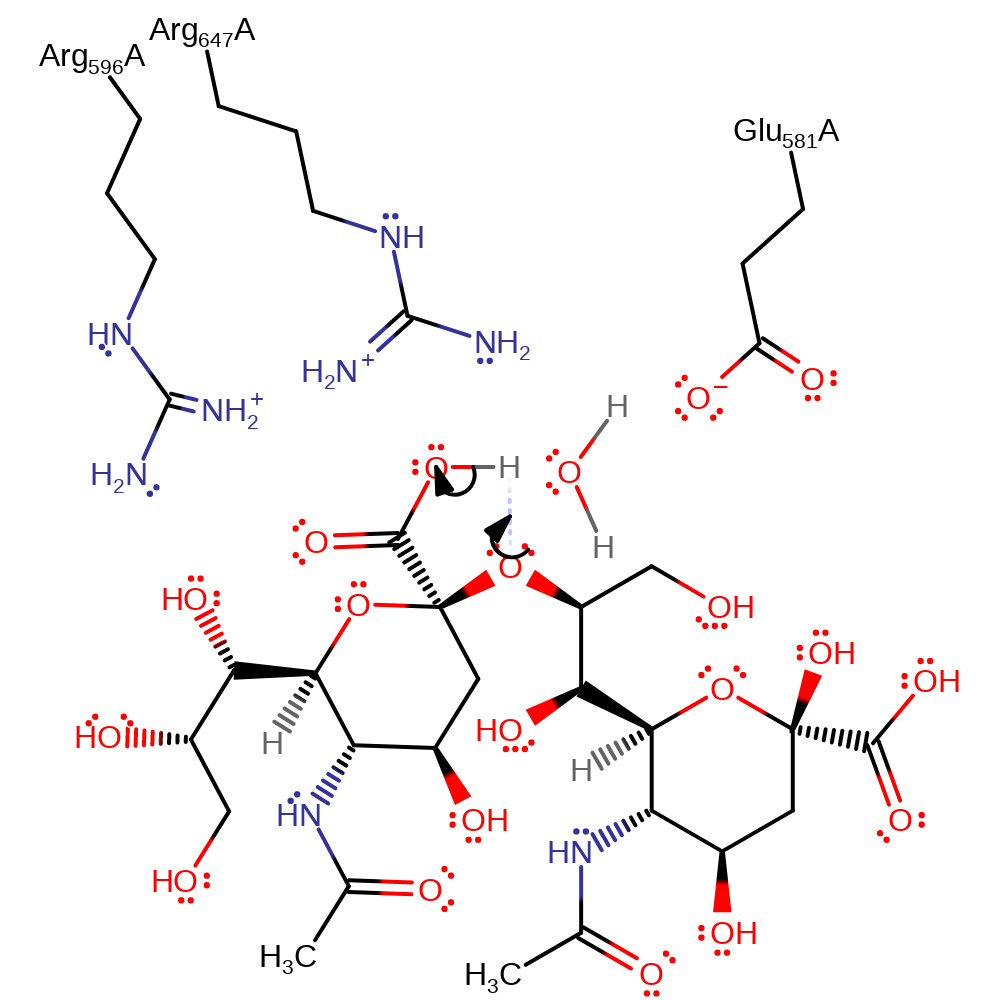
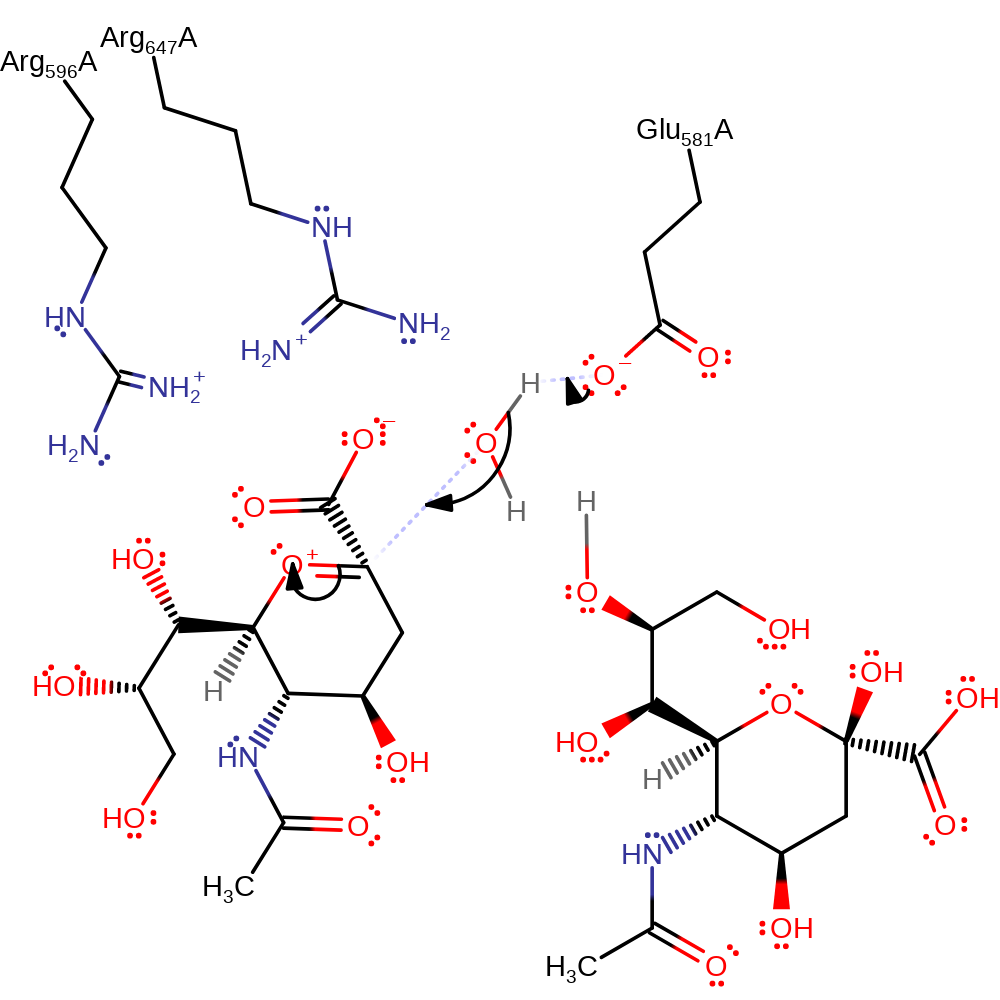
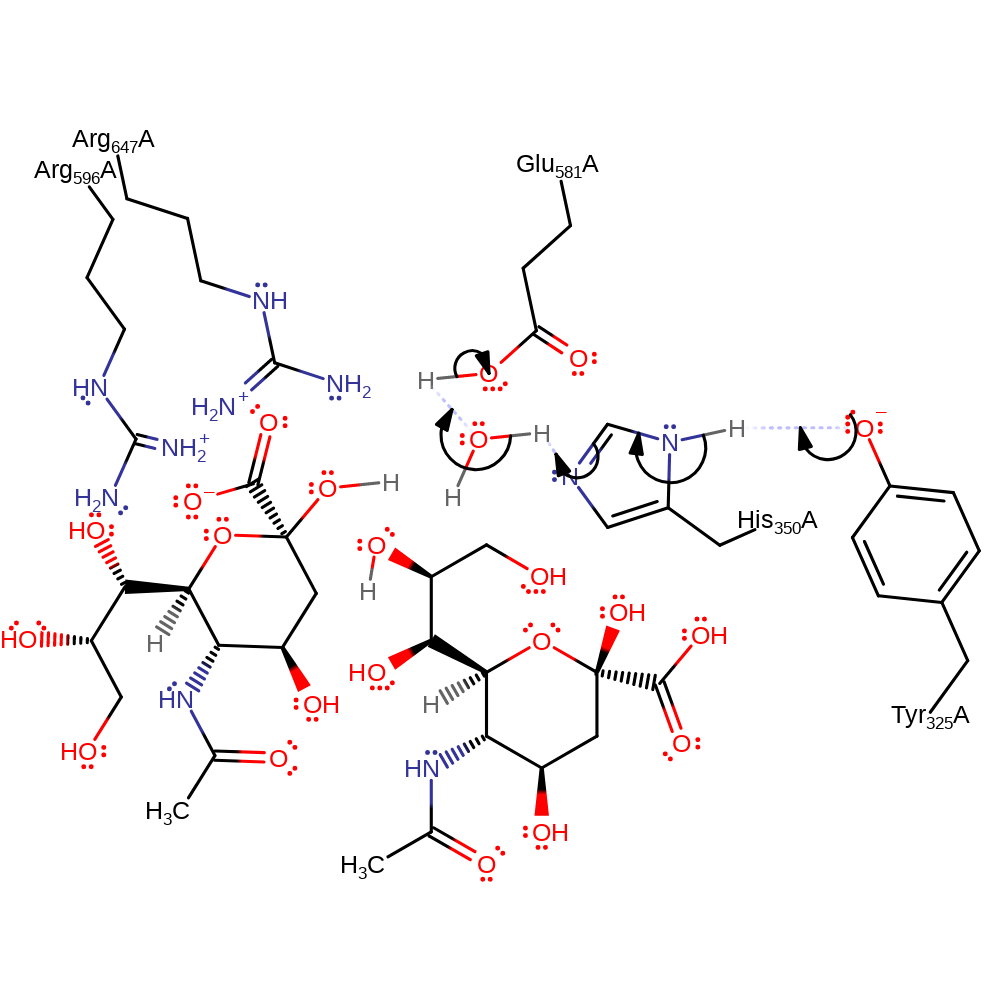
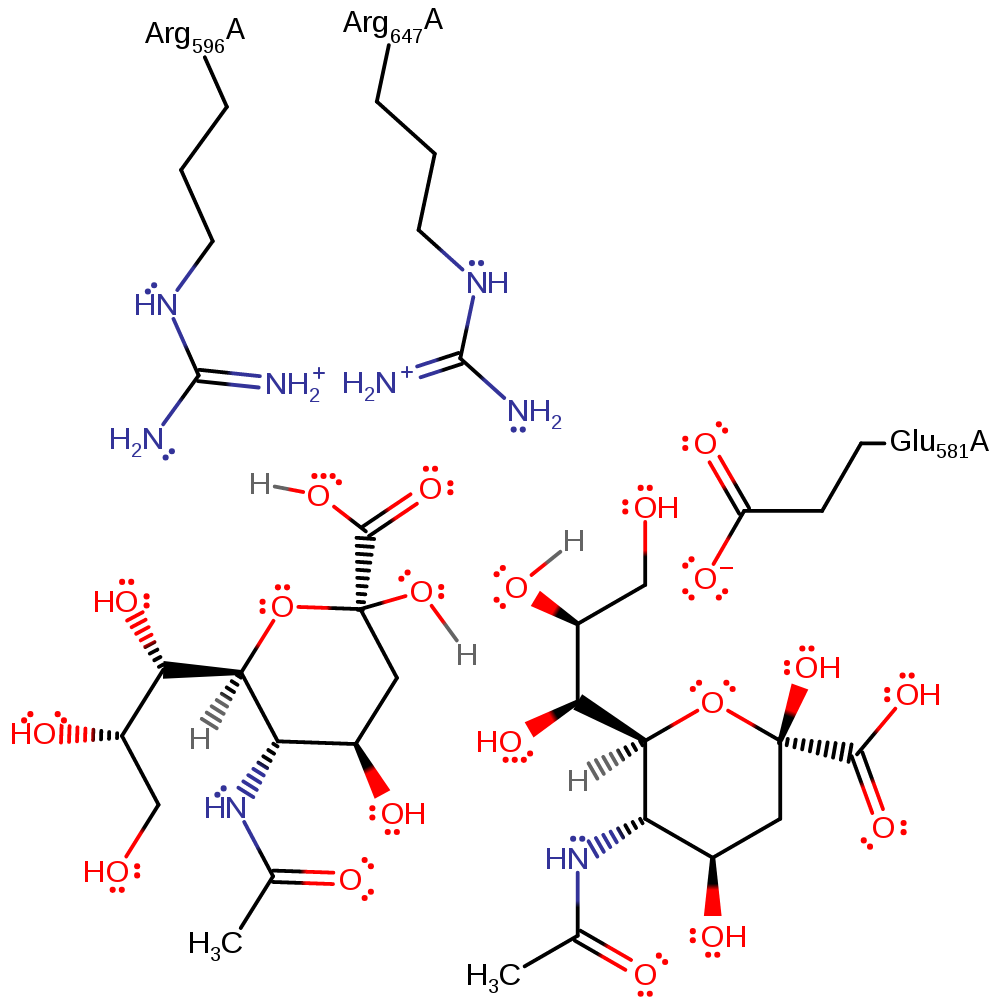
Endosialidases are proposed to work by catalysing the intramolecular self-cleavage of polySia that occurs spontaneously in mild acidic conditions: Arg 596 and Arg 647 bind the carboxyl group of polySia. This raises the pKa of the carboxyl so that it is protonated. The binding may also force the pyranose ring into an unfavourable boat conformation. The proton is transferred (intramolecularly) between the carboxyl and the oxygen atom in the glycosidic linkage, making the linking oxygen a good leaving group. The lone pair on the ring oxygen forms a -C=O+- bond, triggering the cleavage of the glycosidic bond and creating a planar, cationic transition state and intermediate that is stabilised by Glu 581. Water is nucleophilic and attacks the carbon of the -C=O+- group, quenching the positive charge on oxygen and relieving the strained planar conformation of the intermediate. Water is activated by Glu581. The products formed have terminal sialic acid units, one a hemiacetal and the other a primary alcohol.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1v0e) | ||
| Glu581 | Glu581(337)A | Stabilises the planar cationic transition states and intermediate. Activates the water for nucleophilic attack. | proton acceptor, increase nucleophilicity, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg596 | Arg596(352)A | Arg 596 increases the pKa of the carboxylate group of the substrate and effects the change of pyranose conformation. | electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Arg647 | Arg647(403)A | Arg 647 increases the pKa of the carboxylate group of the substrate and effects the change of pyranose conformation. | electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, electron transfer, heterolysis, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Stummeyer K et al. (2005), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 12, 90-96. Crystal structure of the polysialic acid–degrading endosialidase of bacteriophage K1F. DOI:10.1038/nsmb874. PMID:15608653.
- Manzi AE et al. (1994), J Biol Chem, 269, 23617-23624. Intramolecular self-cleavage of polysialic acid. PMID:8089131.





 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: