Very short patch repair endonuclease
Very short patch repair protein (VSR) is an endonuclease from Escherichia coli and is a sequence specific mismatch endonuclease. It is responsible for the repair of T:G mismatches arising from the deamination of 5-methylcytosine. E. coli has three discovered systems for mismatched base pair recognition, all with different mechanisms. VSR initiates repair by hydrolysing the phosphate 5' of the mismatched T.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P09184
 (3.1.-.-)
(3.1.-.-)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1cw0
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF VERY SHORT PATCH REPAIR (VSR) ENDONUCLEASE IN COMPLEX WITH A DUPLEX DNA
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.960.10
 (see all for 1cw0)
(see all for 1cw0)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
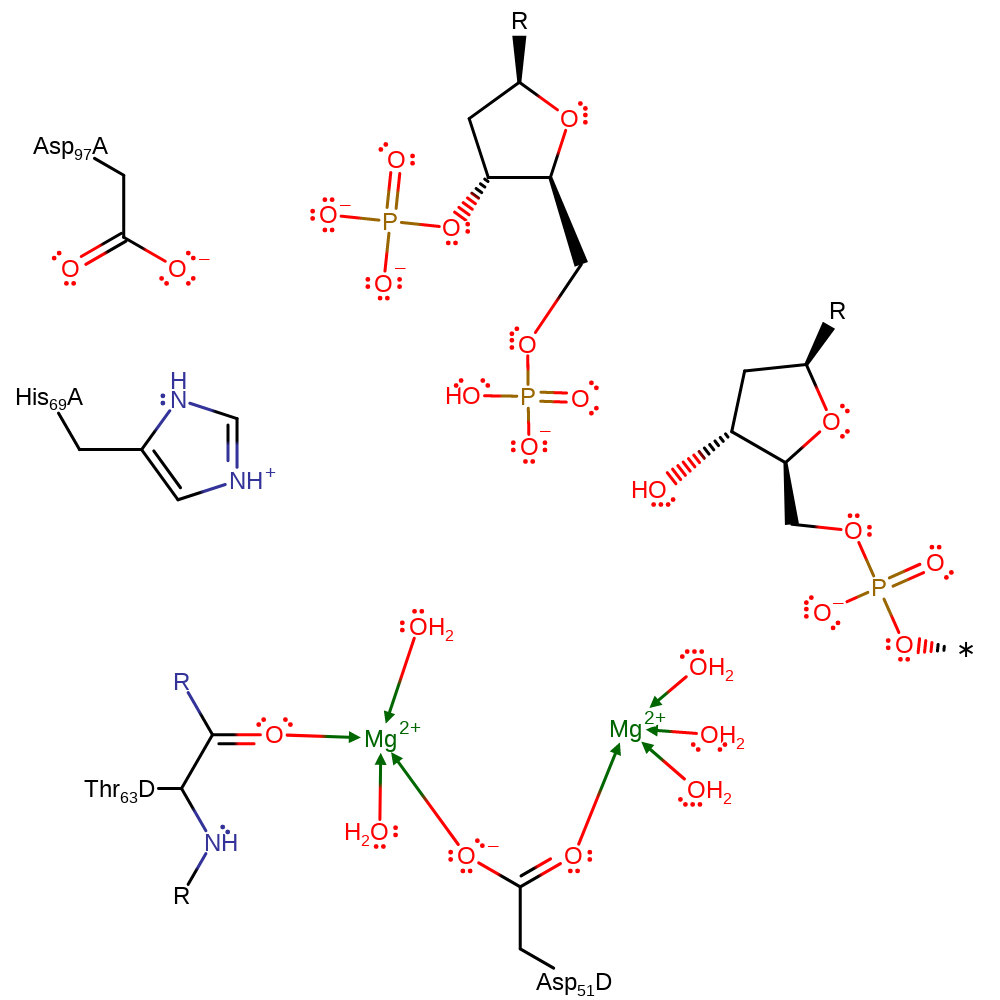
The pKa of His 69 is raised by hydrogen bonding to Asp 97. Its raised pKa enables His 69 to act as a general base and deprotonate a water molecule. The activated water molecule then nucleophilically attacks the scissile phosphate via an SN2 mechanism, going through a trigonal-bipyramidal transition state. This negatively charged transition state is stabilised by two magnesium ions, and possibly the sidechain of His 64.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1cw0) | ||
| Thr63 (main-C), Asp51 | Thr63(62)A(D) (main-C), Asp51(50)A(D) | Forms the Magnesium binding site | metal ligand |
| Asp97 | Asp97(96)A(D) | Hydrogen bonds to His 69, increasing its pKa and thereby facilitating its role as a base. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His69 | His69(68)A(D) | Acts as a general base by deprotonating a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Elliott SL et al. (2005), J Mol Biol, 353, 692-703. Mechanism of the Escherichia coli DNA T:G-mismatch Endonuclease (Vsr protein) Probed with Thiophosphate-containing Oligodeoxynucleotides. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.08.048. PMID:16188275.

Step 1. His69 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to attack the scissile phosphate via an SN2 mechanism.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp97(96)A(D) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp51(50)A(D) | metal ligand |
| Thr63(62)A(D) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| His69(68)A(D) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp97(96)A(D) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp51(50)A(D) | metal ligand |
| Thr63(62)A(D) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| His69(68)A(D) | proton donor |






 Download:
Download: