Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase
Phosphoglucose isomerase (EC:5.3.1.9) (PGI) [PMID:1593646] is a dimeric enzyme that catalyses the reversible isomerisation of glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate. PGI is involved in different pathways: in most higher organisms it is involved in glycolysis; in mammals it is involved in gluconeogenesis; in plants in carbohydrate biosynthesis; in some bacteria it provides a gateway for fructose into the Entner-Doudouroff pathway. The multifunctional protein, PGI, is also known as neuroleukin (a neurotrophic factor that mediates the differentiation of neurons), autocrine motility factor (a tumour-secreted cytokine that regulates cell motility), differentiation and maturation mediator and myofibril-bound serine proteinase inhibitor, and has different roles inside and outside the cell. In the cytoplasm, it catalyses the second step in glycolysis, while outside the cell it serves as a nerve growth factor and cytokine [PMID:10653639].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9N1E2
 (5.3.1.9)
(5.3.1.9)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)

- PDB
-
1dqr
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RABBIT PHOSPHOGLUCOSE ISOMERASE, A GLYCOLYTIC ENZYME THAT MOONLIGHTS AS NEUROLEUKIN, AUTOCRINE MOTILITY FACTOR, AND DIFFERENTIATION MEDIATOR
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.10490
 1.10.1390.10
1.10.1390.10  (see all for 1dqr)
(see all for 1dqr)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.1.9)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The proposed mechanism for sugar isomerisation involves several steps and is thought to occur via general acid/base catalysis. Since glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate exist predominantly in their cyclic forms, PGI is believed to catalyse first the opening of the hexose ring to yield the straight chain form of the substrates. Glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate then undergo isomerisation via formation of a cis-enediol intermediate with the double bond located between C-1 and C-2. The intermediate then undergoes a second keto-enol tautomerisation with reprotonation of the substrate occuring at C1. This is then followed by ring closure.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dqr) | ||
| Gly272 (main-N) | Gly271A (main-N) | Helps stabilise the transition states formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys211 | Lys210A | Lys210 supplies some positive charge to the phosphate binding site helping to bind the substrate (also helps determine substrate specificity) and also to stabilise the transition states formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu217 | Glu216A | Forms a catalytic dyad with His388; stabilises and activates the histidine to act as a general acid/base. | modifies pKa |
| Arg273 | Arg272A | Arg272 in PGI may serve a function similar to that of Lys12 in triosephosphate isomerase; it sets the overall electrostatic potential at the substrate to be positive and provides stabilisation for the negative charges that develop on the enediolate-like transition states. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu358 | Glu357A | Acts as a general acid/base. Proposed to be the base that abstracts the proton from C2 and then returns it to C1. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys519 | Lys518A | Lys518 acts as the general acid catalyst to complete the formation of the enediol intermediate. It also acts as a general base catalyst to form the ring-opened form of fructose 6-phosphate. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His389 | His388B | Acts as a general acid/base. This residue is most likely the base that catalyses ring opening, but it has also been suggested to abstracts the proton from C2. In either case, it is activated by Glu216. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
decyclisation, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intramolecular elimination, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regenerated, cyclisationReferences
- Jeffery CJ et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 1560-1566. Crystal Structure of Rabbit Phosphoglucose Isomerase Complexed with 5-Phospho-d-Arabinonate Identifies the Role of Glu357 in Catalysis‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0018483.
- Lee JH et al. (2005), Protein Sci, 14, 727-734. The crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with D-sorbitol-6-phosphate, an analog of the open chain form of D-glucose-6-phosphate. DOI:10.1110/ps.041070205. PMID:15689508.
- Solomons JT et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 342, 847-860. The crystal structure of mouse phosphoglucose isomerase at 1.6A resolution and its complex with glucose 6-phosphate reveals the catalytic mechanism of sugar ring opening. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.085. PMID:15342241.
- Arsenieva D et al. (2002), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 99, 5872-5877. The crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with 5-phospho-D-arabinonohydroxamic acid. DOI:10.1073/pnas.052131799. PMID:11983887.
- Lee JH et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 7799-7805. Crystal Structure of Rabbit Phosphoglucose Isomerase Complexed with Its Substrated-Fructose 6-Phosphate‡. DOI:10.1021/bi002916o.
- Jeffery CJ et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 955-964. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase, a glycolytic enzyme that moonlights as neuroleukin, autocrine motility factor, and differentiation mediator. DOI:10.2210/pdb1dqr/pdb. PMID:10653639.
- Achari A et al. (1981), Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 293, 145-157. Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase. PMID:6115414.

Step 1. Ring opening step. His388 abstracts a proton from substrate, breaking the C-O bond and forming the open sugar ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu216A | modifies pKa |
| Lys210A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His388B | proton acceptor |
| Lys518A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
decyclisation, proton transfer, overall reactant used, ingold: intramolecular elimination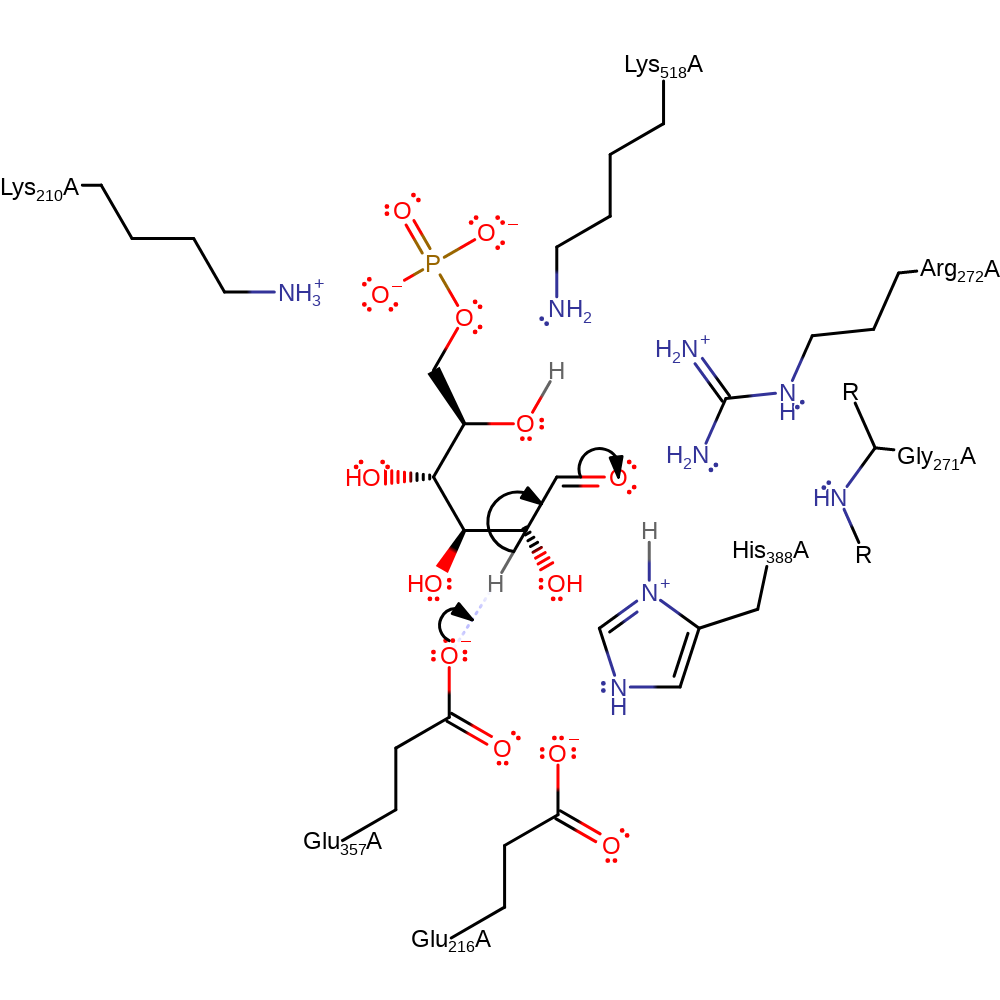
Step 2. Glu357 abstracts a proton from the C2 position of the open chain form of the substrate, resulting in the cis-enediol(ate) intermediate. His398 is inferred to act as the general acid in this step due to its proximity.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys210A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly271A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu216A | modifies pKa |
| Glu357A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer
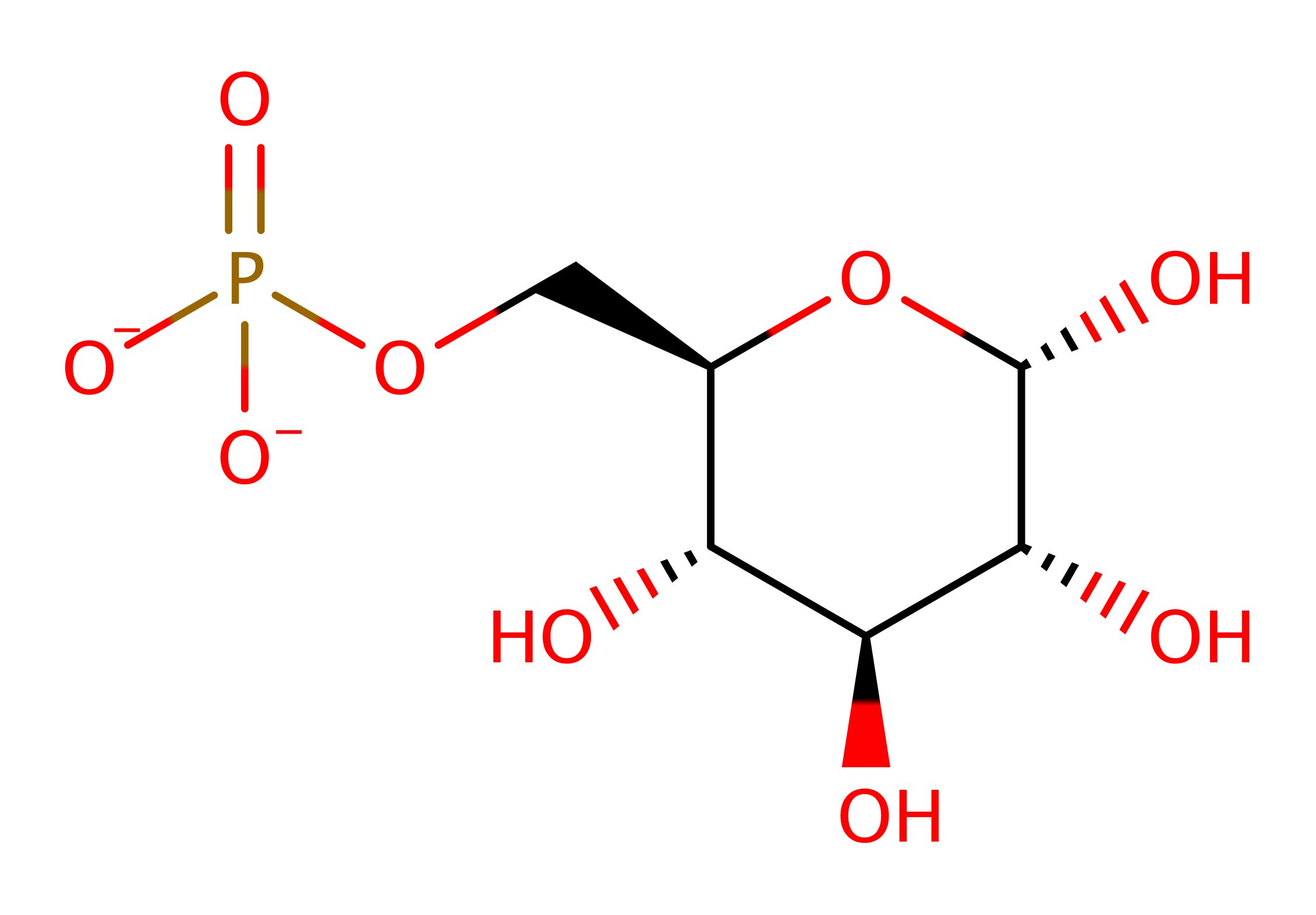
Step 3. The protonated Glu357 side chain then transfers the same proton to the C-1 position of the intermediate, yielding the open chain form of d-fructose-6-phosphate
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys210A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly271A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu216A | modifies pKa |
| Glu357A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer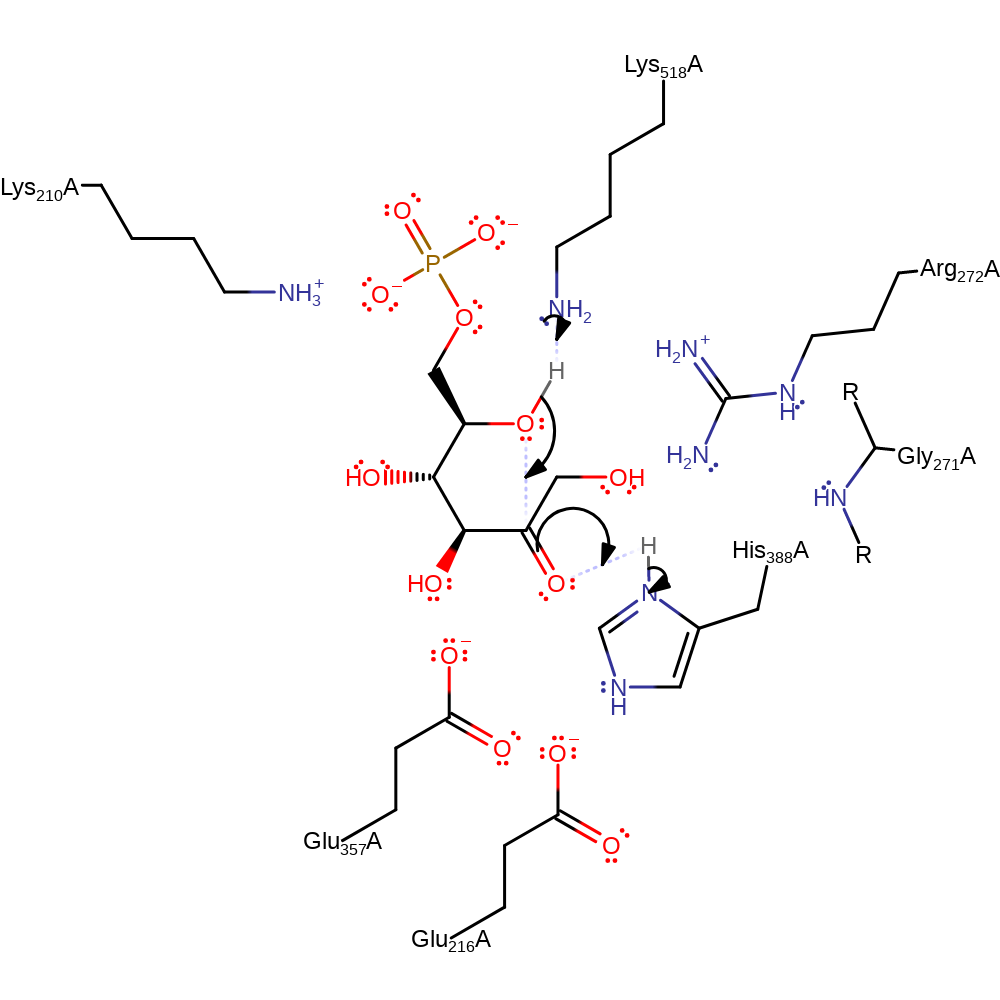
Step 4. Lys518 initiates the catalytic ring closure reaction to form the final product,
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys210A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly271A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu216A | modifies pKa |
| Lys518A | proton acceptor |
| His388B | proton donor |

 Download:
Download: