Methylglyoxal synthase
Methylglyoxyl synthase catalyses the first reaction in the methylglyoxyl bypass of the Embden-Myerhoff pathway (glycolysis), the conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate into methylglyoxal and orthophosphate. The physiological benefits of this are yet to be understood as the final product of methylglyoxal synthase is cytotoxic in small quantities and has been shown to be mutagenic and to interfere with de novo protein and nucleic acid synthesis. The intermediate, D-lactoylglutathione is also toxic in millimolar quantities, interfering with intermediate filament synthesis. The methylglyoxyl bypass system is inhibited allosterically by phosphate suggesting that is only functions in times of phosphate deprivation although more recent data imply that it may facilitate the transition between conditions of high and low phosphate. There is much interest in this enzyme for two reasons: firstly it has been implicated in diabetic complications and secondly due to its ability to metabolise anti-cancer drugs rendering treatments ineffective.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A731
 (4.2.3.3)
(4.2.3.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1b93
- METHYLGLYOXAL SYNTHASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1380
 (see all for 1b93)
(see all for 1b93)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.3.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The first step of the reaction mechanism involves the stereospecific abstraction of the C3 hydrogen of the substrate to form a common enediol enzyme intermediate. Asp71 abstracts a proton from the substrate whilst His98 protonates the ene-diol. His19 then abstracts the hydroxyl proton to initiate the phosphate elimination. Numerous other ligands stabilise intermediates formed in the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1b93) | ||
| Arg107 | Arg107C | Stabilises the negative charge on Asp101. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His19 | His19A | Acts as a general acid/base, activated by Asp91. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp91 | Asp91A | Activates the general acid/base His19. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp71, His98 | Asp71A, His98A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp101 | Asp101A | Activates Asp71 to act as the general acid/base through a repulsive charge-charge interaction. | repulsive charge-charge interaction, activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly66 (main-N) | Gly66A (main-N) | The amide nitrogen of Gly66 positions and stabilises the bridging phosphoryl oxygen for bond cleavage. | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular elimination, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step, reaction occurs outside the enzymeReferences
- Saadat D et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 2950-2960. Mirroring Perfection: The Structure of Methylglyoxal Synthase Complexed with the Competitive Inhibitor 2-Phosphoglycolate†. DOI:10.1021/bi992666f. PMID:10715115.
- Marks GT et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 3802-3813. Mutagenic Studies on Histidine 98 of Methylglyoxal Synthase: Effects on Mechanism and Conformational Change†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi035838o. PMID:15049687.
- Zhang X et al. (2002), J Am Chem Soc, 124, 14871-14878. Functional Specificities of Methylglyoxal Synthase and Triosephosphate Isomerase: A Combined QM/MM Analysis. DOI:10.1021/ja027063x.
- Marks GT et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 6805-6818. Mechanistic implications of methylglyoxal synthase complexed with phosphoglycolohydroxamic acid as observed by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. PMID:11389594.
- Saadat D et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 309-317. The crystal structure of methylglyoxal synthase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80041-0. PMID:10368300.
- Saadat D et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 10074-10086. Identification of Catalytic Bases in the Active Site ofEscherichia coliMethylglyoxal Synthase: Cloning, Expression, and Functional Characterization of Conserved Aspartic Acid Residues†. DOI:10.1021/bi980409p. PMID:9665712.

Step 1. Asp71 deprotonates the terminal CH2, initiating a double bond rearrangement to form the enol-form of the substrate, with concomitant deprotonation of His98.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His19A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly66A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp71A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp91A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His98A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp101A | hydrogen bond acceptor, repulsive charge-charge interaction, activator |
| Arg107C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp71A | proton acceptor |
| His98A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. His19 deprotonates the terminal alcohol group, initiating double bond rearrangement and the elimination of the phosphate group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His19A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly66A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp71A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp91A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His98A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp101A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg107C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His19A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 3. His98 deprotonates His19 and the phosphate group is assumed to deprotonate Asp71 in an inferred step that returns the enzyme to its active state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His19A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly66A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp71A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp91A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His98A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp101A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg107C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His98A | proton acceptor |
| Asp71A | proton donor |
| His19A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step
Step 4. The final tautomerisation occurs outside of the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
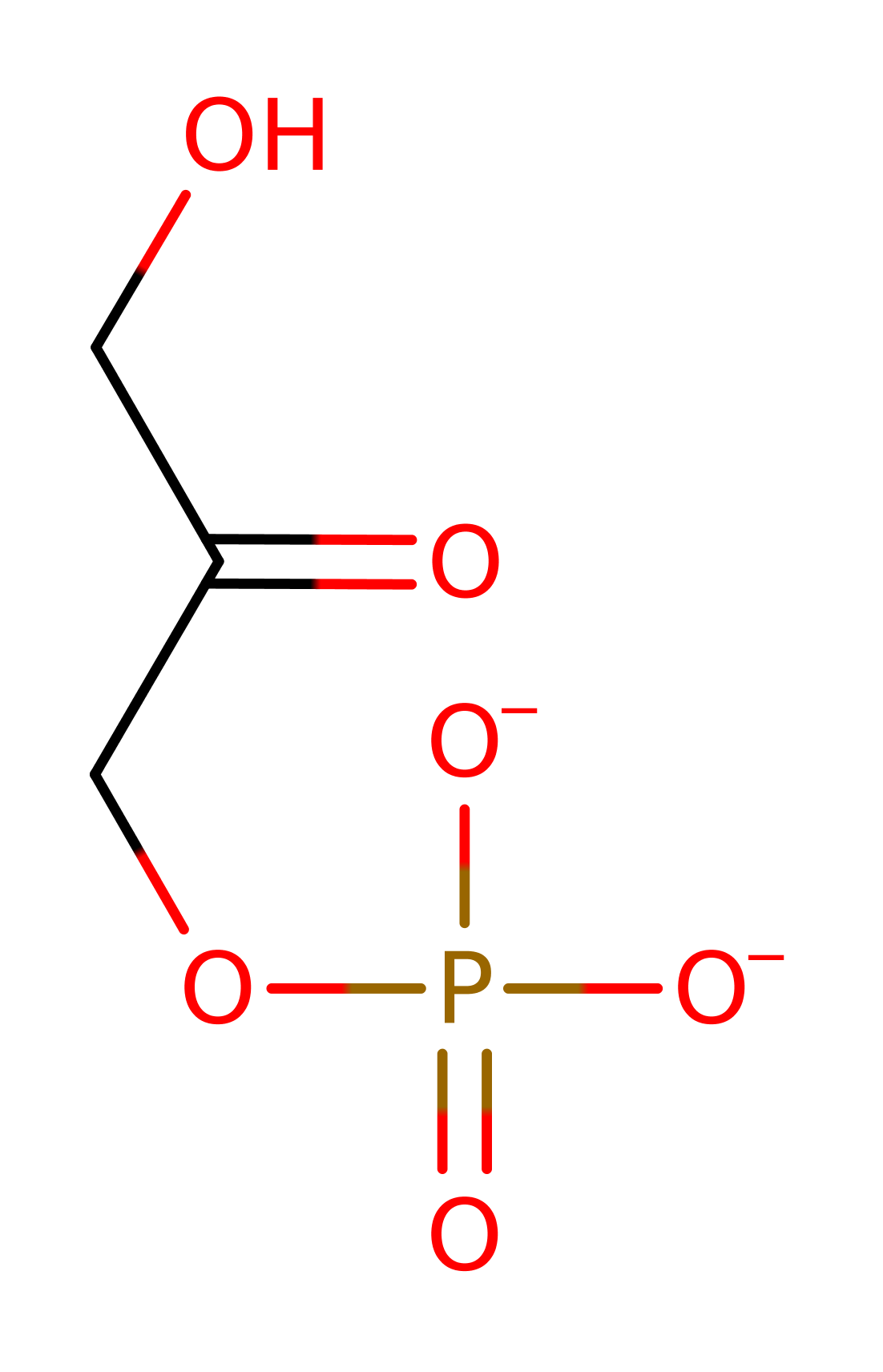
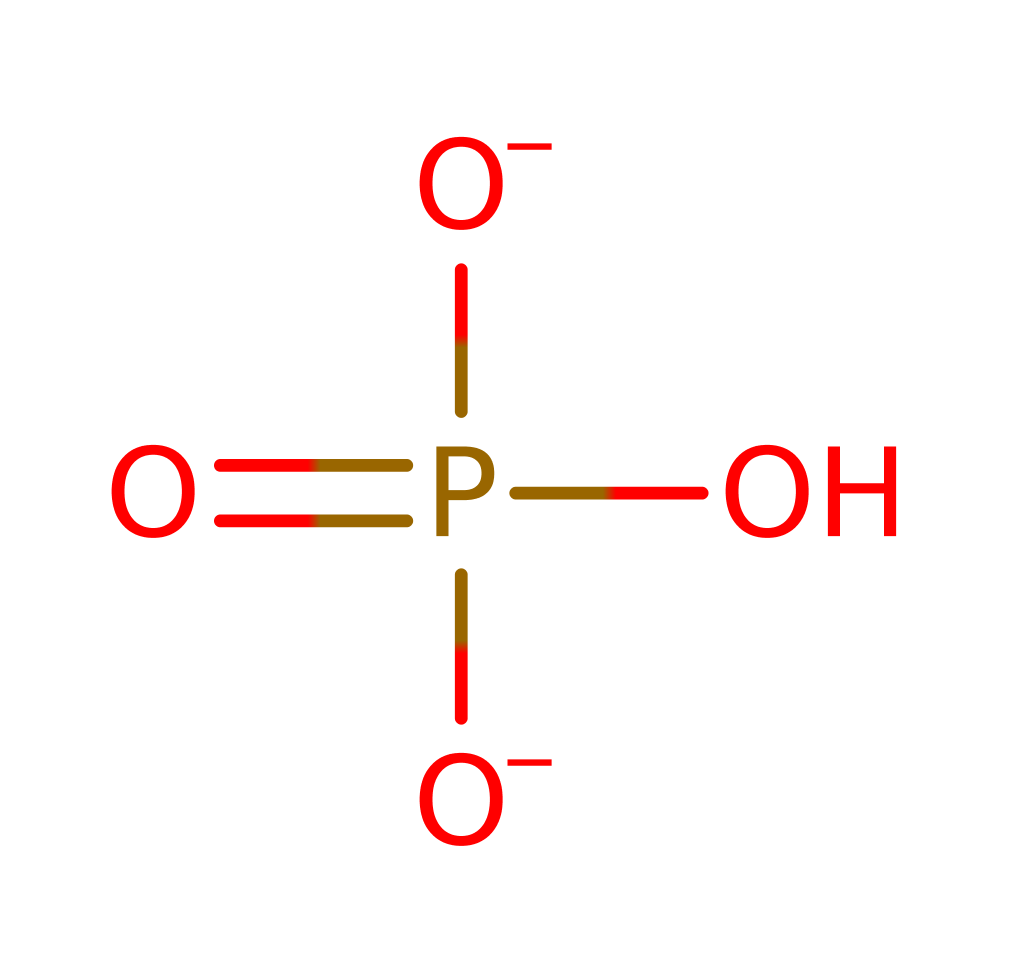

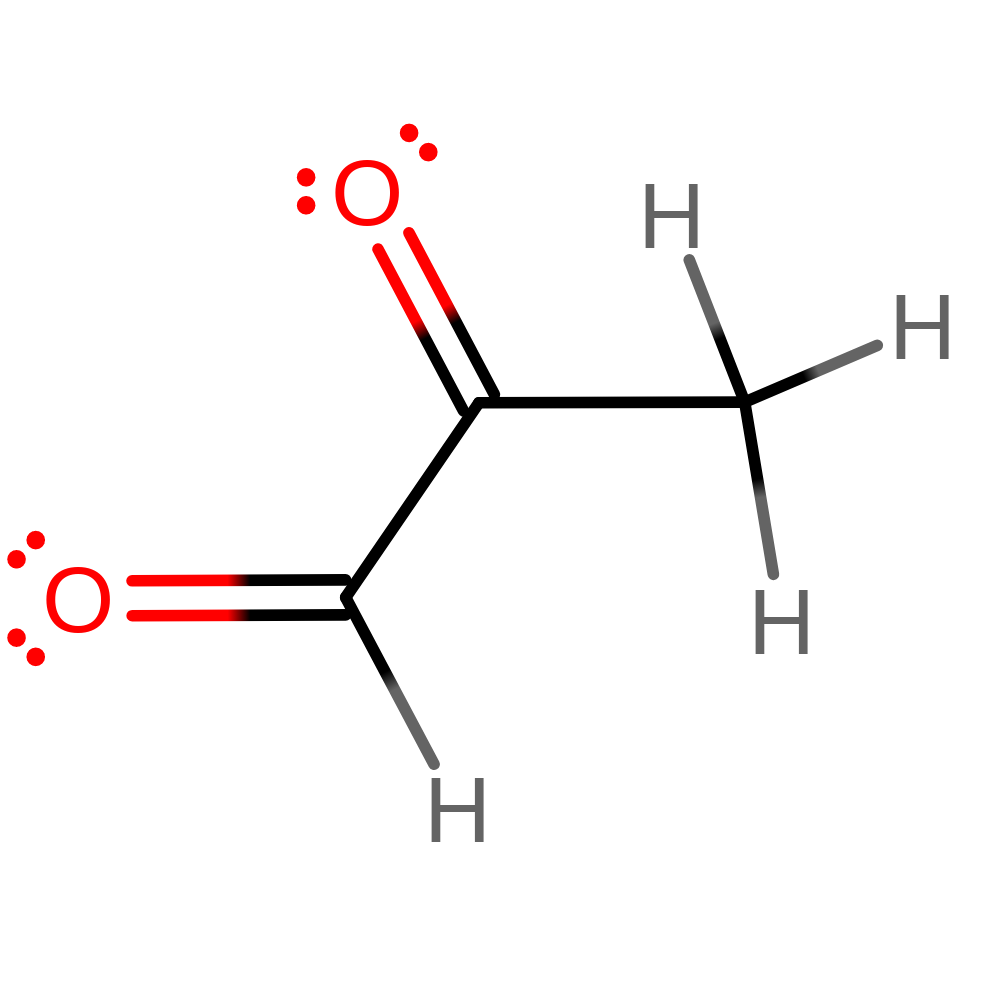 Download:
Download: