Inositol-1,4-bisphosphate 1-phosphatase
Inositol polyphosphate 1 -phosphatase (l-ptase) removes the l-position phosphate from inositol 1,4-bisphosphate, yielding inositol 4-phosphate. l-Ptase is a ubiquitous monomeric enzyme that requires Mg2+ for activity and is potently inhibited by Li+, leading to its use in therapeutic targets of lithium treatment for manic-depressive illnesses.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P21327
 (3.1.3.57)
(3.1.3.57)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1inp
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF INOSITOL POLYPHOSPHATE 1-PHOSPHATASE AT 2.3 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.540.10
 3.40.190.80
3.40.190.80  (see all for 1inp)
(see all for 1inp)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.3.57)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
As with most phosphatases the mechanism involves nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group. The nucleophile is an activated water molecule, which is co-ordinated to two magnesium cofactors and then activated by Thr158. This attacks the phosphate group forming a trigonal bipyramidal intermediate which is stabilised by the magnesium ions, break down of this leads to the the inositol 4-phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1inp) | ||
| Glu79, Asp153, Asp156, Asp317, Ile155 (main-N) | Glu79A, Asp153A, Asp156A, Asp317A, Ile155A (main-N) | Coordinate the magnesium ions. | metal ligand |
| Asp54, Thr158 | Asp54A, Thr158A | Part of the hydrogen bonding network that activates the nucleophilic water molecule. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, proton transfer, proton relay, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- York JD et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 13164-13171. Crystal structure of inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase at 2.3-A resolution. DOI:10.2210/pdb1inp/pdb. PMID:7947723.
- Faisal Tarique K et al. (2014), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 70, 2019-2031. Structural elucidation of a dual-activity PAP phosphatase-1 from Entamoeba histolytica capable of hydrolysing both 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate and inositol 1,4-bisphosphate. DOI:10.1107/S1399004714010268. PMID:25004978.
- Patel S et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 315, 677-685. Crystal structure of an enzyme displaying both inositol-polyphosphate-1-phosphatase and 3′-phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphate phosphatase activities: a novel target of lithium therapy. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5271. PMID:11812139.

Step 1. The Asp54/Thr158 network deprotonates a water molecule activating it for nucleophilic attack on the phosphate. The penta-covalent intermediate formed is stabilized by the magnesium ions.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr158A | enhance reactivity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu79A | metal ligand |
| Asp153A | metal ligand |
| Ile155A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp156A | metal ligand |
| Asp317A | metal ligand |
| Thr158A | proton relay, increase nucleophilicity |
| Asp54A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr158A | proton acceptor |
| Asp54A | proton acceptor |
| Thr158A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, proton transfer, proton relay, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu79A | metal ligand |
| Asp153A | metal ligand |
| Ile155A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp156A | metal ligand |
| Asp317A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base
Step 3. Inferred step- product is protonated and the enzyme is regenerated in its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr158A | proton relay, proton acceptor |
| Asp54A | proton donor |
| Thr158A | proton donor |



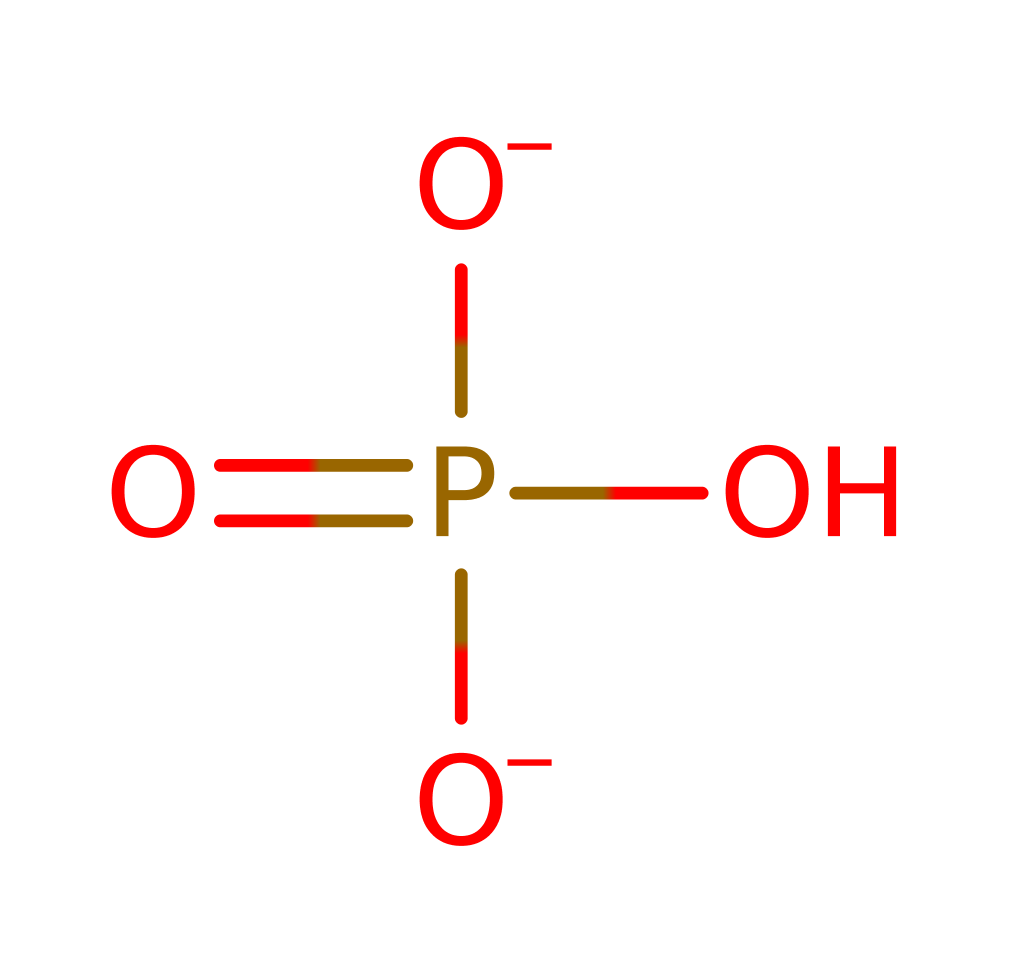

 Download:
Download: