Acetylglutamate kinase
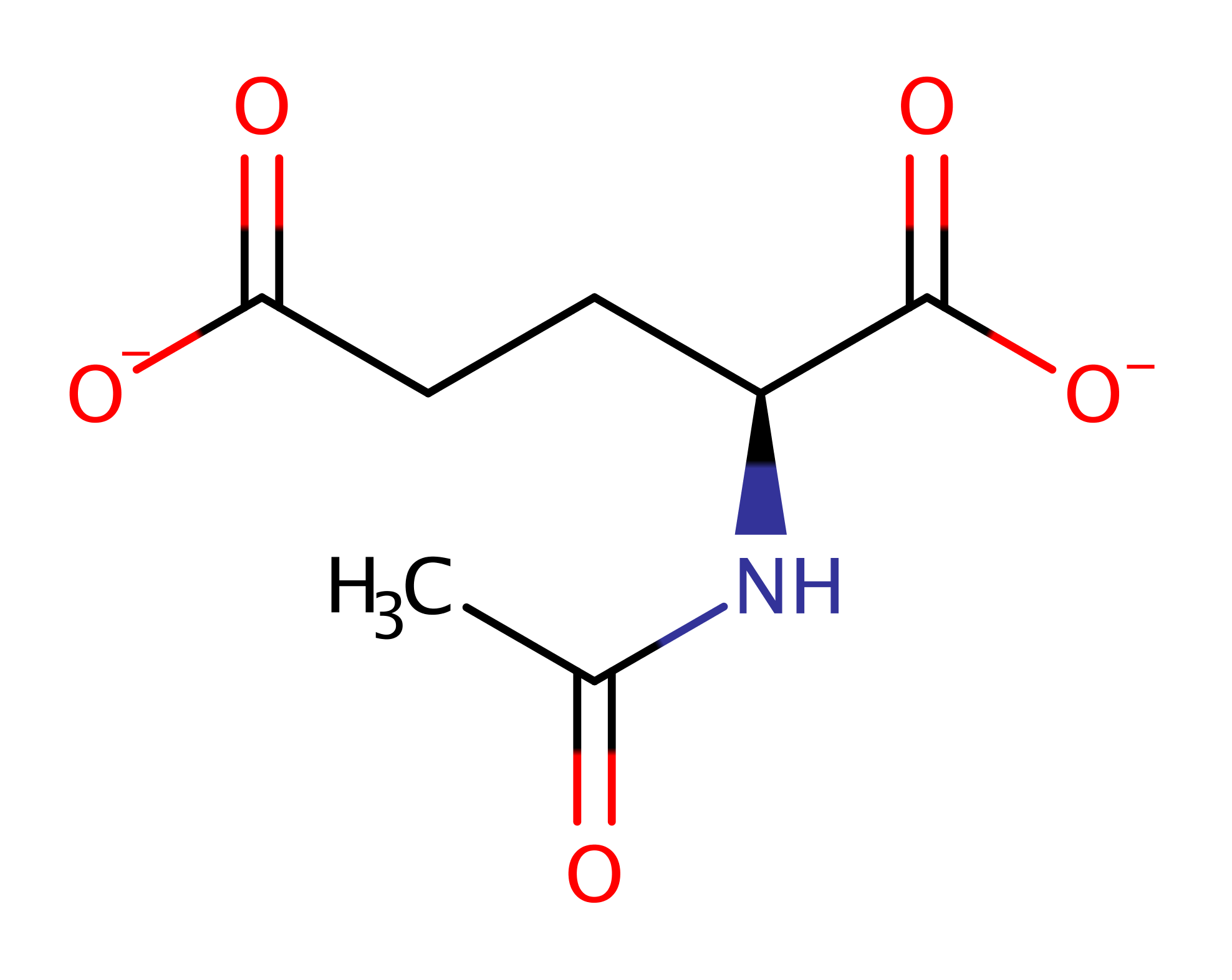
Catalyses the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of N-acetyl-L-glutamate (NAG). NAG fulfils distinct biological roles in lower and higher organisms. In prokaryotes, lower eukaryotes and plants it is the first intermediate in the biosynthesis of arginine, whereas in ureotelic (excreting nitrogen mostly in the form of urea) vertebrates, it is an essential allosteric cofactor for carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI), the first enzyme of the urea cycle. This enzyme is present only in microorganisms and plants but absent in mammals, and as a result it is an attractive target for antimicrobial or biocidal development.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9SCL7
 (2.7.2.8)
(2.7.2.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)

- PDB
-
4usj
- N-acetylglutamate kinase from Arabidopsis thaliana in complex with PII from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
(2.85 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1160.10
 (see all for 4usj)
(see all for 4usj)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.2.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Three successive steps have been proposed during phosphoryl transfer based on crystal structure: at the beginning, when the attacking and leaving O atoms and the P atom are imperfectly aligned and the distance between the attacking O atom and the P atom is 2.8A; midway, at the bipyramidal intermediate, with nearly perfect alignment and a distance of 2.3A; and, when the transfer is completed. The transfer occurs in line and is strongly associative, with Lys8 and Lys217 stabilising the transition state and the leaving group, respectively.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (4usj) | ||
| Asp162 | Asp162A | D162 organises and activates the catalytic groups. | activator, steric role |
| Lys8, Gly11 (main-N), Gly45 (main-N), Lys217 | Lys8A, Gly11A (main-N), Gly45A (main-N), Lys217A | Acts as a transition state stabiliser. | transition state stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Gil-Ortiz F et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 331, 231-244. The Course of Phosphorus in the Reaction of N-Acetyl-l-glutamate Kinase, Determined from the Structures of Crystalline Complexes, Including a Complex with an AlF4− Transition State Mimic. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00716-2. PMID:12875848.
- Gil-Ortiz F et al. (2010), J Mol Biol, 399, 476-490. Two crystal structures of Escherichia coli N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase demonstrate the cycling between open and closed conformations. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.04.025. PMID:20403363.
- Marco-Marín C et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 334, 459-476. Site-directed mutagenesis of Escherichia coli acetylglutamate kinase and aspartokinase III probes the catalytic and substrate-binding mechanisms of these amino acid kinase family enzymes and allows three-dimensional modelling of aspartokinase. PMID:14623187.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys8A | transition state stabiliser |
| Lys217A | transition state stabiliser |
| Asp162A | steric role, activator |
| Gly11A (main-N) | transition state stabiliser |
| Gly45A (main-N) | transition state stabiliser |