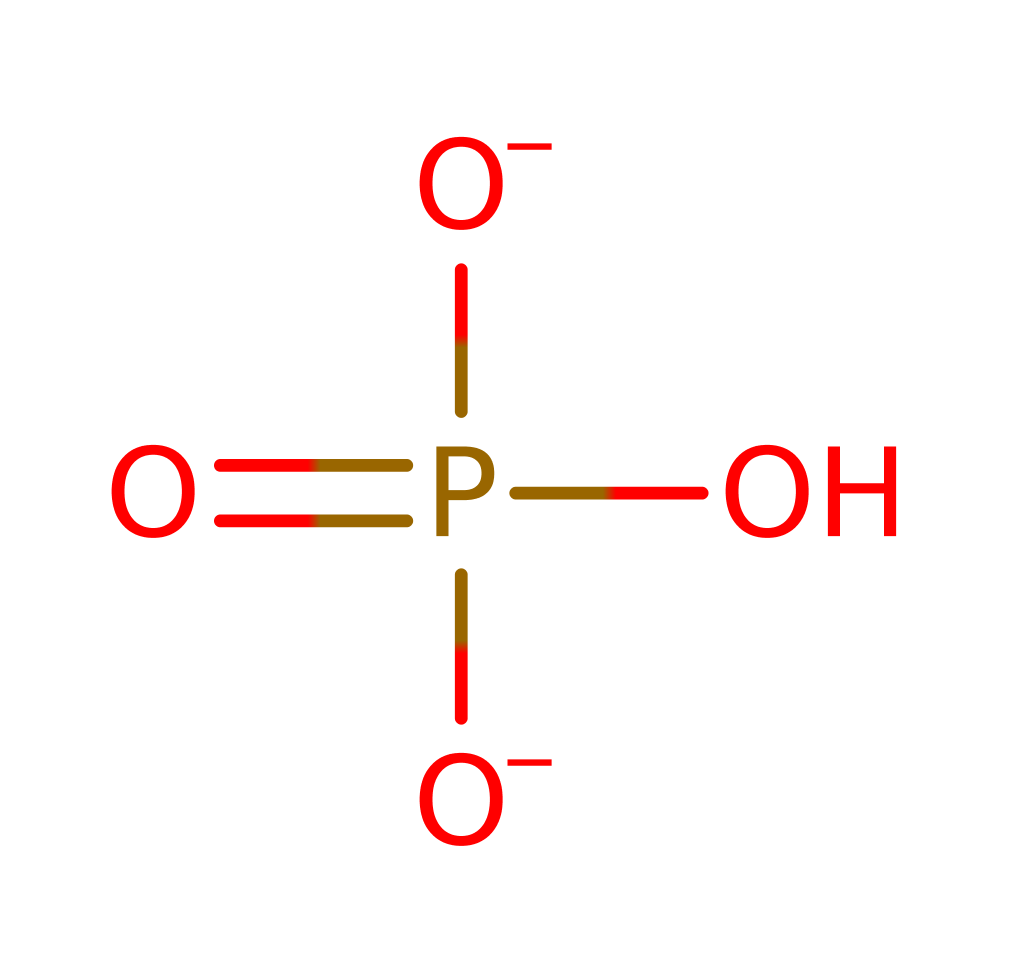
UDP-N-acetylmuramate---L-alanine ligase
UDP-N-acetylmuramate-alanine ligase (MurC) is an essential, cytoplasmic peptidoglycan biosynthetic enzyme that catalyses the ATP-dependent ligation of L-alanine (Ala) and UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid (UNAM) to form UDP-N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine (UNAM-Ala). This reaction is part of the biosynthesis of cell walls in bacteria. MurC is a nonribosomal peptide ligase which utilises ATP to form an amide bond between L-alanine and UNAM. Mechanistic studies on the Escherichia coli enzyme demonstrated that the enzyme-catalysed reaction proceeds through an acyl phosphate UNAM intermediate prior to L-alanine addition.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P45066
 (6.3.2.8)
(6.3.2.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Haemophilus influenzae Rd KW20 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1p3d
- Crystal Structure of UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid:L-alanine ligase (MurC) in Complex with UMA and ANP.
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1190.10
 (see all for 1p3d)
(see all for 1p3d)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.3.2.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
An acyl-phosphate intermediate is formed via transfer of the γ-phosphate of ATP to the carboxylate of UNAM or the C-terminal carboxylate of UNAM peptide. The amide of the incoming amino acid displaces the phosphate by nucleophilic attack, thereby extending the peptide chain.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1p3d) | ||
| Thr130, Glu173 | Thr130A, Glu173A | Forms part of the divalent metal ion binding site. | metal ligand |
| Lys129 | Lys129A | Part of a well conserved ATP binding motif, helps stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. The side chain N-eta of Lys 129 contacts a gamma-phosphate oxygen. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Mol CD et al. (2003), J Bacteriol, 185, 4152-4162. Crystal Structures of Active Fully Assembled Substrate- and Product-Bound Complexes of UDP-N-Acetylmuramic Acid:L-Alanine Ligase (MurC) from Haemophilus influenzae. DOI:10.1128/jb.185.14.4152-4162.2003. PMID:12837790.
- Deva T et al. (2006), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 62, 1466-1474. Structure of Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl:L-alanine ligase (MurC). DOI:10.1107/S0907444906038376. PMID:17139082.
- Marmor S et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 12207-12214. Biochemical Characterization of a Phosphinate Inhibitor ofEscherichia coliMurC. DOI:10.1021/bi015567m.
- Bouhss A et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 11556-11563. Invariant Amino Acids in the Mur Peptide Synthetases of Bacterial Peptidoglycan Synthesis and Their Modification by Site-Directed Mutagenesis in the UDP-MurNAc:l-Alanine Ligase fromEscherichiacoli†. DOI:10.1021/bi970797f. PMID:9305945.
- Falk PJ et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 1417-1422. Biochemical evidence for the formation of a covalent acyl-phosphate linkage between UDP-N-acetylmuramate and ATP in the Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylmuramate:L-alanine ligase-catalyzed reaction. DOI:10.1021/bi952078b. PMID:8634271.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys129A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu173A | metal ligand |
| Thr130A | metal ligand |