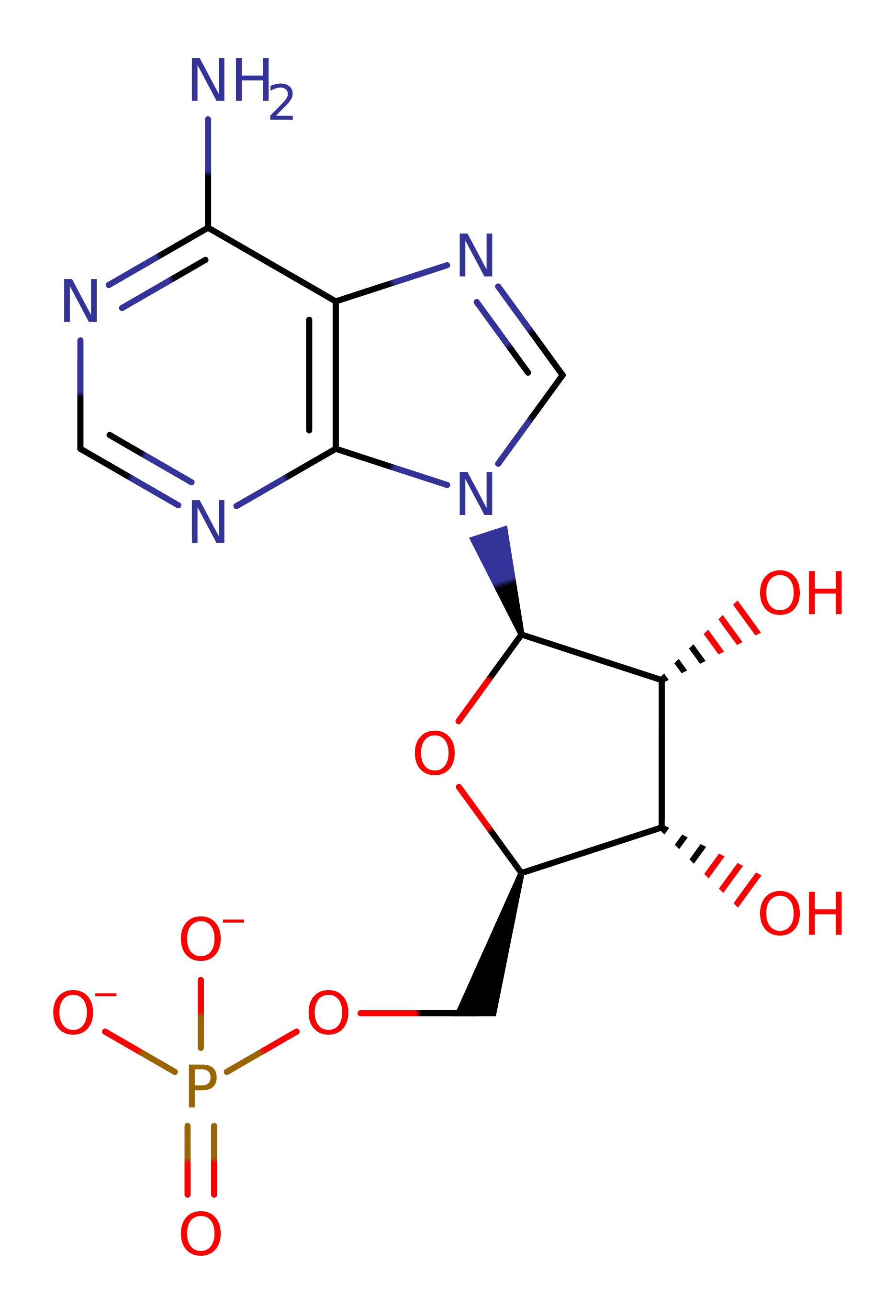
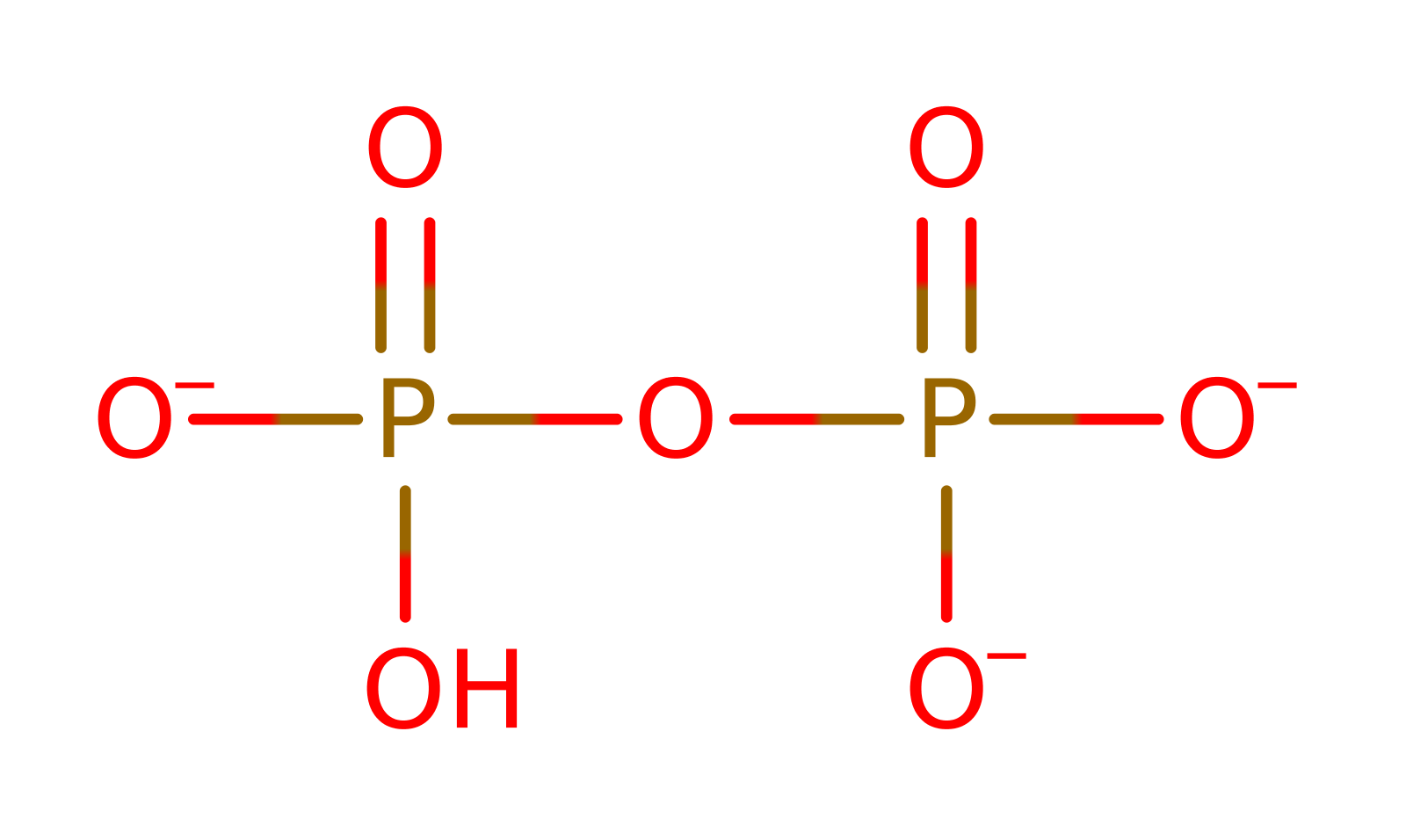
Serine---tRNA ligase
Serine-tRNA ligase (EC:6.1.1.11) exists as monomer and belongs to the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase class IIa. It catalyses the attachment of serine to tRNA (Ser). It is also able to aminoacylate tRNA (Sec) with serine, to form the misacylated tRNA L-seryl-tRNA (Sec), which will be further converted into selenocysteinyl-tRNA (Sec).
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P34945
 (6.1.1.11)
(6.1.1.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermus thermophilus HB27 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ses
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AT 2.5 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION OF SERYL-TRNA SYNTHETASE COMPLEXED WITH TWO DIFFERENT ANALOGUES OF SERYL-ADENYLATE
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.930.10
 (see all for 1ses)
(see all for 1ses)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.1.1.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This enzyme catalyzes two successive transfer reactions. Firstly, it transfers the adenylate from ATP (the first substrate) to the carboxylate of the second substrate, serine, resulting in the formation of seryl-adenylate (intermediate) and the release of the inorganic pyrophosphate. Secondly, it transfers the acyl group from the intermediate to the 3'-OH of tRNA(Ser). The ATP is found in an unusual bent conformation, stabilised by interactions with conserved arginines and three manganese ions.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ses) | ||
| Glu345, Ser348 | Glu345A, Ser348A | Forms the metal binding site. | metal ligand |
| Arg386, Arg256, Arg271 | Arg386A, Arg256A, Arg271A | Stabilises the negatively charged groups, the acceptor group (the carboxylate) and the transferred group (apha-phosphate of ATP), by neutralising the charged groups. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Belrhali H et al. (1995), Structure, 3, 341-352. The structural basis for seryl-adenylate and Ap4A synthesis by seryl-tRNA synthetase. PMID:7613865.
- Cusack S et al. (1996), EMBO J, 15, 2834-2842. The crystal structure of the ternary complex of T.thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase with tRNA(Ser) and a seryl-adenylate analogue reveals a conformational switch in the active site. PMID:8654381.
- Belrhali H et al. (1994), Science, 263, 1432-1436. Crystal structures at 2.5 angstrom resolution of seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with two analogs of seryl adenylate. PMID:8128224.
- Fujinaga M et al. (1993), J Mol Biol, 234, 222-233. Refined crystal structure of the seryl-tRNA synthetase from Thermus thermophilus at 2.5 A resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1993.1576. PMID:8230201.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu345A | metal ligand |
| Ser348A | metal ligand |
| Arg256A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg271A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg386A | electrostatic stabiliser |