Ketol-acid reductoisomerase
Ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) is a Mg(2+) -dependent enzyme in the branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathway. KARI catalyses two steps in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids. The reaction involves an Mg(II) dependent alkyl migration followed by an NADPH-dependent reduction of the 2-keto group.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q01292
 (1.1.1.86)
(1.1.1.86)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Spinacia oleracea (spinach)

- PDB
-
1yve
- ACETOHYDROXY ACID ISOMEROREDUCTASE COMPLEXED WITH NADPH, MAGNESIUM AND INHIBITOR IPOHA (N-HYDROXY-N-ISOPROPYLOXAMATE)
(1.65 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.1040.10
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1yve)
(see all for 1yve)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2), Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.86)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction is initiated by a proton abstraction (by the hydroxide ion bridging the two metal ions), followed by a concerted isomerisation and hydride transfer. The two protons needed to protonate the product are proposed to be donated from the bridging water ligand and a conserved lysine
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1yve) | ||
| Asp315 | Asp315(244)K(C) | Acts as a bridging ligand between the two divalent metal ions. | metal ligand |
| Glu319 | Glu319(248)K(C) | Forms part of the metal 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Lys252 | Lys252(181)K(C) | Proposed to act as the general acid/base in the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intramolecular rearrangement, overall reactant used, hydride transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Tadrowski S et al. (2016), Chemistry, 22, 7427-7436. Metal Ions Play an Essential Catalytic Role in the Mechanism of Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerase. DOI:10.1002/chem.201600620. PMID:27136273.
- Leung EW et al. (2009), J Mol Biol, 389, 167-182. Conformational changes in a plant ketol-acid reductoisomerase upon Mg(2+) and NADPH binding as revealed by two crystal structures. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.012. PMID:19362563.
- Tyagi R et al. (2005), FEBS J, 272, 593-602. Probing the mechanism of the bifunctional enzyme ketol-acid reductoisomerase by site-directed mutagenesis of the active site. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2004.04506.x. PMID:15654896.
- Dumas R et al. (2001), Acc Chem Res, 34, 399-408. Enzymology, Structure, and Dynamics of Acetohydroxy Acid Isomeroreductase. DOI:10.1021/ar000082w. PMID:11352718.
- Thomazeau K et al. (2000), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 56, 389-397. Structure of spinach acetohydroxyacid isomeroreductase complexed with its reaction product dihydroxymethylvalerate, manganese and (phospho)-ADP-ribose. PMID:10739911.
- Halgand F et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 6025-6034. Characterization of the conformational changes of acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase induced by the binding of Mg2+ ions, NADPH, and a competitive inhibitor. DOI:10.1021/bi982412e. PMID:10320328.
- Biou V et al. (1997), EMBO J, 16, 3405-3415. The crystal structure of plant acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase complexed with NADPH, two magnesium ions and a herbicidal transition state analog determined at 1.65 A resolution. DOI:10.1093/emboj/16.12.3405. PMID:9218783.
- Dumas R et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 6026-6036. Evidence for two catalytically different magnesium-binding sites in acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase by site-directed mutagenesis. PMID:7742305.
- Mrachko GT et al. (1992), Arch Biochem Biophys, 294, 446-453. The pH dependence of the kinetic parameters of ketol acid reductoisomerase indicates a proton shuttle mechanism for alkyl migration. PMID:1567200.
- Aulabaugh A et al. (1990), Biochemistry, 29, 2824-2830. Oxalyl hydroxamates as reaction-intermediate analogues for ketol-acid reductoisomerase. PMID:2189496.

Step 1. A magnesium activated water molecule abstracts the proton from the alcohol, initiating a 1,2-alkyl shift with concomitant deprotonation of the conserved Lys252 residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp315(244)K(C) | metal ligand |
| Glu319(248)K(C) | metal ligand |
| Lys252(181)K(C) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intramolecular rearrangement, overall reactant used
Step 2. NADPH eliminates a hydride ion, that is added to the newly formed carbonyl group, which in turn abstracts the proton from the magnesium bound water molecule, regenerating the bound hydroxide ion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp315(244)K(C) | metal ligand |
| Glu319(248)K(C) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, proton transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, overall reactant used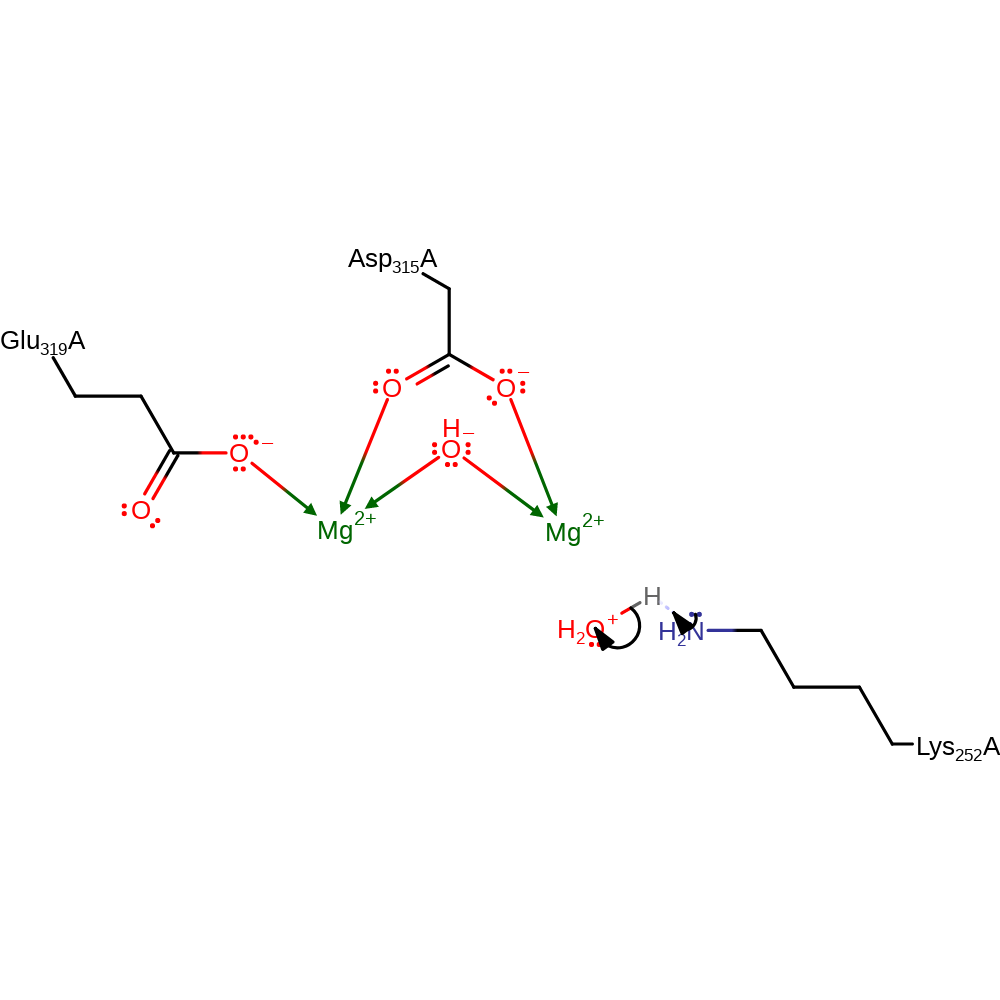
Step 3. In an inferred return step, water donates a proton to the lysine to regenerate the enzyme's active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp315(244)K(C) | metal ligand |
| Glu319(248)K(C) | metal ligand |
| Lys252(181)K(C) | proton acceptor |
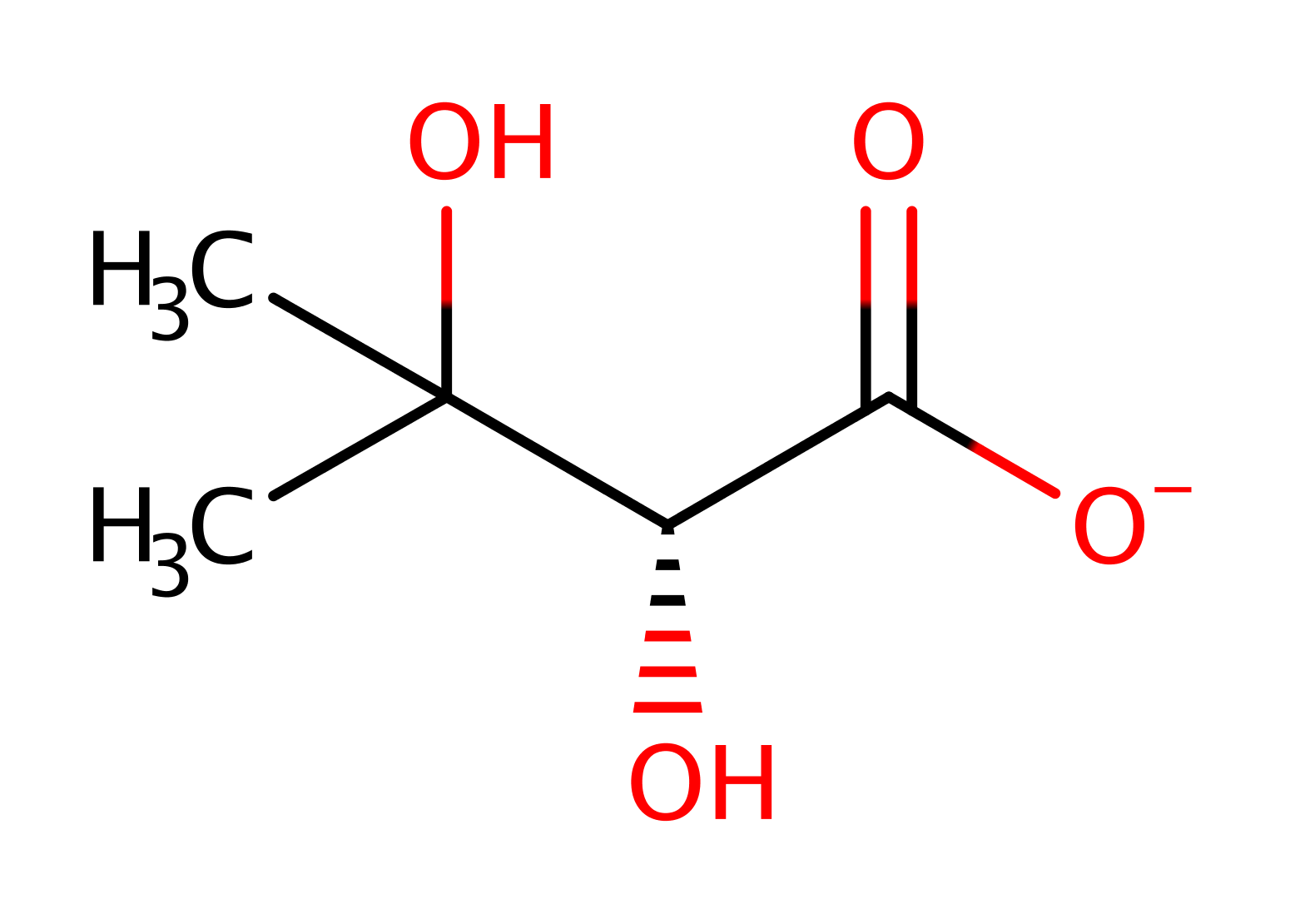



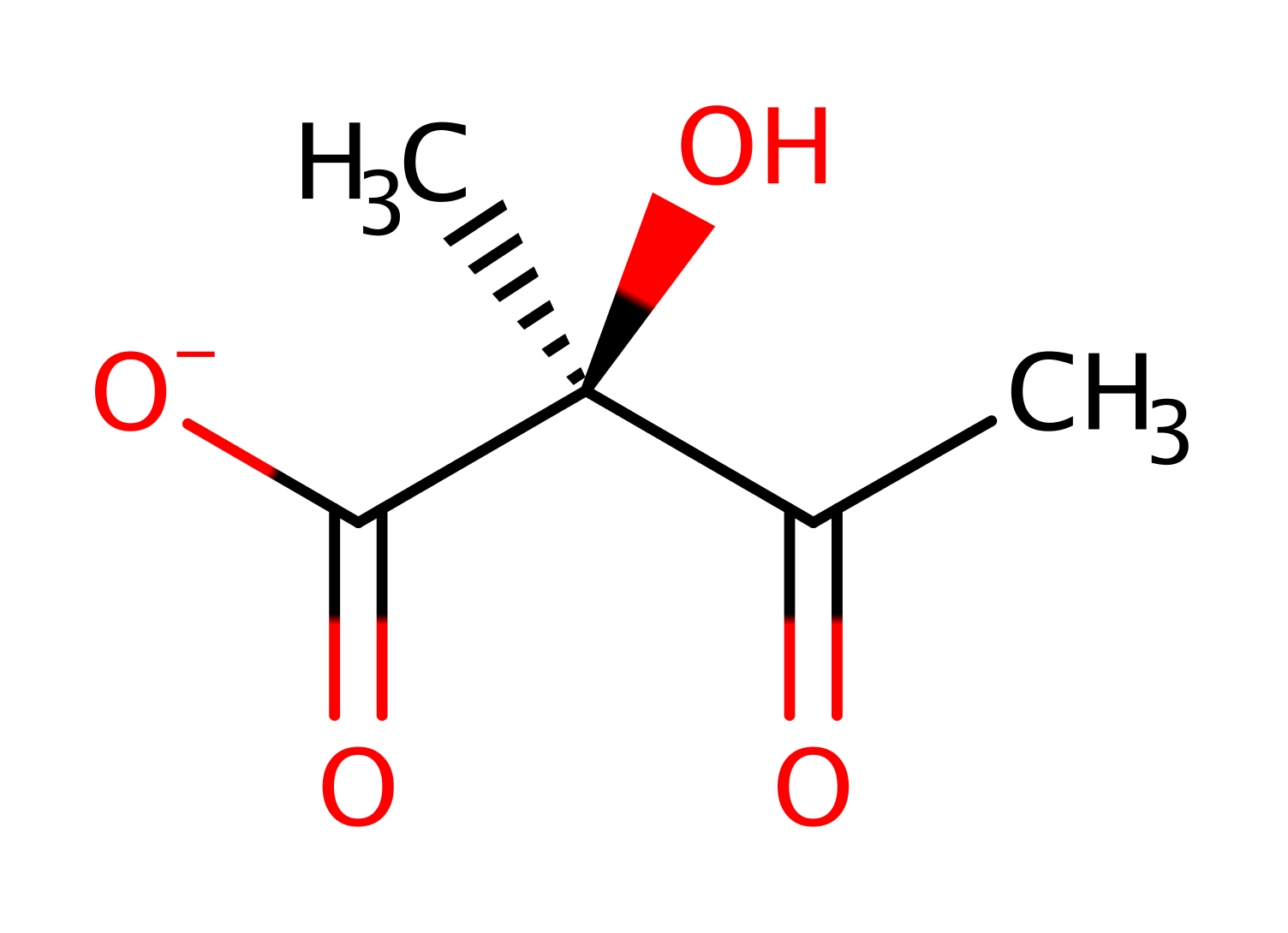
 Download:
Download: