Adenosylhomocysteinase
Adenosylhomocysteinase (AdoHcyase) catalyses the reversible hydrolysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy). AdoHcyase is a tetrameric enzyme with 431 amino acid residues in each identical subunit. The subunit is composed of the catalytic domain, the NAD+-binding domain, and the small C-terminal domain. Both catalytic and NAD+-binding domains are folded into an ellipsoid with a typical alpha / beta twisted open sheet structure. The catalytic domain is quite mobile, whereas the NAD+-binding domain and the small C-terminal domain are less mobile. The high mobility of the catalytic domain is due to the unique architecture of the tetramer.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P10760
 (3.3.1.1)
(3.3.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)

- PDB
-
1b3r
- RAT LIVER S-ADENOSYLHOMOCYSTEIN HYDROLASE
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1480
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1b3r)
(see all for 1b3r)
- Cofactors
- Nadh(2-) (1), Nadph(4-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.3.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
It is likely that binding of AdoHcy induces a large conformational change so as to place the ribose moiety of AdoHcy in close proximity to the nicotinamide moiety of NAD+. A catalytic mechanism is proposed based on crystal structures and results from site-directed mutagenesis.
In the hydrolysis, the neutral side chain of Lys185 serves as a base to accept a proton from 3'-OH in concomitant to the abstraction of the 3'-CH proton by NAD+, forming a 3'keto-AdoHcy intermediate and a NADH molecule. Asp130 then acts as a base to abstract the proton from C4'and the 3'-keto-AdoHcy carbanion intermediate is produced. His54 donates a proton to Hcy delta-S of the resulting carbanion, leading to the release of Hcy to form 3'-keto-4',5'-dehydroadenosine. A water molecule, activated by His54 and His300, then acts as a nucleophile to attack C5' of 3'-keto-4',5'-dehydroadenosine and the proton abstracted from C4' by Asp130 is donated back. Reduction of the keto intermediate by NADH forms the product adenosine.
Asp189 acts as a general acid-base catalyst, protonating and deprotonating Lys185, in order to retain the proton removed by Lys185 from ribose 3'-OH group in the enzyme to ensure catalytic efficiency. Asn190 facilitates the formation of neutral Lys185 to promote the reduction of the keto-intermediate by NADH. Cys194 modulates the oxidation state of the bound NAD+ and facilitates abstraction of the C3'-H of the substrate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1b3r) | ||
| Gln365 | Gln364A | Acts to stabilise and activate Glu155. | activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His301 | His300A | It polarises a water molecule to activate it for the nucleophilic attack on C5' of 3'-keto-4',5'-dehydroadenosine during hydrolysis. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp131 | Asp130A | It acts as a general acid-base catalyst, protonating and deprotonating the 4'-carbon. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Lys186 | Lys185A | It acts as a general acid-base catalyse, protonating and deprotonating the 3'-OH group during the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp190 | Asp189A | It acts as a general acid-base catalyst, protonating and deprotonating Lys185, in order to retain the proton removed by Lys185 from ribose 3'-OH group in the enzyme to ensure catalytic efficiency. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Cys195 | Cys194A | It modulates the oxidation state of the bound NAD+ and facilitates abstraction of the C3'-H of the substrate. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| His55 | His54A | It acts as an acid to donate a proton to the leaving Hcy/H2O. It polarises a water molecule to activate it for the nucleophilic attack on C5' of 3'-keto-4',5'-dehydroadenosine in hydrolysis. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Glu156 | Glu155A | Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting a proton from Asp130. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Ser78, Ser83 | Ser77A, Ser82A | Form a His-Ser-Ser triad, activating and stabilising His54 to act as a general acid/base. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn191, Asn181 | Asn190A, Asn180A | Facilitates the formation of neutral Lys185 to promote the reduction of the keto-intermediate by NADH. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser361, His353 | Ser360A, His352A | Acts to stabilise the neutral form of Asp189. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, bimolecular elimination, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Yamada T et al. (2005), Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 37, 2417-2435. Catalytic mechanism of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase: Roles of His 54, Asp130, Glu155, Lys185, and Aspl89. DOI:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.06.009. PMID:16061414.
- Kusakabe Y et al. (2015), Sci Rep, 5, 16641-. Structural insights into the reaction mechanism of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. DOI:10.1038/srep16641. PMID:26573329.
- Ishihara M et al. (2010), Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun, 66, 313-315. Crystallization of mouseS-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. DOI:10.1107/s1744309110000771. PMID:20208169.
- Reddy MC et al. (2008), Protein Sci, 17, 2134-2144. Crystal structures ofMycobacterium tuberculosisS-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase in ternary complex with substrate and inhibitors. DOI:10.1110/ps.038125.108. PMID:18815415.
- Takata Y et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 22670-22676. Catalytic Mechanism of S-Adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase. SITE-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS OF ASP-130, LYS-185, ASP-189, AND ASN-190. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m201116200. PMID:11927587.
- Komoto J et al. (2000), J Biol Chem, 275, 32147-32156. Effects of Site-directed Mutagenesis on Structure and Function of Recombinant Rat Liver S-Adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF D244E MUTANT ENZYME. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m003725200. PMID:10913437.
- Hu Y et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 8323-8333. Crystal Structure ofS-Adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase from Rat Liver†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi990332k. PMID:10387078.
- Yuan CS et al. (1996), J Biol Chem, 271, 28009-28016. Chemical Modification and Site-directed Mutagenesis of Cysteine Residues in Human Placental S-Adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.271.45.28009. PMID:8910410.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn180A | activator |
| Gln364A | activator |
| Ser77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp130A | proton donor |
| Asp189A | proton acceptor |
| Glu155A | proton acceptor |
| Lys185A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer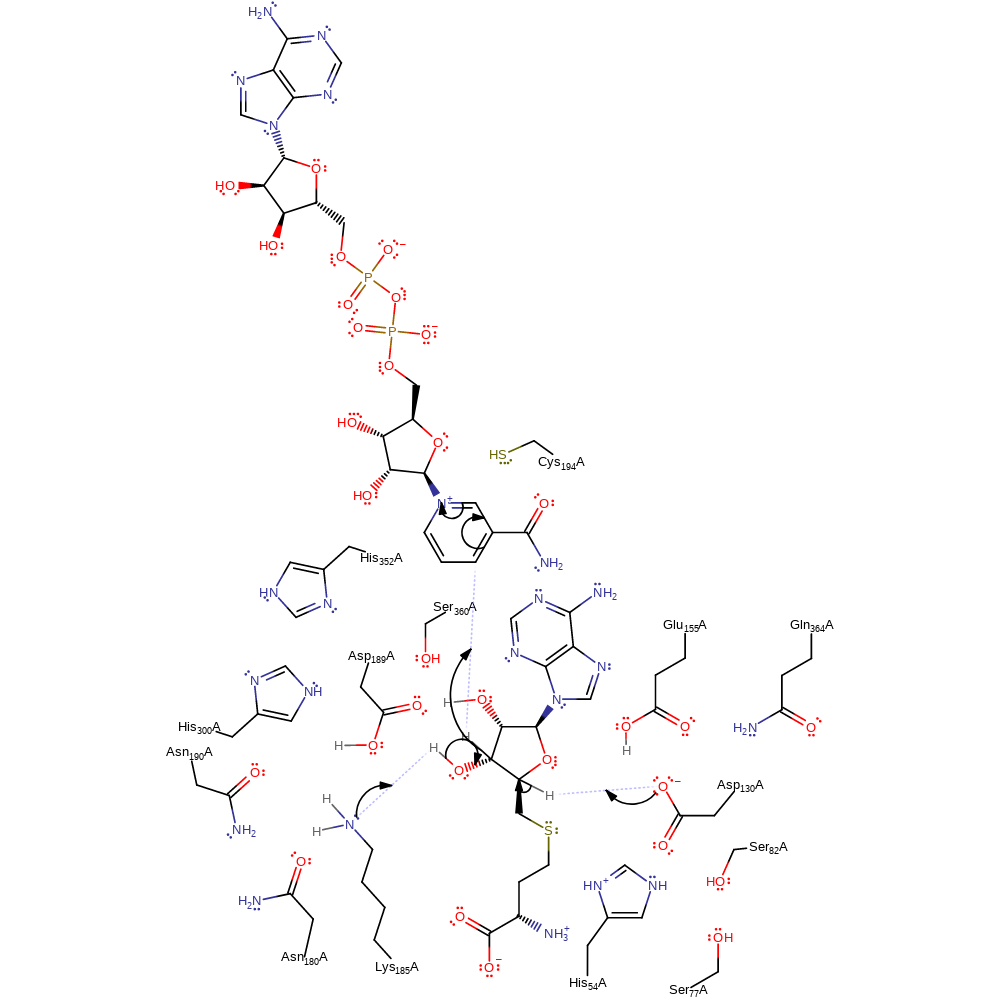
Step 2. Lys185 deprotonates 3'-OH of the substrate. This cause the elimination of a hydride ion, which is transferred to the NAD cofactor. Concurrently, Asp130 deprotonates the C4' position to produce the 3′-keto-4′-dehydro-AdoHcy carbanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His54A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn180A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp189A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn190A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His300A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His352A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp130A | proton acceptor |
| Lys185A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, proton transfer
Step 3. C5′–SD bond is cleaved by H54, and Hcy and 3′-keto-4′,5′-dehydro-Ado are produced. Hcy is released through the solvent channel, and the catalytic domain increases in mobility because the domain and the intermediate interactions are decreased.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn180A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys185A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp189A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His352A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln364A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Asn190A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser360A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp189A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys185A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp130A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His54A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base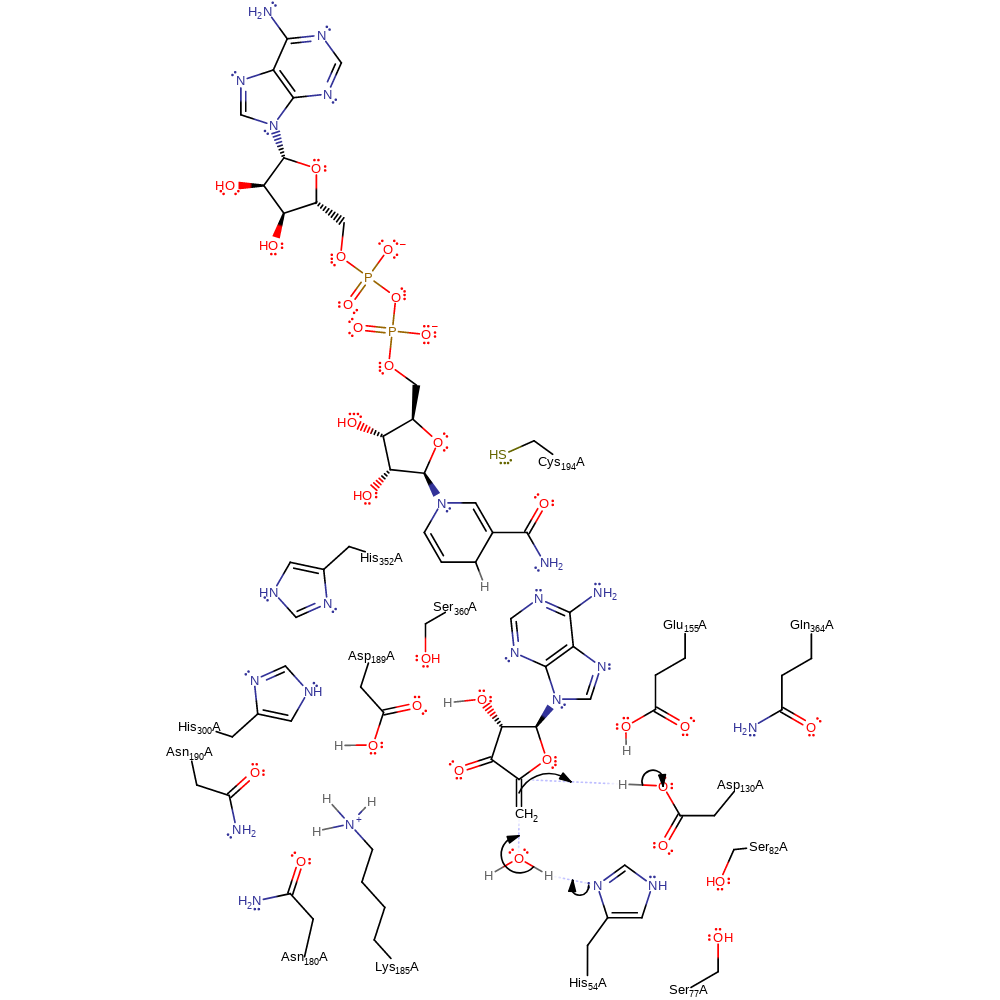
Step 4. A water molecule enters the SD-binding site, is polarized by H54, and nucleophilically attacks the C5′ of 3′-keto-4′, 5′-dehydroadenosine to produce Ado.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp130A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn180A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp189A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His300A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His352A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser360A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln364A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Asn190A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser360A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp189A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys185A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp130A | proton donor |
| His54A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition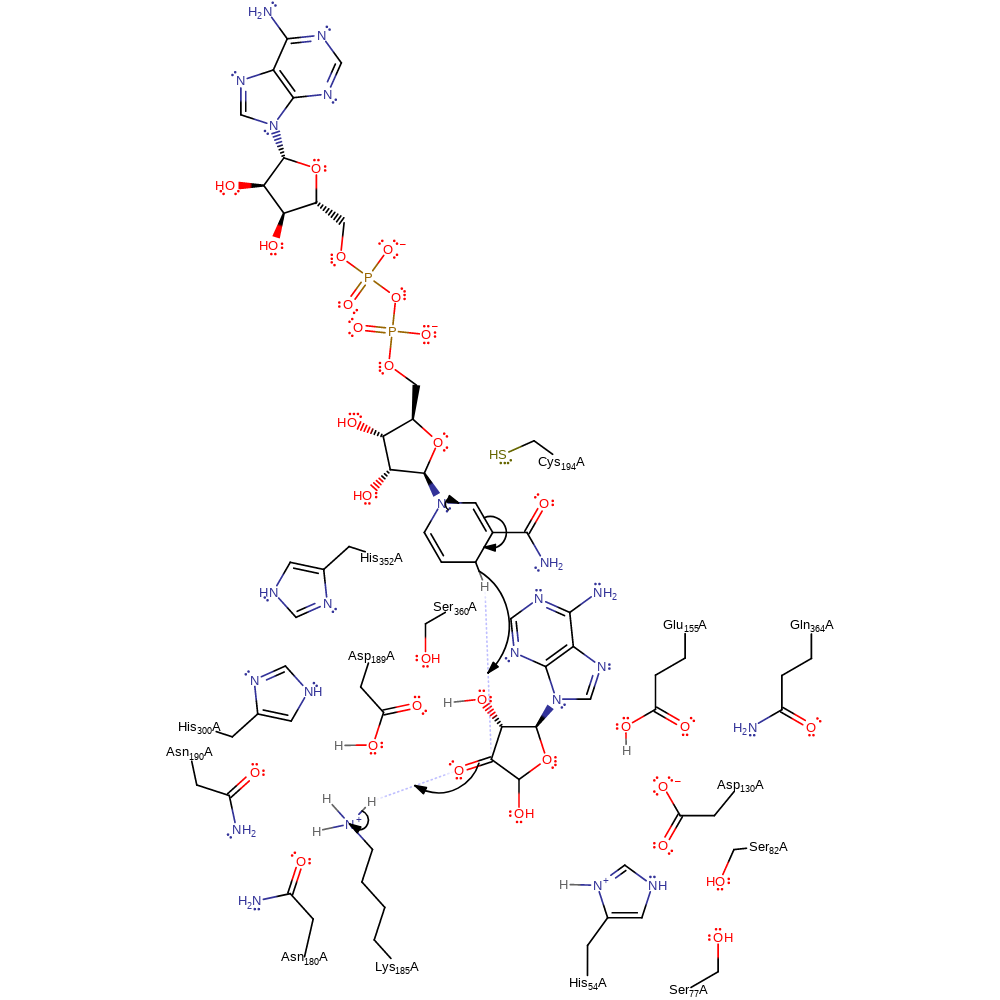
Step 5. The NAD cofactor eliminates the hydride ion, which adds to the 3'-C initiating the oxyanion to deprotonate Lys185.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His54A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp130A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn180A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp189A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His300A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His352A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser360A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln364A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys194A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Asn190A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser360A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His54A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His300A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp189A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys185A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp130A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys185A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base
Step 6. The catalytic cleft is opened by rotating the catalytic domain by 18°, and Ado is released from the active site and the native state of the protein is regenerated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn180A | activator |
| Gln364A | activator |
| Lys185A | proton acceptor |
| Asp189A | proton donor |
| Glu155A | proton donor |
| Asp130A | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: