Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase
Myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase (Nmt) [PMID:8322618] is the enzyme responsible for transferring a myristate group on the N-terminal glycine of a number of cellular eukaryotics and viral proteins.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P14743
 (2.3.1.97)
(2.3.1.97)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
2nmt
- MYRISTOYL-COA:PROTEIN N-MYRISTOYLTRANSFERASE BOUND TO MYRISTOYL-COA AND PEPTIDE ANALOGS
(2.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.630.30
 (see all for 2nmt)
(see all for 2nmt)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.97)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
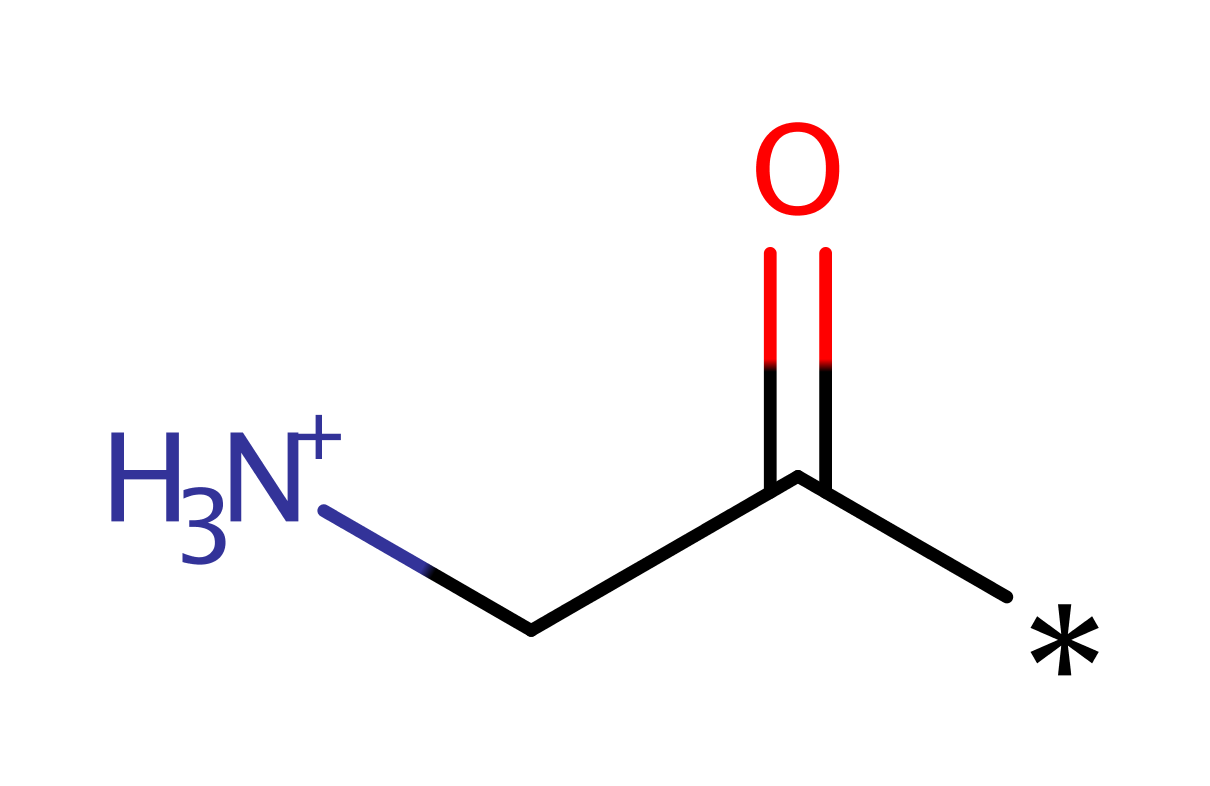
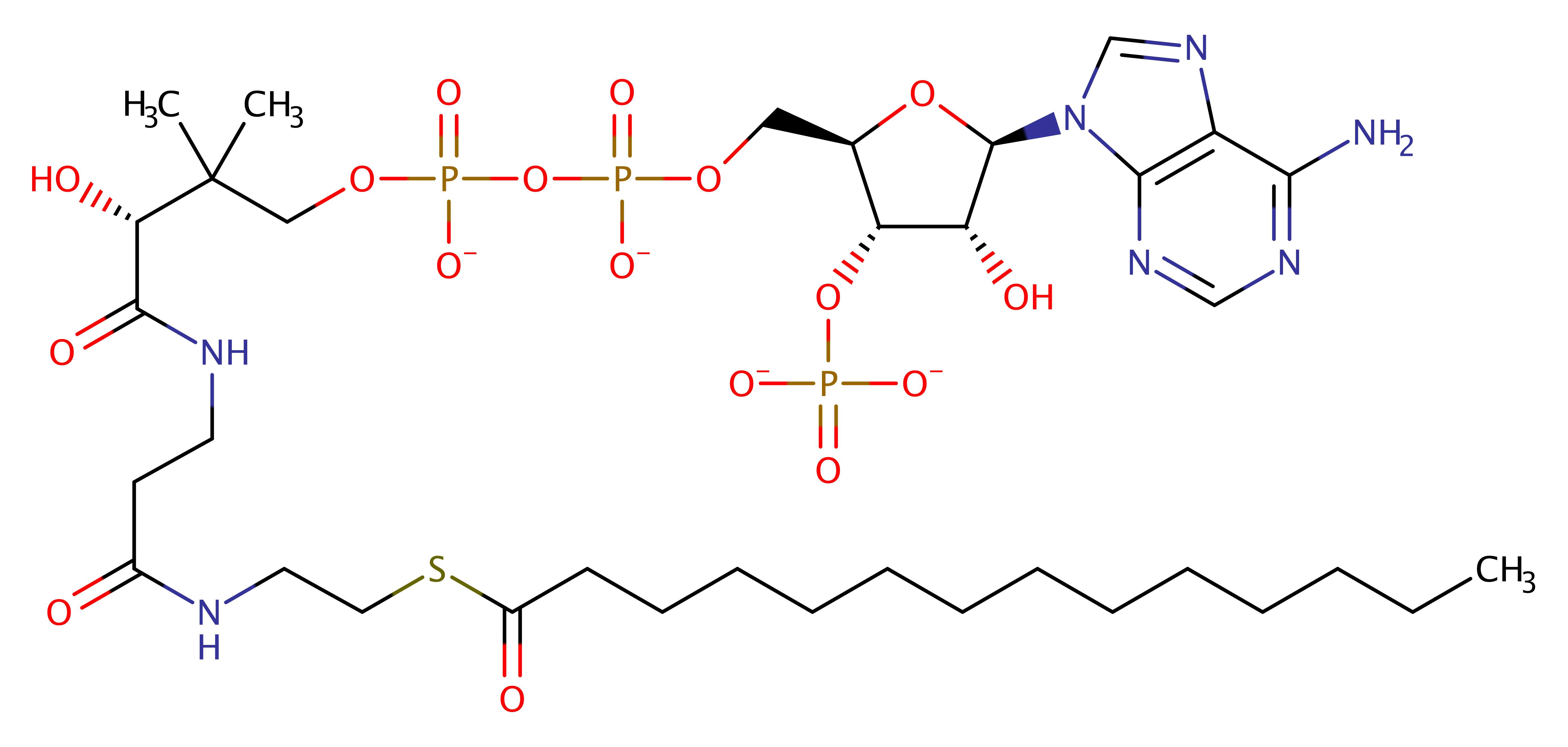
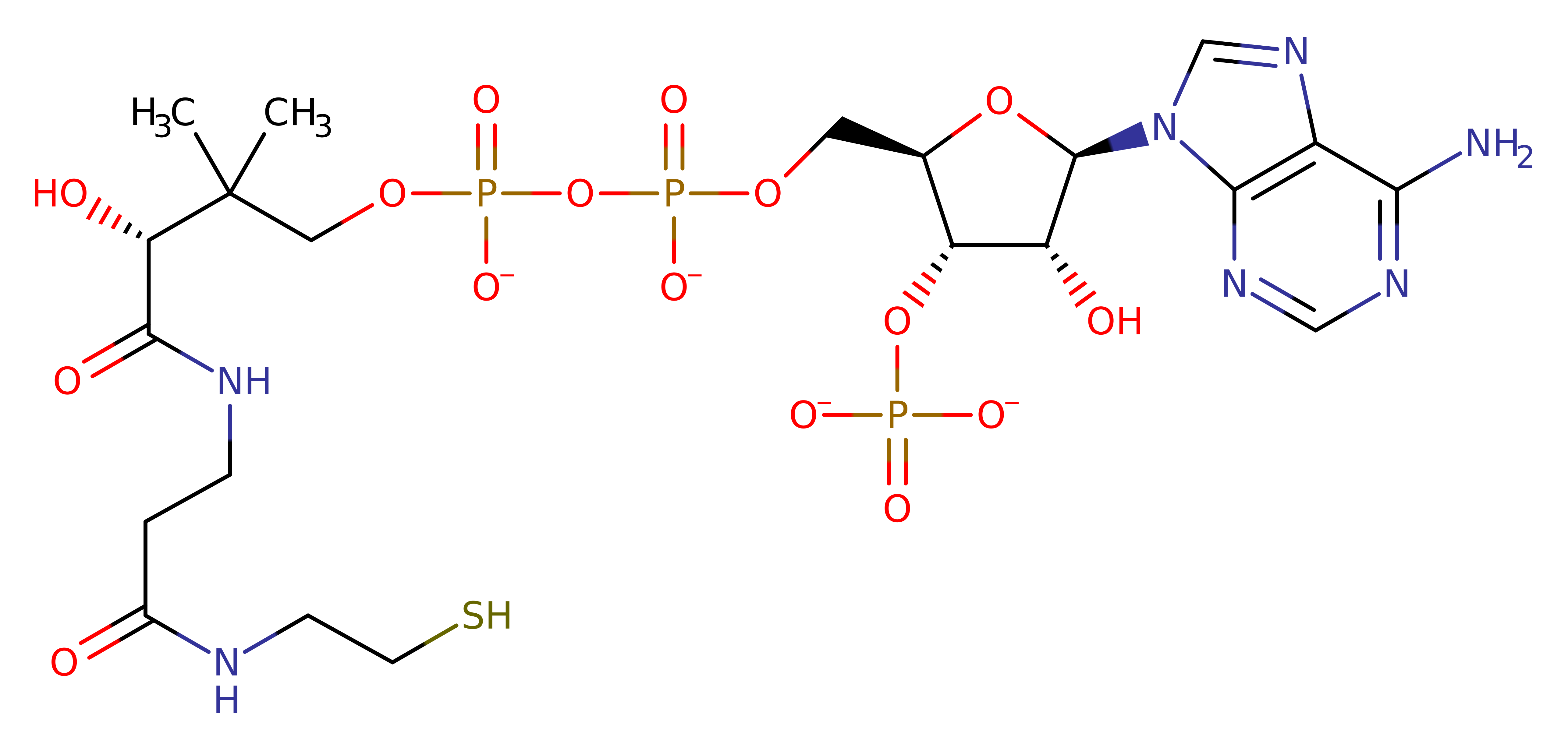
Its reaction mechanism is ordered bi-bi. MyristoylCoA binds first, followed by peptide. After the catalytic transfer of myristate, CoA and subsequently myristoylpeptide are released. Due to the fact that N169 and T205 are not critical for catalysis, it is assumed that this enzyme doesn't proceed via a covalent enzyme-acyl intermediate. The C-terminus of the residue abstracts a proton from the N-terminal glycine of the substrate. This then attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acyl-CoA substrate. The oxyanion formed then collapses to eliminate CoA and the acylated substrate protein.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2nmt) | ||
| Leu455 (C-term) | Leu455(422)A (C-term) | The main chain C-terminal carboxylate of L455 functioning as a catalytic base that abstracts a proton from the N-terminal Gly ammonium of the bound peptide to generate the nucleophilic amine. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Asn169, Thr205 | Asn169(136)A, Thr205(172)A | These residues form part of an H-bonding network that facilitates attack of the Gly1 amine and stabilises the tetrahedral intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe170 (main-N), Leu171 (main-N) | Phe170(137)A (main-N), Leu171(138)A (main-N) | The main chain amides of these residues function as an oxyanion hole to polarise the thioester carbonyl of bound myristoyl-CoA prior to subsequent nucleophilic attack. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Farazi TA et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 9177-9186. Pre-Steady-State Kinetic Studies ofSaccharomyces cerevisiaeMyristoylCoA:ProteinN-Myristoyltransferase Mutants Identify Residues Involved in Catalysis†. DOI:10.1021/bi0107997. PMID:11478885.
- Farazi TA et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 6335-6343. Structures ofSaccharomyces cerevisiaeN-myristoyltransferase with Bound MyristoylCoA and Peptide Provide Insights about Substrate Recognition and Catalysis†. DOI:10.1021/bi0101401. PMID:11371195.
- Farazi TA et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 39501-39504. The Biology and Enzymology of ProteinN-Myristoylation. DOI:10.1074/jbc.r100042200. PMID:11527981.
- Bhatnagar RS et al. (1999), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1441, 162-172. The structure of myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00155-9. PMID:10570244.
- Bhatnagar RS et al. (1998), Nat Struct Biol, 5, 1091-1097. Structure of N-myristoyltransferase with bound myristoylCoA and peptide substrate analogs. DOI:10.1038/4202. PMID:9846880.
- Rudnick DA et al. (1993), Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol, 67, 375-430. MyristoylCoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase. PMID:8322618.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu455(422)A (C-term) | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Phe170(137)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu171(138)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn169(136)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr205(172)A | electrostatic stabiliser |