1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase
2-acetyl-1-alkylglycerophosphocholine esterase, also known as known as platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH).
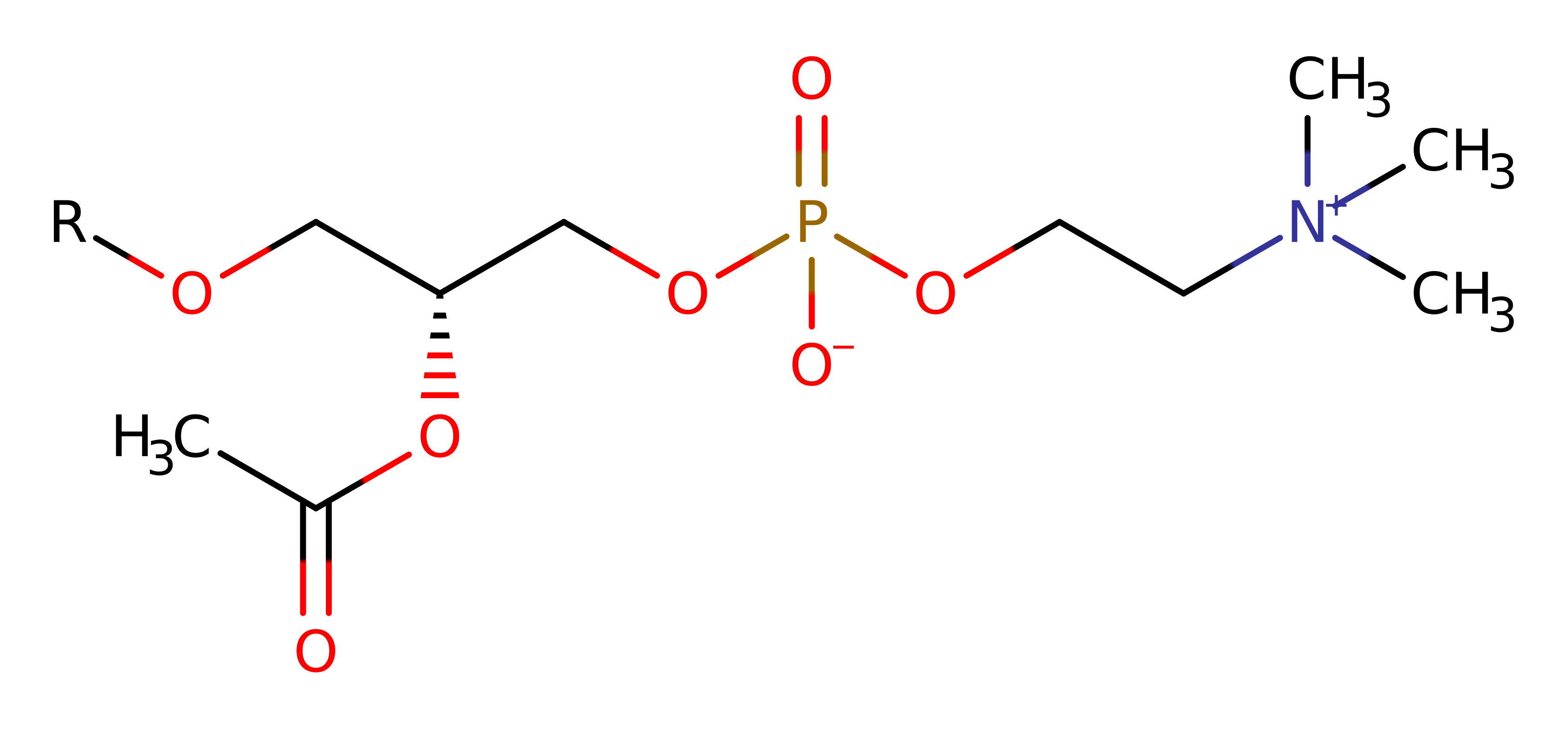
Mammalian brain contains significant levels of platelet activating-factor (PAF), these act as a synapse messenger and transcription inducer of the early response genes c-fos and c-jun. The platelet-activating factor PAF is a potent lipid first messenger active in general cell activation, fertilisation, inflammatory and allergic reactions, asthma, HIV pathogenesis, carcinogenesis, and apoptosis. PAF has also been implicated as a messenger in long-term potentiation, a cellular model of memory formation.
Inactivation of this factor is carried out by PAF-AH, a subfamily of phospholipases A2 that remove the sn-2 acetyl group. Mammalian brain contains at least three intracellular isoforms, 1b being the best characterised. From experimentation it can be assumed that PAF-AH maintains the PAF concentration within a certain range during brain development.
The protein is an unusual G-protein like (alpha1/alpha2)beta trimer. PAF-AH is a heterotrimer composed of 26-,26-, and 45-Kda polypeptides. The alpha (26KDa) is the catalytic subunit. The active site is made up of a trypsin-like triad of Ser 47, His 195 and Asp 192. The other subunit is not essential for the catalytic activity. The catalytic subunit contains a single alpha/beta domain with a central, parallel, 6-stranded beta sheet. This fold is very like that found in GTPase. Experimental data has demonstrated that the catalytic subunit of brain PAF acetylhydrolase is a novel type of serine esterase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q29460
 (3.1.1.47)
(3.1.1.47)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1wab
- PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR ACETYLHYDROLASE
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1110
 (see all for 1wab)
(see all for 1wab)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.47)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Ser47 is close to His195, the imidazole ring of His195 is hydrogen-bonded through its nitrogen (delta 1) atom to the side-chain carboxyl of Asp192. This forms a classical Ser-His-Asp triad, and Ser47 is thought to be the catalytic nucleophile. The chirality of the triad is the same as that found in the active sites of other esterases and neutral lipases, where nucleophilic attack is on the re face of the ester. The main chain amide of Gly74 and Nd1 of Asn104 stabilise oxyanion hole.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1wab) | ||
| Ser47 | Ser47A | Acts as the catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Gly74 (main-N), Asn104 | Gly74A (main-N), Asn104A | Forms the oxyanion hole. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp192 | Asp192A | Activates His195 to act as the general acid/base, forms part of the Ser-His-Asp triad. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His195 | His195A | Acts as a general acid/base, forms part of the Ser-His-Asp triad. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Ho YS et al. (1997), Nature, 385, 89-93. Brain acetylhydrolase that inactivates platelet-activating factor is a G-protein-like trimer. DOI:10.1038/385089a0. PMID:8985254.
- Epstein TM et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 3425-3435. Crystal Structures of Brain Group-VIII Phospholipase A2 in Nonaged Complexes with the Organophosphorus Nerve Agents Soman and Sarin†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi8023527. PMID:19271773.
- McIntyre TM et al. (2009), J Lipid Res, 50, S255-S259. The emerging roles of PAF acetylhydrolase. DOI:10.1194/jlr.r800024-jlr200. PMID:18838739.
- Karasawa K et al. (2003), Prog Lipid Res, 42, 93-114. Plasma platelet activating factor-acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH). PMID:12547653.
- McMullen TW et al. (2000), Protein Eng, 13, 865-871. The functional implications of the dimerization of the catalytic subunits of the mammalian brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (Ib). PMID:11239086.
- Ho YS et al. (1999), Protein Eng, 12, 693-700. Probing the substrate specificity of the intracellular brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. DOI:10.2210/pdb1bwr/pdb. PMID:10469831.
- Hattori M et al. (1994), J Biol Chem, 269, 23150-23155. The catalytic subunit of bovine brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is a novel type of serine esterase. PMID:8083218.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp192A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Gly74A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn104A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His195A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser47A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His195A | proton acceptor |
| Ser47A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. Ser47 initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the carbonyl carbon of the substrate in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp192A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly74A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn104A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His195A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser47A | hydrogen bond acceptor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 3. The oxyanion formed collapses, eliminating phosphocholine with concomitant deprotonation of His195.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp192A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly74A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn104A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His195A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser47A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His195A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 4. His195 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the carbonyl carbon of the acyl-intermediate in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp192A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly74A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn104A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His195A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser47A | covalently attached |
| His195A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 5. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating Ser47 with concomitant deprotonation of His195.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp192A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly74A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn104A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His195A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser47A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His195A | proton donor |
| Ser47A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: