Peptide deformylase
In prokaryotes, proteins are synthesised with an N-terminal formylmethionine which is removed by peptide deformylase. Eukaryotes do not use this enzyme, so it represents a potential drug target for the treatment of bacterial infections.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A6K3
 (3.5.1.88)
(3.5.1.88)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1bsz
- PEPTIDE DEFORMYLASE AS FE2+ CONTAINING FORM (NATIVE) IN COMPLEX WITH INHIBITOR POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.45.10
 (see all for 1bsz)
(see all for 1bsz)
- Cofactors
- Iron(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
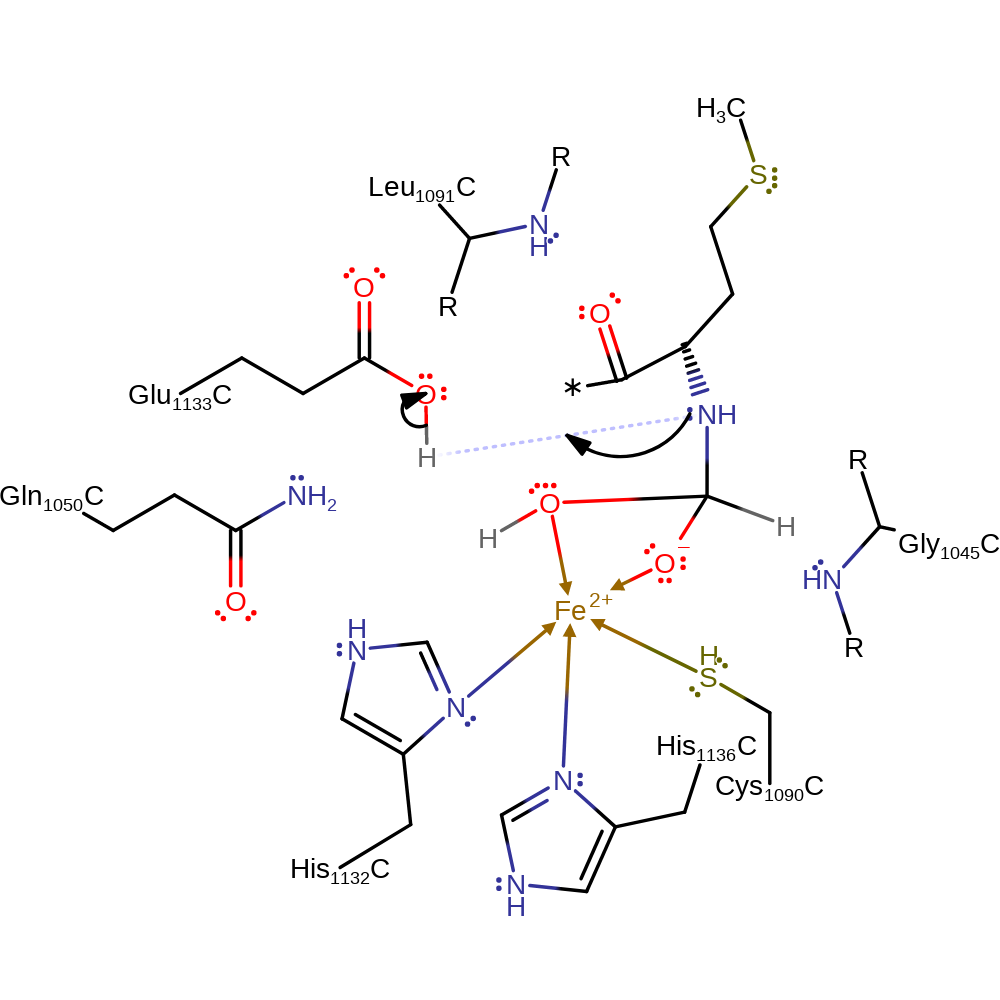
Glu133 abstracts a proton from the metal activated water molecule in the first step of this reaction. Computational studies have suggested that the nucleophilic attack of the resulting hydroxide ion occurs in a concerted manner. The nitrogen of the peptide bond then abstracts the proton from Glu133, making it a better leaving group for the final step. In this final step, the oxyanion collapses, eliminating methionine, which dissociates from the active site first. The formic acid is displaced by an incoming water molecule.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bsz) | ||
| Glu134 | Glu1133(133)C | Acts as the general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys91, His133, His137 | Cys1090(90)C, His1132(132)C, His1136(136)C | Form part of the iron binding site. | metal ligand |
| Gln51, Gly46 (main-N), Leu92 (main-N) | Gln1050(50)C, Gly1045(45)C (main-N), Leu1091(91)C (main-N) | Act to stabilise the negatively charged intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, coordination to a metal ion, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Wu XH et al. (2007), J Phys Chem B, 111, 6236-6244. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Mechanism and Metal-Ion Dependence of Peptide Deformylase. DOI:10.1021/jp068611m. PMID:17497768.
- Fell JS et al. (2015), Theor Chem Acc, 134,Electronic effects on the reaction mechanism of the metalloenzyme peptide deformylase. DOI:10.1007/s00214-015-1674-y.
- Hao B et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 4712-4719. Structural Basis for the Design of Antibiotics Targeting Peptide Deformylase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi982594c. PMID:10200158.
- Becker A et al. (1998), Nat Struct Biol, 5, 1053-1058. Iron center, substrate recognition and mechanism of peptide deformylase. DOI:10.1038/4162. PMID:9846875.
- Rajagopalan PT et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 13910-13918. Purification, Characterization, and Inhibition of Peptide Deformylase fromEscherichia coli†. DOI:10.1021/bi971155v. PMID:9374870.
- Chan MK et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 13904-13909. Crystal Structure of theEscherichia coliPeptide Deformylase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi9711543. PMID:9374869.
- Meinnel T et al. (1997), J Mol Biol, 267, 749-761. Structure-function relationships within the peptide deformylase family. Evidence for a conserved architecture of the active site involving three conserved motifs and a metal ion. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.0904. PMID:9126850.

Step 1. Glu133 deprotonates iron bound water. The activated water initiates a nucleophilic attack on the peptide substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln1050(50)C | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu1133(133)C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys1090(90)C | metal ligand |
| His1132(132)C | metal ligand |
| His1136(136)C | metal ligand |
| Glu1133(133)C | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, coordination to a metal ionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln1050(50)C | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly1045(45)C (main-N) | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Glu1133(133)C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu1091(91)C (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys1090(90)C | metal ligand |
| His1132(132)C | metal ligand |
| His1136(136)C | metal ligand |
| Glu1133(133)C | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer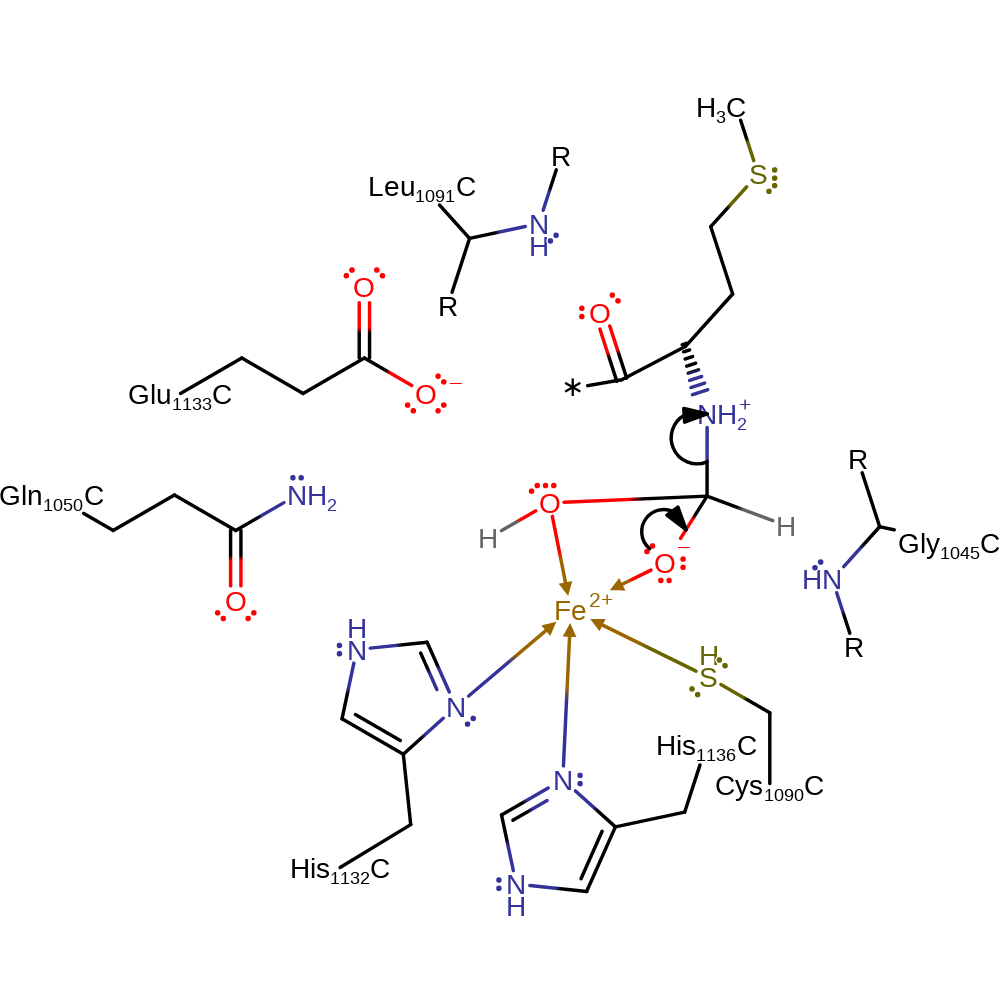
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating methionine. L-methionine dissociates from the active site first. Then water displaces formic acid to regenerate the starting state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln1050(50)C | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly1045(45)C (main-N) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu1091(91)C (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1090(90)C | metal ligand |
| His1132(132)C | metal ligand |
| His1136(136)C | metal ligand |



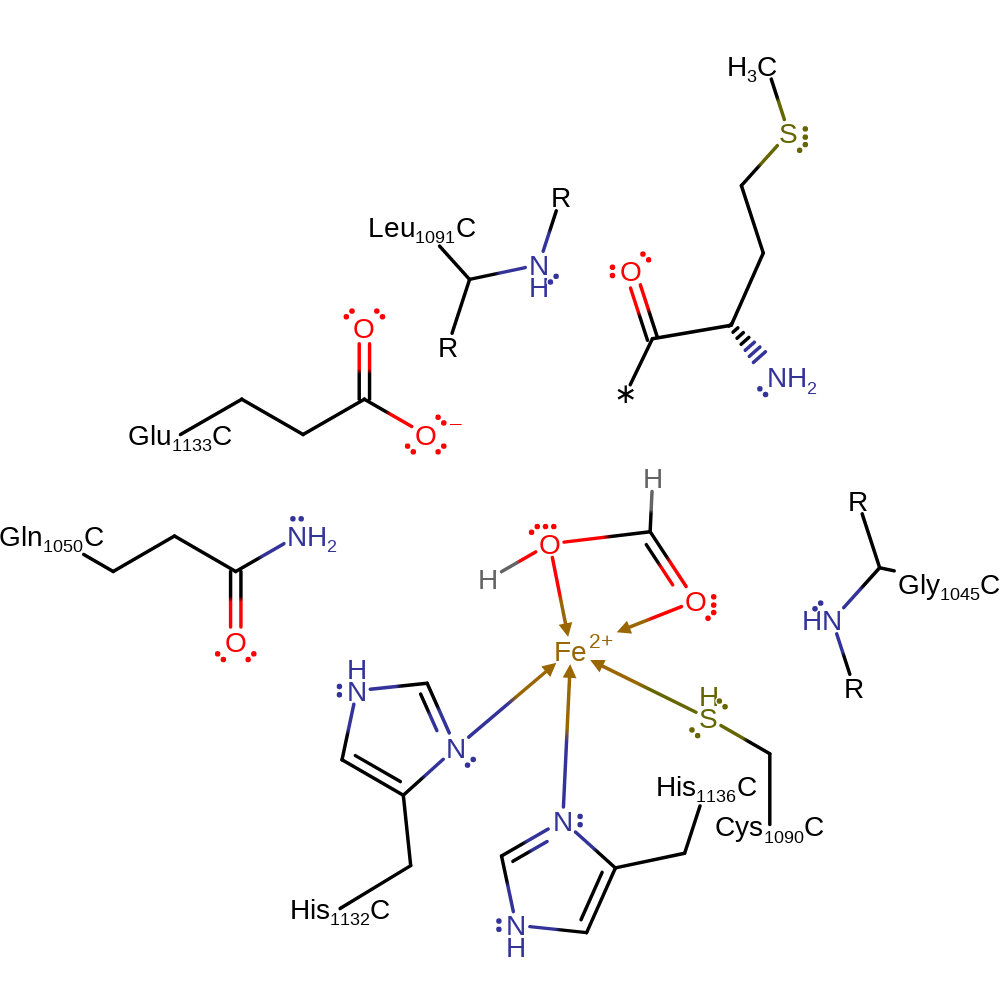 Download:
Download: