Thiosulfate dehydrogenase
Thiosulphate dehydrogenase (TsdA) catalyses the oxidation of two thiosulphate molecules to form tetrathionate and is predicted to use an unusual cysteine-ligated heme as the catalytic cofactor. Thiosulfate and polythionates serve as energy-yielding or electron-donating substrates in the metabolism of a wide range of chemolithotrophic and photolithotrophic bacteria, as well as some heterotrophs. This reaction is interesting because of its potential applications in bioleaching and metal solubilisation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
D3RVD4
 (1.8.2.2)
(1.8.2.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Allochromatium vinosum DSM 180 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
4v2k
- Crystal structure of the thiosulfate dehydrogenase TsdA in complex with thiosulfate
(1.29 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.760.10
 (see all for 4v2k)
(see all for 4v2k)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.8.2.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Thiosulphate is brought to the active center of the enzyme and stabilised by Arg109 and Arg119 because of their positively charged side chains. The Cys123 bound to heme acts as an electron relay for thiosulphate and propagates it down a chain of heme molecules within the heterodimer. This causes the thiosulphate to bond with Cys123. Another thiosulphate then enters the active site with the help of Ser127 and attacks the S-S bond made by the first thiosulphate and Cys123. This forms tetrathionate from the two thiosulphurs and regenerates the negative charge on the Cys123 sulphur atom.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (4v2k) | ||
| Cys123 | Cys123(96)A | Cys123 transfers electrons from thiosulphate to the adjacent heme irons, binds to thiosuphate and coordinates back to the Fe(III) heme atom after tetrathionate formation. | electron pair donor, covalently attached, nucleofuge, electrophile |
| Ser127 | Ser127(100)A | Ser127 is responsible for guiding and stabilising the second thiosulphur molecule via hydrogen bonding of its OH group from its side chain. | hydrogen bond donor, transition state stabiliser |
| Arg119, Arg109 | Arg119(92)A, Arg109(82)A | Electrostatic stabilisers that stabilise the negative charge of the thiosulphates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron relay, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, electron transfer, enzyme-substrate complex cleavageReferences
- Grabarczyk DB et al. (2015), J Biol Chem, 290, 9209-9221. Mechanism of thiosulfate oxidation in the SoxA family of cysteine-ligated cytochromes. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.618025. PMID:25673696.
- Kurth JM et al. (2016), J Biol Chem, 291, 24804-24818. Electron Accepting Units of the Diheme Cytochrome c TsdA, a Bifunctional Thiosulfate Dehydrogenase/Tetrathionate Reductase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M116.753863. PMID:27694441.
- Brito JA et al. (2015), J Biol Chem, 290, 9222-9238. Thiosulfate dehydrogenase (TsdA) from Allochromatium vinosum: structural and functional insights into thiosulfate oxidation. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.623397. PMID:25673691.
- Denkmann K et al. (2012), Environ Microbiol, 14, 2673-2688. Thiosulfate dehydrogenase: a widespread unusual acidophilic c-type cytochrome. DOI:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02820.x. PMID:22779704.
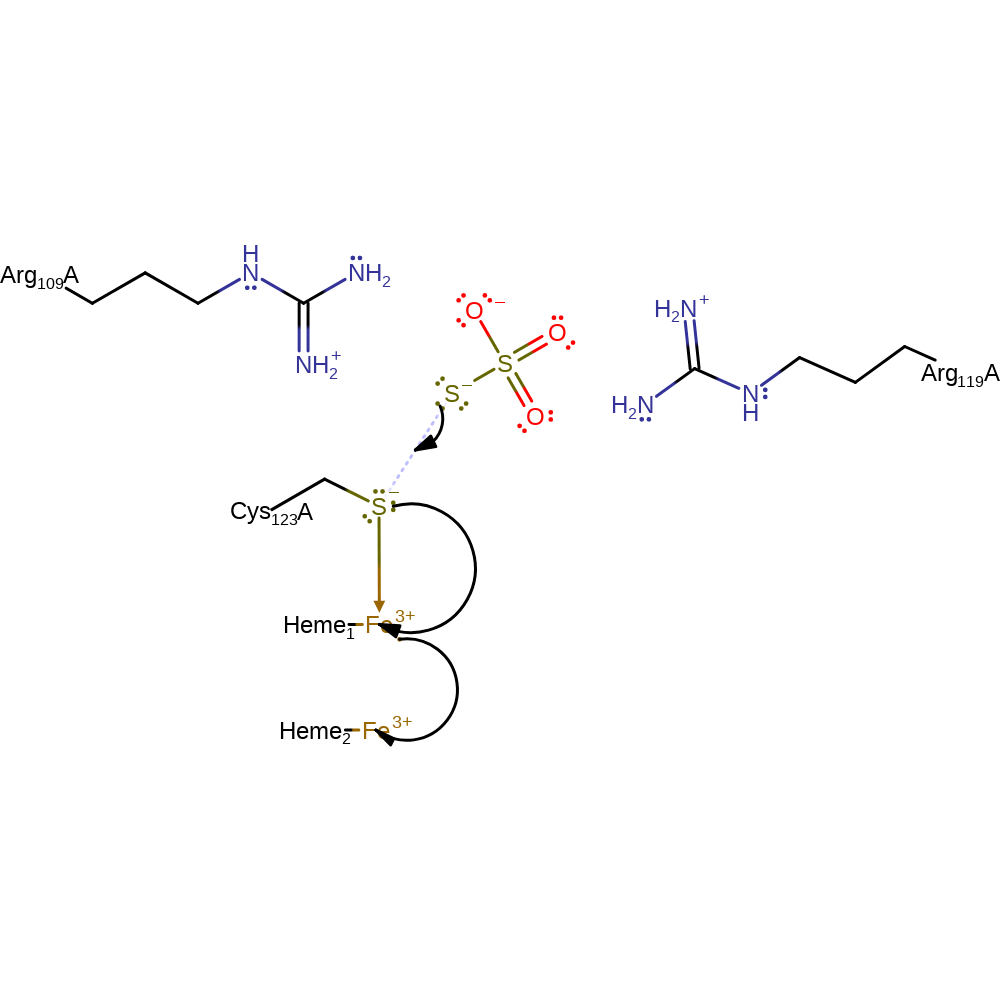
Step 1. The thiosulphate is brought in and stabilised by Arg109 and Arg119 through their positively charged side chains. The negative sulphur from the thiosulphate donates its electrons to form a S-S bond between itself and the Cys123. The Cys123 relays the electrons it gained to the heme 1 iron reducing it to Fe(II) while forming a bond with thiosulphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg119(92)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg109(82)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys123(96)A | electron pair donor, electrophile |
Chemical Components
electron relay, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, electron transfer
Step 2. The iron atoms in the heme molecules are regenerated to Fe(III) by transferring electrons further down the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys123(96)A | covalently attached |
| Arg119(92)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg109(82)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser127(100)A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
electron relay, electron transfer
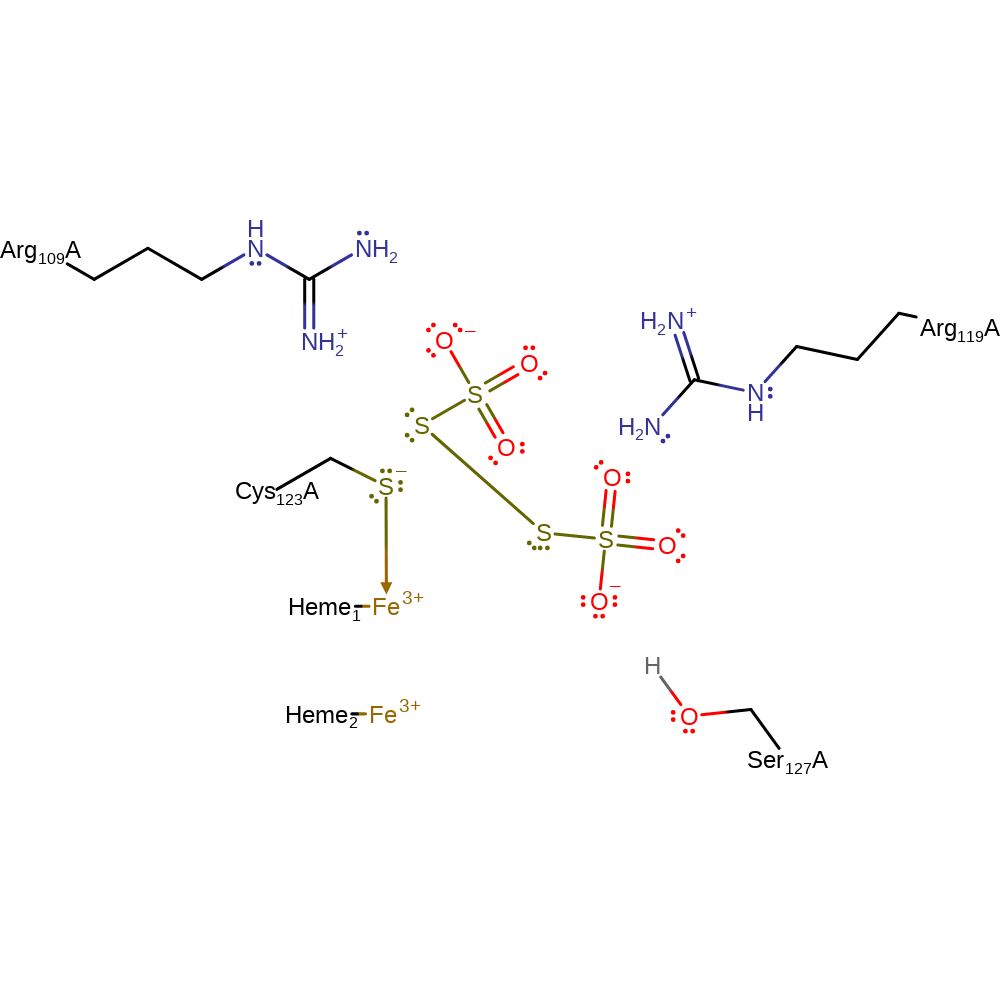
Step 3. The second thiosulphate is brought in to react with the S-S bond between Cys123 and the first thiosulphate. This causes the two thiosulphates to form tetrathionate and Cys123 to become negatively charged and coordinate the iron atom of the same heme molecule again.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys123(96)A | nucleofuge |
| Arg119(92)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg109(82)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser127(100)A | transition state stabiliser |





 Download:
Download: