7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll A reductase (HCAR)
7-Hydroxymethyl chlorophyll (HCAR) is a member of the family of chlorophyll catabolic enzymes (CCEs). Its a reductase that catalyses one of the reactions in chlorophyll conversion. HCAR is required for the degradation of light-harvesting complexes and is necessary for efficient photosynthesis by balancing the chlorophyll A/B ratio. Specifically, its a protein containing both 4Fe-4S complexes and FAD cofactor that converts 7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll (HMChl) a to chlorophyll A using ferredoxin for reduction of the substrate. HCAR catalyses the reduction of a hydroxymethyl group to a methyl group.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q8GS60
 (1.17.7.2)
(1.17.7.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)

- PDB
-
5dqr
- The crystal structure of Arabidopsis 7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll a reductase (HCAR)
(2.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
- (see all for 5dqr)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.17.7.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The 7-hydroxychlorophyll (HMChl) to chlorophyll A (ChlA) reaction is done by a mechanism in which protons coming from Asp237 and solution and electrons coming from ferrodoxin, through 2 4Fe-4S molecules and to an FAD molecule, are able to dehydrate and reduce the HMChl. Asp237 donates a proton to dehydrate the HMChl, this causes bond rearrangement in the chlorophyll structure and the formation of a double bond on the C atom that lost its hydroxyl group. The electron transfer then begins with an external ferrodoxin protein donating 2 electrons. These electrons pass over two 4Fe-4S molecules onto an FAD cofactor. FAD then donates these electrons to the methenyl group on the substrate, resulting in a methyl group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (5dqr) | ||
| Asp237 | Asp237(212)D | Proton donor crucial for dehydrating the HMChl. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His417 | His417(392)D | Stabilises and binds the HMChl molecule. | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu262, Gln332 | Glu262(237)D, Gln332(307)D | Glu262 and Gln332 stabilise and anchor FAD. Mutations on these residues lead to complete loss of function. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
dehydration, intramolecular rearrangement, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, radical formation, electron transfer, electron relay, proton transfer, inferred reaction step, radical termination, hydride transfer, redox reaction, overall product formed, overall reactant usedReferences
- Wang X et al. (2016), J Biol Chem, 291, 13349-13359. Crystal Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of 7-Hydroxymethyl Chlorophyll a Reductase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M116.720342. PMID:27072131.
- Meguro M et al. (2011), Plant Cell, 23, 3442-3453. Identification of the 7-Hydroxymethyl Chlorophyll a Reductase of the Chlorophyll Cycle in Arabidopsis . DOI:https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.089714.
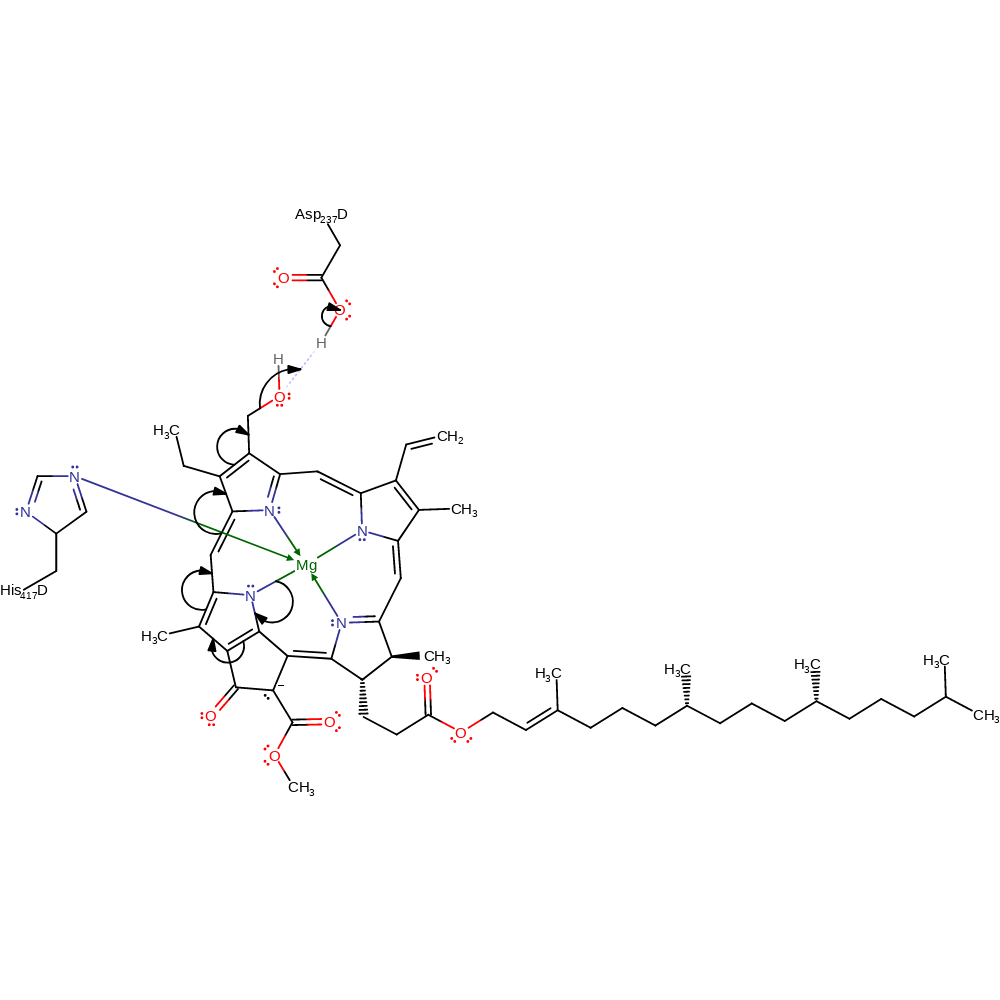
Step 1. Asp237 protonates the OH group on the 7-hydroxychlorophyll a (HMChl). This causes a water molecule to leave HMChl. The substrate then goes through bond rearrangement and creates a double bond towards the carbon atom that lost its hydroxyl group to stabilise the molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His417(392)D | electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand |
| Asp237(212)D | proton donor |
Chemical Components
dehydration, intramolecular rearrangement, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base
Step 2. Ferrodoxin donates a electron to the 4Fe-4S molecules which relay them to FAD. This process is stabilised by Gln332 and Glu262. The protonation from the bulk solvent is inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu262(237)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln332(307)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His417(392)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
radical formation, intramolecular rearrangement, electron transfer, electron relay, proton transfer, inferred reaction step
Step 3. Ferrodoxin donates a second electron which is used to fully reduce FAD. Another proton from solution is used to stabilise the negative charge.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu262(237)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln332(307)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His417(392)D | electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand |
Chemical Components
radical termination, electron relay, electron transfer, proton transfer, inferred reaction step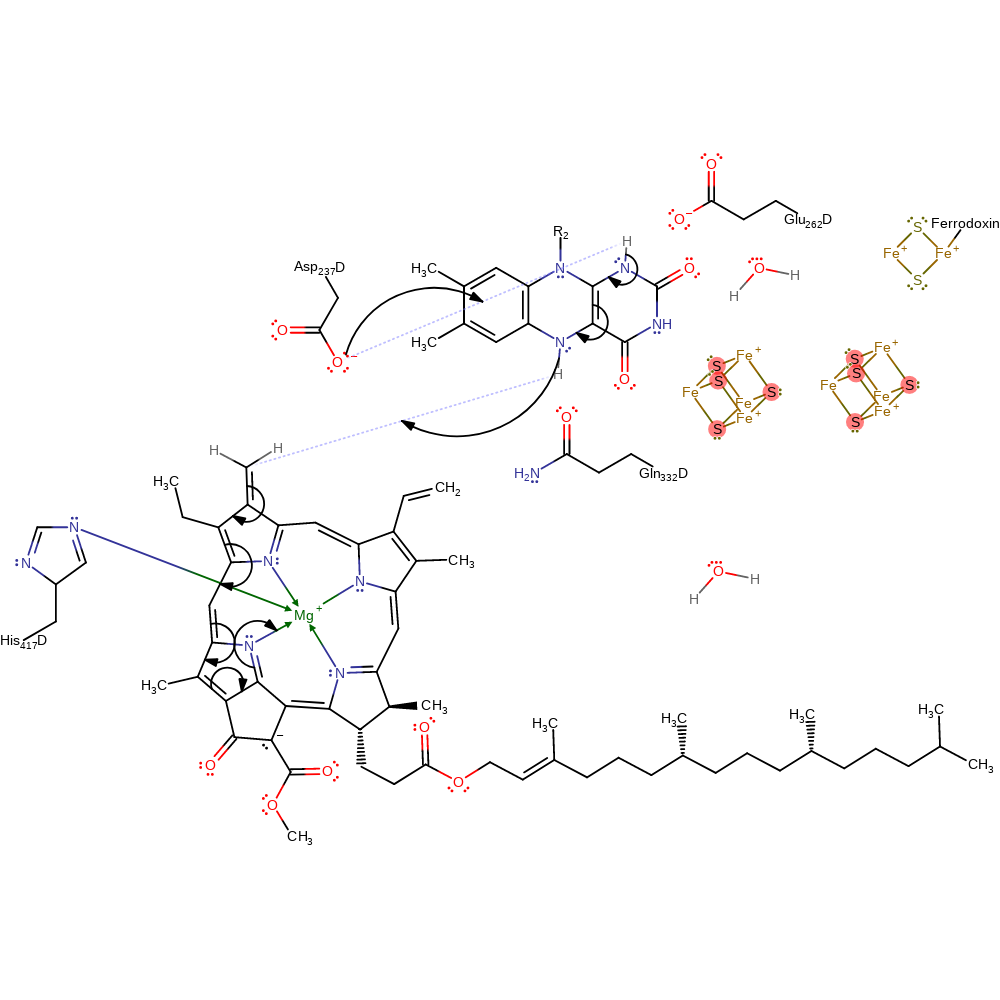
Step 4. The electrons gained by FAD are given to the chlorophyll substrate in the form of a hydride transfer. Asp237 is regenerated to its protonated state. The chlorophyll substrate undergoes some bond rearrangements to stabilise the added electrons.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp237(212)D | proton acceptor |
| His417(392)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu262(237)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln332(307)D | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His417(392)D | metal ligand |


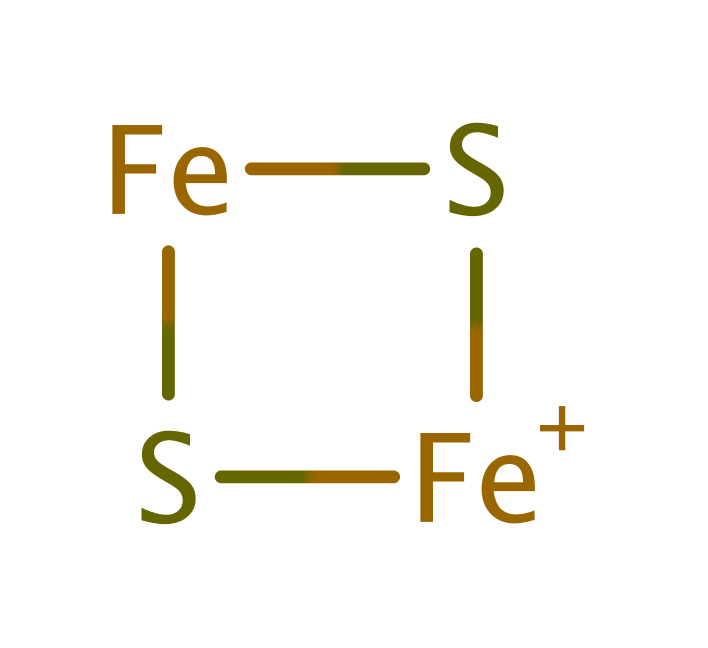


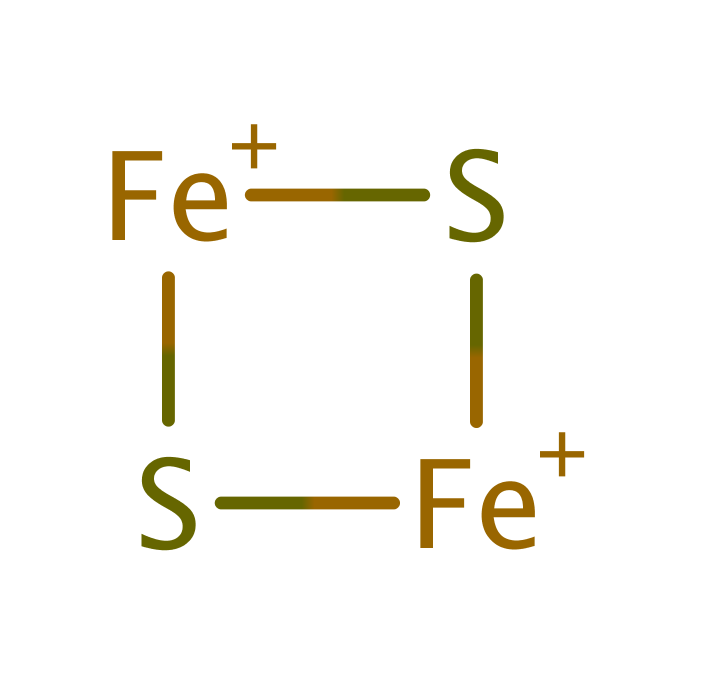
 Download:
Download: