Histone deacetylase 6 enzyme (HDAC6)
Histone deacetylase 6 enzyme (HDAC6) is a metalloenzyme, part of the HDAC family. The HDAC family includes 18 isoforms which are grouped into four classes (I, II, III, and IV). HDACs in class III use an NAD+ cofactor, whilst the others are metalloenzymes which use a Zn(II) metal ion centre. HDAC6 is in class II and is involved in the maintenance of a cell's shape and its polarity during cell division and migration, intracellular transport and angiogenesis.
HDACs catalyse the removal of the acyl group from a lysine amino acid of the substrate of nuclear and cytosol proteins. In general, protein acylation and deacylation processes are a key part of cell cycle regulation.
HDAC6 has a heterodimeric structure with two different catalytic domains, CD1 and CD2. The domains present a similar structure but show differing substrate specificities and their roles remain unclear. HDAC6 is of interest for its role in the fight against cancer and various other pathologies.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
F8W4B7
 (3.5.1.98)
(3.5.1.98)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Danio rerio (Zebrafish)

- PDB
-
5g0i
- Crystal structure of Danio rerio HDAC6 CD1 and CD2 (linker cleaved) in complex with Nexturastat A
(1.99 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.800.20
 (see all for 5g0i)
(see all for 5g0i)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In this mechanism proposed for both the CD1 and CD2 domains of HDAC6, a hydrogen bond network activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the amide carbon of the substrate, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. A proton from the protonated imidazole ring of His193 is transferred to the nitrogen of the substrate, forming acetic acid and eliminating the deacylated Lys product. Entry of a water molecule and substrate molecule into the active site regenerates the enzyme for another turnover. DFT-based computations show the rate-limiting step of the reaction is the nucleophilic attack of the catalytic water for peptide bond hydrolysis in both the CD1 and CD2 domains.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (5g0i) | ||
| Tyr363 | Tyr363(341)A | Tyr363 hydrogen bonds the substrate. | hydrogen bond donor |
| His193 | His193(171)A | Involved in a hydrogen bonding network in the enzyme-substrate complex. | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
| His192 | His192(170)A | His192 activates the water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp228 | Asp228(206)A | Asp228 accepts a proton from His192 in the first step of the reaction. This enables His192 to activate the water molecule for nucleophilic attack. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor |
| His232, Asp323, Asp230 | His232(210)A, Asp323(301)A, Asp230(208)A | Asp230, His232 and Asp323 coordinate to the Zn(II) centre. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, coordination to a metal ion, overall product formed, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseReferences
- Prejanò M et al. (2021), ACS Catal, 11, 3084-3093. Insights into the Catalytic Mechanism of Domains CD1 and CD2 in Histone Deacetylase 6 from Quantum Calculations. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.0c04729.
- Hai Y et al. (2016), Nat Chem Biol, 12, 741-747. Histone deacetylase 6 structure and molecular basis of catalysis and inhibition. DOI:10.1038/nchembio.2134. PMID:27454933.

Step 1. A structured hydrogen bond network activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on amide carbon of the substrate. This forms a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His193(171)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His192(170)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr363(341)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His232(210)A | metal ligand |
| Asp323(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp230(208)A | metal ligand |
| Asp228(206)A | proton acceptor |
| His192(170)A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, coordination to a metal ion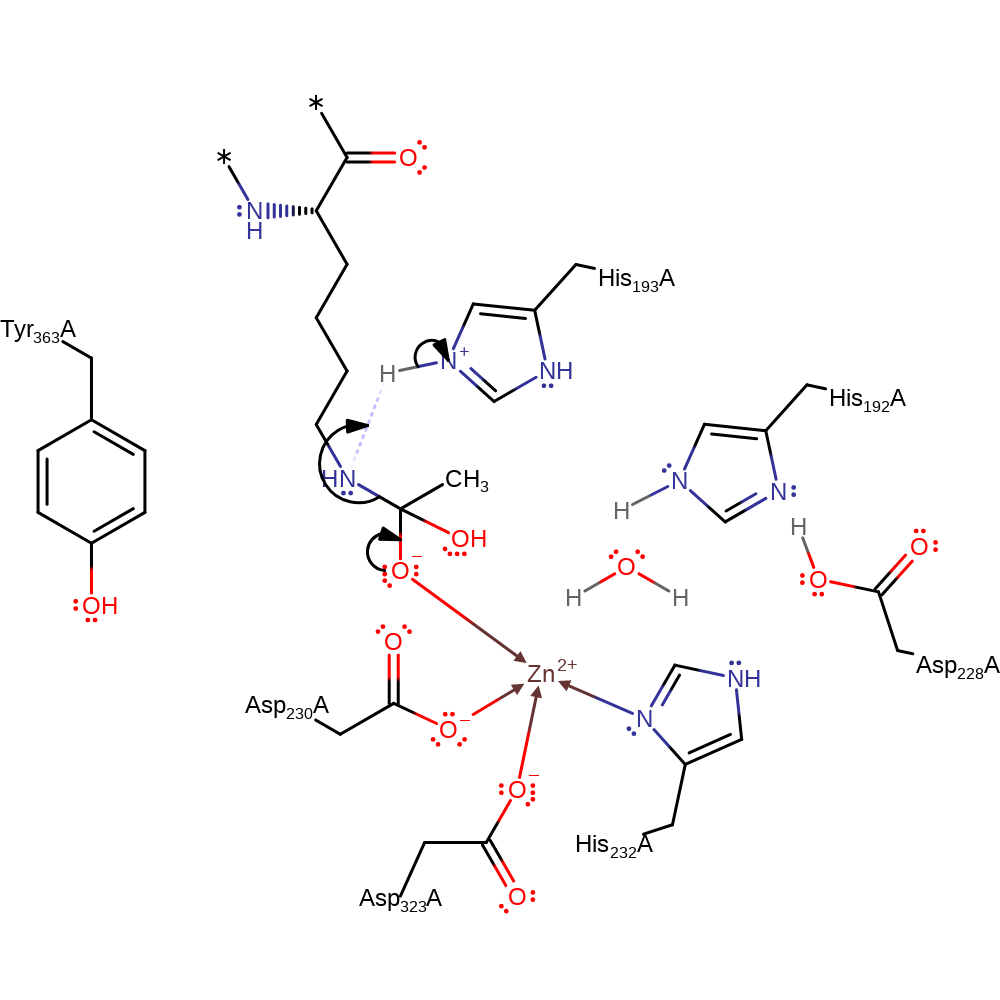
Step 2. A proton from the protonated imidazole ring of His193 is transferred to the nitrogen of the substrate. This induces C-N bond cleavage and forms the deacylated Lys and acetic acid products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232(210)A | metal ligand |
| Asp323(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp230(208)A | metal ligand |
| Asp228(206)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His192(170)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His193(171)A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: