Protein classification
Proteins are the macromolecules responsible for the biological processes in the cell. They consist at their most basic level of a chain of amino acids, determined by the sequence of nucleotides in a gene.
Depending on the amino acid sequence (different amino acids have different biochemical properties) and interactions with their environment, proteins fold into a three-dimensional structure, which allows them to interact with other proteins and molecules and perform their function (Figure 1).
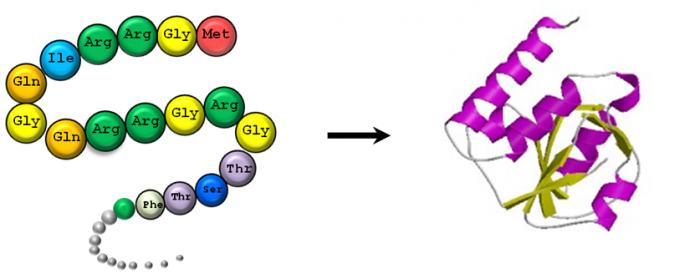
Proteins that have diverged from a common ancestral gene are known as homologous. Proteins with similar sequences are assumed to be homologous and usually (within certain limits) have similar structures and functions.