How do protein signatures compare to other ways of classifying proteins?
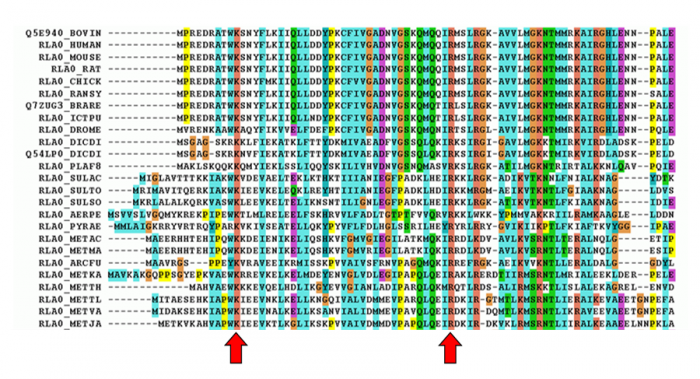
Multiple sequence alignments can provide us with valuable information for protein classification since they allow us to identify the (often few) amino acid residues that are conserved in distantly related proteins (Figure 11). It is not possible to identify such important residues with pairwise alignment techniques, such as BLAST. As a consequence, protein signatures built from multiple sequence alignments are usually better at detecting divergent homologues than pairwise comparison methods.