EMD-10050
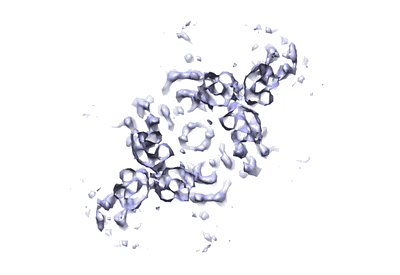
Structure of the E. coli Chemotaxis Core Signaling Unit
EMD-10050
Subtomogram averaging8.4 Å
 Deposition: 07/06/2019
Deposition: 07/06/2019Map released: 05/02/2020
Last modified: 05/02/2020
Sample Organism:
Escherichia coli
Sample: Bacterial chemotaxis core signaling complex
Deposition Authors: Zhang P
Sample: Bacterial chemotaxis core signaling complex
Deposition Authors: Zhang P
Structure and dynamics of the E. coli chemotaxis core signaling complex by cryo-electron tomography and molecular simulations.
Cassidy CK  ,
Himes BA,
Sun D
,
Himes BA,
Sun D  ,
Ma J,
Zhao G
,
Ma J,
Zhao G  ,
Parkinson JS
,
Parkinson JS  ,
Stansfeld PJ
,
Stansfeld PJ  ,
Luthey-Schulten Z
,
Luthey-Schulten Z  ,
Zhang P
,
Zhang P 
(2020) Commun Biol , 3 , 24 - 24
 ,
Himes BA,
Sun D
,
Himes BA,
Sun D  ,
Ma J,
Zhao G
,
Ma J,
Zhao G  ,
Parkinson JS
,
Parkinson JS  ,
Stansfeld PJ
,
Stansfeld PJ  ,
Luthey-Schulten Z
,
Luthey-Schulten Z  ,
Zhang P
,
Zhang P 
(2020) Commun Biol , 3 , 24 - 24
Abstract:
To enable the processing of chemical gradients, chemotactic bacteria possess large arrays of transmembrane chemoreceptors, the histidine kinase CheA, and the adaptor protein CheW, organized as coupled core-signaling units (CSU). Despite decades of study, important questions surrounding the molecular mechanisms of sensory signal transduction remain unresolved, owing especially to the lack of a high-resolution CSU structure. Here, we use cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram averaging to determine a structure of the Escherichia coli CSU at sub-nanometer resolution. Based on our experimental data, we use molecular simulations to construct an atomistic model of the CSU, enabling a detailed characterization of CheA conformational dynamics in its native structural context. We identify multiple, distinct conformations of the critical P4 domain as well as asymmetries in the localization of the P3 bundle, offering several novel insights into the CheA signaling mechanism.
To enable the processing of chemical gradients, chemotactic bacteria possess large arrays of transmembrane chemoreceptors, the histidine kinase CheA, and the adaptor protein CheW, organized as coupled core-signaling units (CSU). Despite decades of study, important questions surrounding the molecular mechanisms of sensory signal transduction remain unresolved, owing especially to the lack of a high-resolution CSU structure. Here, we use cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram averaging to determine a structure of the Escherichia coli CSU at sub-nanometer resolution. Based on our experimental data, we use molecular simulations to construct an atomistic model of the CSU, enabling a detailed characterization of CheA conformational dynamics in its native structural context. We identify multiple, distinct conformations of the critical P4 domain as well as asymmetries in the localization of the P3 bundle, offering several novel insights into the CheA signaling mechanism.
