EMD-11616
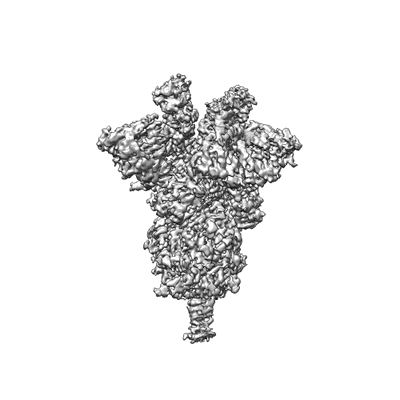
Cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein bound to neutralizing sybodies (Sb23)
EMD-11616
Single-particle3.06 Å
 Deposition: 16/08/2020
Deposition: 16/08/2020Map released: 25/11/2020
Last modified: 20/11/2024
Sample Organism:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2,
synthetic construct
Sample: SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in 1-up conformation bound by 3 neutralising Sybodies (Sb23)
Fitted models: 7a25 (Avg. Q-score: 0.386)
Deposition Authors: Hallberg BM ,
Das H
,
Das H 
Sample: SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in 1-up conformation bound by 3 neutralising Sybodies (Sb23)
Fitted models: 7a25 (Avg. Q-score: 0.386)
Deposition Authors: Hallberg BM
 ,
Das H
,
Das H 
Selection, biophysical and structural analysis of synthetic nanobodies that effectively neutralize SARS-CoV-2.
Custodio TF  ,
Das H
,
Das H  ,
Sheward DJ
,
Sheward DJ  ,
Hanke L
,
Hanke L  ,
Pazicky S
,
Pazicky S  ,
Pieprzyk J,
Sorgenfrei M,
Schroer MA
,
Pieprzyk J,
Sorgenfrei M,
Schroer MA  ,
Gruzinov AY
,
Gruzinov AY  ,
Jeffries CM
,
Jeffries CM  ,
Graewert MA
,
Graewert MA  ,
Svergun DI,
Dobrev N
,
Svergun DI,
Dobrev N  ,
Remans K
,
Remans K  ,
Seeger MA
,
Seeger MA  ,
McInerney GM
,
McInerney GM  ,
Murrell B
,
Murrell B  ,
Hallberg BM
,
Hallberg BM  ,
Low C
,
Low C 
(2020) Nat Commun , 11 , 5588 - 5588
 ,
Das H
,
Das H  ,
Sheward DJ
,
Sheward DJ  ,
Hanke L
,
Hanke L  ,
Pazicky S
,
Pazicky S  ,
Pieprzyk J,
Sorgenfrei M,
Schroer MA
,
Pieprzyk J,
Sorgenfrei M,
Schroer MA  ,
Gruzinov AY
,
Gruzinov AY  ,
Jeffries CM
,
Jeffries CM  ,
Graewert MA
,
Graewert MA  ,
Svergun DI,
Dobrev N
,
Svergun DI,
Dobrev N  ,
Remans K
,
Remans K  ,
Seeger MA
,
Seeger MA  ,
McInerney GM
,
McInerney GM  ,
Murrell B
,
Murrell B  ,
Hallberg BM
,
Hallberg BM  ,
Low C
,
Low C 
(2020) Nat Commun , 11 , 5588 - 5588
Abstract:
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 is the cause of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Therapeutic neutralizing antibodies constitute a key short-to-medium term approach to tackle COVID-19. However, traditional antibody production is hampered by long development times and costly production. Here, we report the rapid isolation and characterization of nanobodies from a synthetic library, known as sybodies (Sb), that target the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Several binders with low nanomolar affinities and efficient neutralization activity were identified of which Sb23 displayed high affinity and neutralized pseudovirus with an IC50 of 0.6 µg/ml. A cryo-EM structure of the spike bound to Sb23 showed that Sb23 binds competitively in the ACE2 binding site. Furthermore, the cryo-EM reconstruction revealed an unusual conformation of the spike where two RBDs are in the 'up' ACE2-binding conformation. The combined approach represents an alternative, fast workflow to select binders with neutralizing activity against newly emerging viruses.
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 is the cause of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Therapeutic neutralizing antibodies constitute a key short-to-medium term approach to tackle COVID-19. However, traditional antibody production is hampered by long development times and costly production. Here, we report the rapid isolation and characterization of nanobodies from a synthetic library, known as sybodies (Sb), that target the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Several binders with low nanomolar affinities and efficient neutralization activity were identified of which Sb23 displayed high affinity and neutralized pseudovirus with an IC50 of 0.6 µg/ml. A cryo-EM structure of the spike bound to Sb23 showed that Sb23 binds competitively in the ACE2 binding site. Furthermore, the cryo-EM reconstruction revealed an unusual conformation of the spike where two RBDs are in the 'up' ACE2-binding conformation. The combined approach represents an alternative, fast workflow to select binders with neutralizing activity against newly emerging viruses.
