EMD-12282
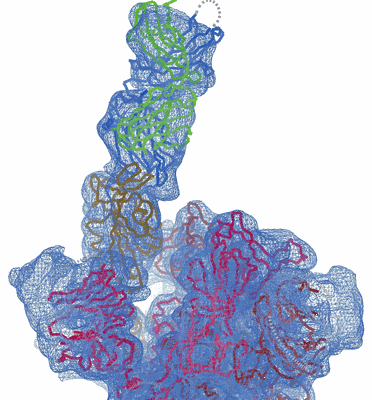
EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein in complex with COVOX-253H165L Fab
EMD-12282
Single-particle4.6 Å
 Deposition: 30/01/2021
Deposition: 30/01/2021Map released: 03/03/2021
Last modified: 16/10/2024
Sample Organism:
Homo sapiens,
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Sample: Complex of SARS-COV-2 spike glycoprotein with COVOX-253H165L Fab
Fitted models: 7ndb (Avg. Q-score: 0.197)
Deposition Authors: Duyvesteyn HME ,
Zhao Y
,
Zhao Y  ,
Ren J
,
Ren J  ,
Stuart D
,
Stuart D
Sample: Complex of SARS-COV-2 spike glycoprotein with COVOX-253H165L Fab
Fitted models: 7ndb (Avg. Q-score: 0.197)
Deposition Authors: Duyvesteyn HME
 ,
Zhao Y
,
Zhao Y  ,
Ren J
,
Ren J  ,
Stuart D
,
Stuart D
The antigenic anatomy of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain.
Dejnirattisai W,
Zhou D  ,
Ginn HM,
Duyvesteyn HME
,
Ginn HM,
Duyvesteyn HME  ,
Supasa P,
Case JB,
Zhao Y
,
Supasa P,
Case JB,
Zhao Y  ,
Walter TS
,
Walter TS  ,
Mentzer AJ
,
Mentzer AJ  ,
Liu C,
Wang B
,
Liu C,
Wang B  ,
Paesen GC,
Slon-Campos J
,
Paesen GC,
Slon-Campos J  ,
Lopez-Camacho C
,
Lopez-Camacho C  ,
Kafai NM
,
Kafai NM  ,
Bailey AL,
Chen RE,
Ying B,
Thompson C
,
Bailey AL,
Chen RE,
Ying B,
Thompson C  ,
Bolton J,
Fyfe A,
Gupta S,
Tan TK
,
Bolton J,
Fyfe A,
Gupta S,
Tan TK  ,
Gilbert-Jaramillo J,
James W
,
Gilbert-Jaramillo J,
James W  ,
Knight M,
Carroll MW,
Skelly D
,
Knight M,
Carroll MW,
Skelly D  ,
Dold C
,
Dold C  ,
Peng Y,
Levin R,
Dong T
,
Peng Y,
Levin R,
Dong T  ,
Pollard AJ,
Knight JC,
Klenerman P
,
Pollard AJ,
Knight JC,
Klenerman P  ,
Temperton N
,
Temperton N  ,
Hall DR
,
Hall DR  ,
Williams MA,
Paterson NG
,
Williams MA,
Paterson NG  ,
Bertram FKR,
Siebert CA
,
Bertram FKR,
Siebert CA  ,
Clare DK,
Howe A
,
Clare DK,
Howe A  ,
Radecke J,
Song Y
,
Radecke J,
Song Y  ,
Townsend AR,
Huang KA,
Fry EE,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Diamond MS,
Ren J
,
Townsend AR,
Huang KA,
Fry EE,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Diamond MS,
Ren J  ,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR
,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR
(2021) Cell , 184 , 2183
 ,
Ginn HM,
Duyvesteyn HME
,
Ginn HM,
Duyvesteyn HME  ,
Supasa P,
Case JB,
Zhao Y
,
Supasa P,
Case JB,
Zhao Y  ,
Walter TS
,
Walter TS  ,
Mentzer AJ
,
Mentzer AJ  ,
Liu C,
Wang B
,
Liu C,
Wang B  ,
Paesen GC,
Slon-Campos J
,
Paesen GC,
Slon-Campos J  ,
Lopez-Camacho C
,
Lopez-Camacho C  ,
Kafai NM
,
Kafai NM  ,
Bailey AL,
Chen RE,
Ying B,
Thompson C
,
Bailey AL,
Chen RE,
Ying B,
Thompson C  ,
Bolton J,
Fyfe A,
Gupta S,
Tan TK
,
Bolton J,
Fyfe A,
Gupta S,
Tan TK  ,
Gilbert-Jaramillo J,
James W
,
Gilbert-Jaramillo J,
James W  ,
Knight M,
Carroll MW,
Skelly D
,
Knight M,
Carroll MW,
Skelly D  ,
Dold C
,
Dold C  ,
Peng Y,
Levin R,
Dong T
,
Peng Y,
Levin R,
Dong T  ,
Pollard AJ,
Knight JC,
Klenerman P
,
Pollard AJ,
Knight JC,
Klenerman P  ,
Temperton N
,
Temperton N  ,
Hall DR
,
Hall DR  ,
Williams MA,
Paterson NG
,
Williams MA,
Paterson NG  ,
Bertram FKR,
Siebert CA
,
Bertram FKR,
Siebert CA  ,
Clare DK,
Howe A
,
Clare DK,
Howe A  ,
Radecke J,
Song Y
,
Radecke J,
Song Y  ,
Townsend AR,
Huang KA,
Fry EE,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Diamond MS,
Ren J
,
Townsend AR,
Huang KA,
Fry EE,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Diamond MS,
Ren J  ,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR
,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR
(2021) Cell , 184 , 2183
Abstract:
Antibodies are crucial to immune protection against SARS-CoV-2, with some in emergency use as therapeutics. Here, we identify 377 human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognizing the virus spike and focus mainly on 80 that bind the receptor binding domain (RBD). We devise a competition data-driven method to map RBD binding sites. We find that although antibody binding sites are widely dispersed, neutralizing antibody binding is focused, with nearly all highly inhibitory mAbs (IC50 < 0.1 μg/mL) blocking receptor interaction, except for one that binds a unique epitope in the N-terminal domain. Many of these neutralizing mAbs use public V-genes and are close to germline. We dissect the structural basis of recognition for this large panel of antibodies through X-ray crystallography and cryoelectron microscopy of 19 Fab-antigen structures. We find novel binding modes for some potently inhibitory antibodies and demonstrate that strongly neutralizing mAbs protect, prophylactically or therapeutically, in animal models.
Antibodies are crucial to immune protection against SARS-CoV-2, with some in emergency use as therapeutics. Here, we identify 377 human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognizing the virus spike and focus mainly on 80 that bind the receptor binding domain (RBD). We devise a competition data-driven method to map RBD binding sites. We find that although antibody binding sites are widely dispersed, neutralizing antibody binding is focused, with nearly all highly inhibitory mAbs (IC50 < 0.1 μg/mL) blocking receptor interaction, except for one that binds a unique epitope in the N-terminal domain. Many of these neutralizing mAbs use public V-genes and are close to germline. We dissect the structural basis of recognition for this large panel of antibodies through X-ray crystallography and cryoelectron microscopy of 19 Fab-antigen structures. We find novel binding modes for some potently inhibitory antibodies and demonstrate that strongly neutralizing mAbs protect, prophylactically or therapeutically, in animal models.
