EMD-13869
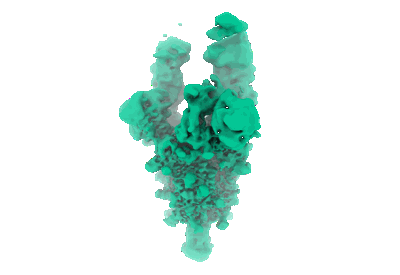
COVOX-222 fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2 beta-Spike glycoprotein
EMD-13869
Single-particle3.3 Å
 Deposition: 12/11/2021
Deposition: 12/11/2021Map released: 15/12/2021
Last modified: 23/10/2024
Sample Organism:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2,
Homo sapiens
Sample: COVOX-222 fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2 beta-Spike glycoprotein
Fitted models: 7q9g (Avg. Q-score: 0.341)
Deposition Authors: Duyvesteyn HME ,
Ren J
,
Ren J  ,
Stuart DI
,
Stuart DI
Sample: COVOX-222 fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2 beta-Spike glycoprotein
Fitted models: 7q9g (Avg. Q-score: 0.341)
Deposition Authors: Duyvesteyn HME
 ,
Ren J
,
Ren J  ,
Stuart DI
,
Stuart DI
The antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 Beta underscores the antigenic distance to other variants.
Liu C,
Zhou D  ,
Nutalai R
,
Nutalai R  ,
Duyvesteyn HME
,
Duyvesteyn HME  ,
Tuekprakhon A
,
Tuekprakhon A  ,
Ginn HM,
Dejnirattisai W,
Supasa P,
Mentzer AJ
,
Ginn HM,
Dejnirattisai W,
Supasa P,
Mentzer AJ  ,
Wang B
,
Wang B  ,
Case JB,
Zhao Y,
Skelly DT
,
Case JB,
Zhao Y,
Skelly DT  ,
Chen RE,
Johnson SA,
Ritter TG
,
Chen RE,
Johnson SA,
Ritter TG  ,
Mason C
,
Mason C  ,
Malik T,
Temperton N
,
Malik T,
Temperton N  ,
Paterson NG
,
Paterson NG  ,
Williams MA,
Hall DR
,
Williams MA,
Hall DR  ,
Clare DK,
Howe A
,
Clare DK,
Howe A  ,
Goulder PJR,
Fry EE,
Diamond MS,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Ren J
,
Goulder PJR,
Fry EE,
Diamond MS,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Ren J  ,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR
,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR 
(2022) Cell Host Microbe , 30 , 53
 ,
Nutalai R
,
Nutalai R  ,
Duyvesteyn HME
,
Duyvesteyn HME  ,
Tuekprakhon A
,
Tuekprakhon A  ,
Ginn HM,
Dejnirattisai W,
Supasa P,
Mentzer AJ
,
Ginn HM,
Dejnirattisai W,
Supasa P,
Mentzer AJ  ,
Wang B
,
Wang B  ,
Case JB,
Zhao Y,
Skelly DT
,
Case JB,
Zhao Y,
Skelly DT  ,
Chen RE,
Johnson SA,
Ritter TG
,
Chen RE,
Johnson SA,
Ritter TG  ,
Mason C
,
Mason C  ,
Malik T,
Temperton N
,
Malik T,
Temperton N  ,
Paterson NG
,
Paterson NG  ,
Williams MA,
Hall DR
,
Williams MA,
Hall DR  ,
Clare DK,
Howe A
,
Clare DK,
Howe A  ,
Goulder PJR,
Fry EE,
Diamond MS,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Ren J
,
Goulder PJR,
Fry EE,
Diamond MS,
Mongkolsapaya J,
Ren J  ,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR
,
Stuart DI,
Screaton GR 
(2022) Cell Host Microbe , 30 , 53
Abstract:
Alpha-B.1.1.7, Beta-B.1.351, Gamma-P.1, and Delta-B.1.617.2 variants of SARS-CoV-2 express multiple mutations in the spike protein (S). These may alter the antigenic structure of S, causing escape from natural or vaccine-induced immunity. Beta is particularly difficult to neutralize using serum induced by early pandemic SARS-CoV-2 strains and is most antigenically separated from Delta. To understand this, we generated 674 mAbs from Beta-infected individuals and performed a detailed structure-function analysis of the 27 most potent mAbs: one binding the spike N-terminal domain (NTD), the rest the receptor-binding domain (RBD). Two of these RBD-binding mAbs recognize a neutralizing epitope conserved between SARS-CoV-1 and -2, while 18 target mutated residues in Beta: K417N, E484K, and N501Y. There is a major response to N501Y, including a public IgVH4-39 sequence, with E484K and K417N also targeted. Recognition of these key residues underscores why serum from Beta cases poorly neutralizes early pandemic and Delta viruses.
Alpha-B.1.1.7, Beta-B.1.351, Gamma-P.1, and Delta-B.1.617.2 variants of SARS-CoV-2 express multiple mutations in the spike protein (S). These may alter the antigenic structure of S, causing escape from natural or vaccine-induced immunity. Beta is particularly difficult to neutralize using serum induced by early pandemic SARS-CoV-2 strains and is most antigenically separated from Delta. To understand this, we generated 674 mAbs from Beta-infected individuals and performed a detailed structure-function analysis of the 27 most potent mAbs: one binding the spike N-terminal domain (NTD), the rest the receptor-binding domain (RBD). Two of these RBD-binding mAbs recognize a neutralizing epitope conserved between SARS-CoV-1 and -2, while 18 target mutated residues in Beta: K417N, E484K, and N501Y. There is a major response to N501Y, including a public IgVH4-39 sequence, with E484K and K417N also targeted. Recognition of these key residues underscores why serum from Beta cases poorly neutralizes early pandemic and Delta viruses.
