EMD-14098
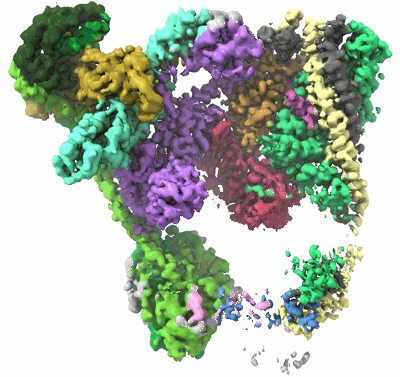
Structure of the human inner kinetochore CCAN complex
EMD-14098
Single-particle4.6 Å
 Deposition: 24/12/2021
Deposition: 24/12/2021Map released: 08/06/2022
Last modified: 17/07/2024
Sample Organism:
Homo sapiens
Sample: human inner kinetochore CCAN complex
Fitted models: 7qoo (Avg. Q-score: 0.202)
Deposition Authors: Vetter IR, Pesenti M, Raisch T
Sample: human inner kinetochore CCAN complex
Fitted models: 7qoo (Avg. Q-score: 0.202)
Deposition Authors: Vetter IR, Pesenti M, Raisch T

Structure of the human inner kinetochore CCAN complex and its significance for human centromere organization.
Pesenti ME  ,
Raisch T
,
Raisch T  ,
Conti D
,
Conti D  ,
Walstein K,
Hoffmann I,
Vogt D,
Prumbaum D,
Vetter IR,
Raunser S,
Musacchio A
,
Walstein K,
Hoffmann I,
Vogt D,
Prumbaum D,
Vetter IR,
Raunser S,
Musacchio A 
(2022) Mol Cell , 82 , 2113
 ,
Raisch T
,
Raisch T  ,
Conti D
,
Conti D  ,
Walstein K,
Hoffmann I,
Vogt D,
Prumbaum D,
Vetter IR,
Raunser S,
Musacchio A
,
Walstein K,
Hoffmann I,
Vogt D,
Prumbaum D,
Vetter IR,
Raunser S,
Musacchio A 
(2022) Mol Cell , 82 , 2113
Abstract:
Centromeres are specialized chromosome loci that seed the kinetochore, a large protein complex that effects chromosome segregation. A 16-subunit complex, the constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN), connects between the specialized centromeric chromatin, marked by the histone H3 variant CENP-A, and the spindle-binding moiety of the kinetochore. Here, we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of human CCAN. We highlight unique features such as the pseudo GTPase CENP-M and report how a crucial CENP-C motif binds the CENP-LN complex. The CCAN structure has implications for the mechanism of specific recognition of the CENP-A nucleosome. A model consistent with our structure depicts the CENP-C-bound nucleosome as connected to the CCAN through extended, flexible regions of CENP-C. An alternative model identifies both CENP-C and CENP-N as specificity determinants but requires CENP-N to bind CENP-A in a mode distinct from the classical nucleosome octamer.
Centromeres are specialized chromosome loci that seed the kinetochore, a large protein complex that effects chromosome segregation. A 16-subunit complex, the constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN), connects between the specialized centromeric chromatin, marked by the histone H3 variant CENP-A, and the spindle-binding moiety of the kinetochore. Here, we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of human CCAN. We highlight unique features such as the pseudo GTPase CENP-M and report how a crucial CENP-C motif binds the CENP-LN complex. The CCAN structure has implications for the mechanism of specific recognition of the CENP-A nucleosome. A model consistent with our structure depicts the CENP-C-bound nucleosome as connected to the CCAN through extended, flexible regions of CENP-C. An alternative model identifies both CENP-C and CENP-N as specificity determinants but requires CENP-N to bind CENP-A in a mode distinct from the classical nucleosome octamer.
