EMD-2925
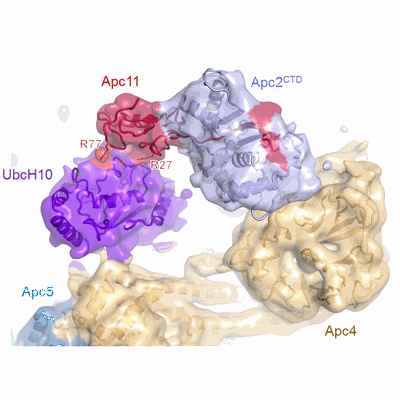
Cryo-EM structure of the human APC/C-Cdh1-Hsl1-UbcH10-Ub complex.
EMD-2925
Single-particle5.7 Å
 Deposition: 09/03/2015
Deposition: 09/03/2015Map released: 17/06/2015
Last modified: 18/11/2015
Sample Organism:
Homo sapiens
Sample: Recombinant human APC/C-Cdh1-Hsl1-UbcH10LR-Ub complex
Fitted models: 5a31 (Avg. Q-score: 0.007)
Deposition Authors: Chang L, Zhang Z ,
Yang J
,
Yang J  ,
McLaughlin SH
,
McLaughlin SH  ,
Barford D
,
Barford D 
Sample: Recombinant human APC/C-Cdh1-Hsl1-UbcH10LR-Ub complex
Fitted models: 5a31 (Avg. Q-score: 0.007)
Deposition Authors: Chang L, Zhang Z
 ,
Yang J
,
Yang J  ,
McLaughlin SH
,
McLaughlin SH  ,
Barford D
,
Barford D 
Atomic structure of the APC/C and its mechanism of protein ubiquitination
Abstract:
The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is a multimeric RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Its regulation by coactivator subunits, phosphorylation, the mitotic checkpoint complex and interphase early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) ensures the correct order and timing of distinct cell-cycle transitions. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine atomic structures of APC/C-coactivator complexes with either Emi1 or a UbcH10-ubiquitin conjugate. These structures define the architecture of all APC/C subunits, the position of the catalytic module and explain how Emi1 mediates inhibition of the two E2s UbcH10 and Ube2S. Definition of Cdh1 interactions with the APC/C indicates how they are antagonized by Cdh1 phosphorylation. The structure of the APC/C with UbcH10-ubiquitin reveals insights into the initiating ubiquitination reaction. Our results provide a quantitative framework for the design of future experiments to investigate APC/C functions in vivo.
The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is a multimeric RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Its regulation by coactivator subunits, phosphorylation, the mitotic checkpoint complex and interphase early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) ensures the correct order and timing of distinct cell-cycle transitions. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine atomic structures of APC/C-coactivator complexes with either Emi1 or a UbcH10-ubiquitin conjugate. These structures define the architecture of all APC/C subunits, the position of the catalytic module and explain how Emi1 mediates inhibition of the two E2s UbcH10 and Ube2S. Definition of Cdh1 interactions with the APC/C indicates how they are antagonized by Cdh1 phosphorylation. The structure of the APC/C with UbcH10-ubiquitin reveals insights into the initiating ubiquitination reaction. Our results provide a quantitative framework for the design of future experiments to investigate APC/C functions in vivo.
