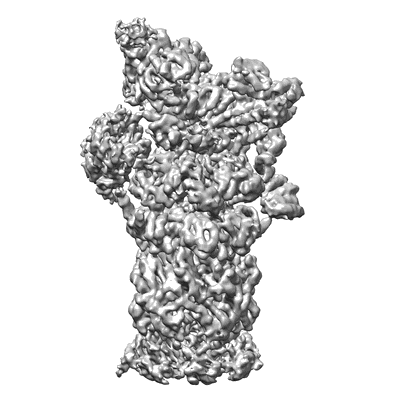
EMD-4321
26S proteasome, s3 state
EMD-4321
Single-particle5.4 Å
 Deposition: 05/03/2018
Deposition: 05/03/2018Map released: 22/08/2018
Last modified: 15/05/2024
Sample Organism:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c)
Sample: 26S proteasome
Fitted models: 6fvv (Avg. Q-score: 0.149)
Deposition Authors: Eisele MR, Reed RG
Sample: 26S proteasome
Fitted models: 6fvv (Avg. Q-score: 0.149)
Deposition Authors: Eisele MR, Reed RG
Expanded Coverage of the 26S Proteasome Conformational Landscape Reveals Mechanisms of Peptidase Gating.
Eisele MR,
Reed RG,
Rudack T,
Schweitzer A,
Beck F,
Nagy I  ,
Pfeifer G,
Plitzko JM
,
Pfeifer G,
Plitzko JM  ,
Baumeister W,
Tomko Jr RJ,
Sakata E
,
Baumeister W,
Tomko Jr RJ,
Sakata E 
(2018) Cell Rep , 24 , 1301 - 1315.e5
 ,
Pfeifer G,
Plitzko JM
,
Pfeifer G,
Plitzko JM  ,
Baumeister W,
Tomko Jr RJ,
Sakata E
,
Baumeister W,
Tomko Jr RJ,
Sakata E 
(2018) Cell Rep , 24 , 1301 - 1315.e5
Abstract:
The proteasome is the central protease for intracellular protein breakdown. Coordinated binding and hydrolysis of ATP by the six proteasomal ATPase subunits induces conformational changes that drive the unfolding and translocation of substrates into the proteolytic 20S core particle for degradation. Here, we combine genetic and biochemical approaches with cryo-electron microscopy and integrative modeling to dissect the relationship between individual nucleotide binding events and proteasome conformational dynamics. We demonstrate unique impacts of ATP binding by individual ATPases on the proteasome conformational distribution and report two conformational states of the proteasome suggestive of a rotary ATP hydrolysis mechanism. These structures, coupled with functional analyses, reveal key roles for the ATPases Rpt1 and Rpt6 in gating substrate entry into the core particle. This deepened knowledge of proteasome conformational dynamics reveals key elements of intersubunit communication within the proteasome and clarifies the regulation of substrate entry into the proteolytic chamber.
The proteasome is the central protease for intracellular protein breakdown. Coordinated binding and hydrolysis of ATP by the six proteasomal ATPase subunits induces conformational changes that drive the unfolding and translocation of substrates into the proteolytic 20S core particle for degradation. Here, we combine genetic and biochemical approaches with cryo-electron microscopy and integrative modeling to dissect the relationship between individual nucleotide binding events and proteasome conformational dynamics. We demonstrate unique impacts of ATP binding by individual ATPases on the proteasome conformational distribution and report two conformational states of the proteasome suggestive of a rotary ATP hydrolysis mechanism. These structures, coupled with functional analyses, reveal key roles for the ATPases Rpt1 and Rpt6 in gating substrate entry into the core particle. This deepened knowledge of proteasome conformational dynamics reveals key elements of intersubunit communication within the proteasome and clarifies the regulation of substrate entry into the proteolytic chamber.
