| Activity |
|---|
| Catalytic type | Metallo |
| Peplist | Included in the Peplist with identifier PL00201 |
| NC-IUBMB | Subclass 3.4 (Peptidases) >> Sub-subclass 3.4.24 (Metalloendopeptidases) >> Peptidase 3.4.24.11
|
| Enzymology | BRENDA database |
| Proteolytic events | CutDB database (55 cleavages) |
| Activity status | human: active (Turner, 2004)
mouse: active (Marr et al., 2004)
|
| Physiology | An ectoenzyme endopeptidase active in the degradation of enkephalins and other bioactive peptides. Also has Alzheimer"s alpha secretase activity, destroying the A beta peptide (Iwata et al., 2001). |
| Knockout | Mice with targeted disruption of the gene show enhanced sensitivity to endotoxin shock (Lu et al., 1995). Deletion of the gene also results in an opioid-related increase in thermonociceptive threshold (Saria et al., 1997), and there is little compensation for the deficiency (Fischer et al., 2000). There was a modified ventilatory response to hypoxia (Grasemann et al., 1999). The severity of experimentally-induced colitis was markedly worse in the knockout mice than in controls, indicating that the enzyme maintains low levels of substance P in the extracellular fluid under basal conditions and terminates its proinflammatory effects (Sturiale et al., 1999). Neprilysin also terminates substance P-induced inflammation in allergic contact dermatitis (Scholzen et al., 2001). Work with knockout mice showed that neprilysin has alpha-secretase activity (Iwata et al., 2001), and down-regulation of neprilysin led to deposition of beta-amyloid (Iwata et al., 2002). |
| Pharmaceutical relevance | Drug target in hypertension and renal disease. However, neprilysin is an alpha-secretase for Alzheimer"s disease, contributing to the destruction of the harmful A beta-peptide, and artificially increasing the activity of neprilysin may be a useful approach to reducing A beta levels in the brain (Shirotani et al., 2001; Hama et al., 2001; Iwata et al., 2004; Marr et al., 2004). |
| Pathways |
KEGG | Alzheimer's disease |
|
KEGG | Protein digestion and absorption |
|
KEGG | Renin-angiotensin system |
|
Other databases
| TREEFAM | http://www.treefam.org/family/TF315192 |
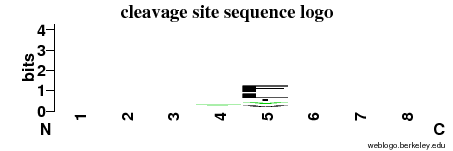
| Cleavage site specificity |
Explanations of how to interpret the
following cleavage site sequence logo and specificity matrix can be found here. |
|---|
| Cleavage pattern | -/-/-/- fl/-/-/- (based on 124 cleavages) fl/-/-/- (based on 124 cleavages) |

 fl/-/-/- (based on 124 cleavages)
fl/-/-/- (based on 124 cleavages)